
Data Handling Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4, Data Handling, continues to build on the basics with Ex 4.2 class 8. This exercise focuses on representing data using bar graphs and double bar graphs. These graphical tools are essential for comparing different sets of data visually, making it easier to identify trends and patterns.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentIn Ex 4.2 class 8, students should pay attention to accurately plotting data on bar graphs and double bar graphs. Understanding how to represent and interpret data visually is crucial, as it enhances analytical skills and prepares students for more advanced data handling tasks. By mastering these concepts, students can boost their confidence and perform better in exams, as highlighted by Vedantu.
Formulas Used in Class 8 Chapter 4 Exercise 4.2
Probability Formula: Probability = $Probability = \dfrac{Number of favorable outcomes}{Total number of outcomes}$
Sum of Probabilities of All Possible Outcomes: $P\left ( E \right )+P\left ( not E \right )= 1$
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Data Handling Exercise 4.2
Refer to pages 8-10 for exercise 4.2 in the PDF
1. List the outcomes you can see in these experiments.
(a) Spinning a wheel (b) Tossing two coins together
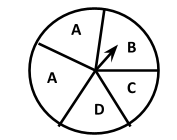
(a) Ans: There are 4 possible outcomes. There are four letters A, B, C and D in a spinning wheel.
(b) Ans: When two coins are tossed together. There are four possible outcomes HH, HT, TH, TT, where H and T means head and tail.
2. When a die is thrown, list the outcomes of an event of getting:
(i) (a) a prime number (b) not a prime number
(ii) (a) a number greater than 5 (b) a number not greater than 5
Ans: When a dice is thrown, the possible outcomes are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6.
(i) (a) Ans: The outcomes of getting a prime number are 2, 3 and 5.
(b) Ans: 1, 4 and 6 are not prime numbers. Outcomes of events of not getting a prime number are 1, 4 and 6.
(ii) (a) Ans: Outcomes of the event of getting a number greater than 5 is only 6.
(b) Ans: Outcomes of events of not getting a number greater than 5 are 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.
3. Find the:
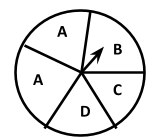
(a) Probability of the pointer stopping on D in (Question 1 (a)).
(b) Probability of getting an ace from a well shuffled deck of 52 playing cards.
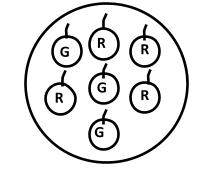
(c) Probability of getting a red apple. (See figure alongside)
(a) Ans: In a spinning wheel, there are five pointers A, A, B, C, D. So there are five outcomes. Pointer stops at D which is one outcome.
So the probability of the pointer stopping on D= \[\dfrac{1}{5}\]
(b) Ans: There are 4 aces in a deck of 52 playing cards. So, there are four events of getting an ace.
So, probability of getting an ace =\[\dfrac{4}{{52}} = \dfrac{1}{{13}}\]
(c) Ans: Total number of apples is 7 and in that there are 4 that are red.
Probability of getting red apple =\[\dfrac{4}{7}\]
4. Numbers 1 to 10 are written on ten separate slips (one number on one slip), kept in a box and
mixed well. One slip is chosen from the box without looking into it. What is the probability of:
(i) Getting a number 6.
(ii) Getting a number less than 6.
(iii) Getting a number greater than 6.
(iv) Getting a 1-digit number.
(i) Ans: There are 10 slips in the box and 6is written on only one slip.
Therefore, probability of getting a number 6 =\[\dfrac{1}{{10}}\]
(ii) Ans: Numbers less than 6 are 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. So there are 5 outcomes.
Then the probability of getting a number less than 6 =\[\dfrac{5}{{10}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
(iii) Ans: Number greater than 6 out of ten that are 7, 8, 9, 10. So there are 4 possible outcomes.
Therefore, probability of getting a number greater than 6 =\[\dfrac{4}{{10}} = \dfrac{2}{5}\]
(iv) Ans: One digit numbers are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 out of ten outcomes.
Therefore, probability of getting a 1-digit number =\[\dfrac{9}{{10}}\]
5. If you have a spinning wheel with 3 green sectors, 1 blue sector and 1 red sector, what is the probability of getting a green sector? What is the probability of getting a none-blue sector?
Ans: There are five sectors. Three sectors are green out of five sectors.
Therefore, probability of getting a green sector =\[\dfrac{3}{5}\]
There is one blue sector out of five sectors.
Non-blue sectors $ = 5 - 1 = 4$ sectors
Therefore, probability of getting a non-blue sector =\[\dfrac{4}{5}\]
6. Find the probability of the events given in Question 2.
Ans: When a die is thrown, there are a total six outcomes, i.e., 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6.
(i) (a) Ans: The outcomes of the event of getting a prime number are 2, 3 and 5. So there are 3 outcomes out of 6.
Therefore, probability of getting a prime number =\[\dfrac{3}{6} = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
(b) Ans: 1, 4, 6 are not the prime numbers. So there are 3 outcomes out of 6.
Therefore, probability of getting a prime number =\[\dfrac{3}{6} = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
(ii) (a) Ans: Only 6 is greater than 5 in the possible outcomes. So there is one outcome out of 6.
Therefore, probability of getting a number greater than 5 =\[\dfrac{1}{6}\]
(b) Ans: Out of the 6 possible outcomes the number not greater than 5 are 5.
Therefore, probability of not getting a number greater than 5 = \[\dfrac{5}{6}\]
Conclusion
In Class 8 Maths Exercise 4.2 of Chapter 4 Data Handling, students dive into the practical application of probability concepts. Class 8 maths ex 4.2 emphasizes understanding the probability formula and applying it to various scenarios. Practicing these problems will enhance students' ability to solve probability-related questions efficiently, boosting their confidence in exams. Mastering these concepts is essential for tackling real-life problems involving chance and probability. By practicing these solutions, students can improve their problem-solving skills and achieve better results, as highlighted by Byju's and Vedantu.
Class 8 Maths Chapter 4: Exercises Breakdown
Exercise | Number of Questions |
5 Questions & Solutions |
CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Other Study Materials
S. No | Important Links for Chapter 4 Data Handling |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 |
Chapter-Specific NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths
Given below are the chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths. Go through these chapter-wise solutions to be thoroughly familiar with the concepts.
S. No | NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter-wise List |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 | |
11 | |
12 | |
13 |
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 8 Maths
S. No | Other Study Materials for CBSE Class 8 Maths |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 |

















