Alternating Current: An Important Concept for NEET
The chapter of Alternating Current starts with the basic revision of all the concepts we have studied in our lower grades and helps to build a connection between the advanced parts of Alternating Current. In the following chapter, we have discussed alternating and direct current, average and rms value of alternating current, resistance offered by various elements (inductor, resistor and capacitor) to a.c , impedances and phases of ac circuits containing different elements, etc.
While deriving the formulae and equations for resistance offered by various elements (inductor, resistor and capacitor) to a.c., L.C Oscillations, we will also study about transformers and the power losses in a transformer with examples in the chapter Alternating Current.
In this chapter, students will also get to learn about the Power in AC Circuit and Resonance, where we will study about the sharpness of resonance along with other major topics.
Now, let us move on to the important concepts and formulae related to NEET exams along with a few solved examples.
Important Topics of Alternating Current
Alternating Current
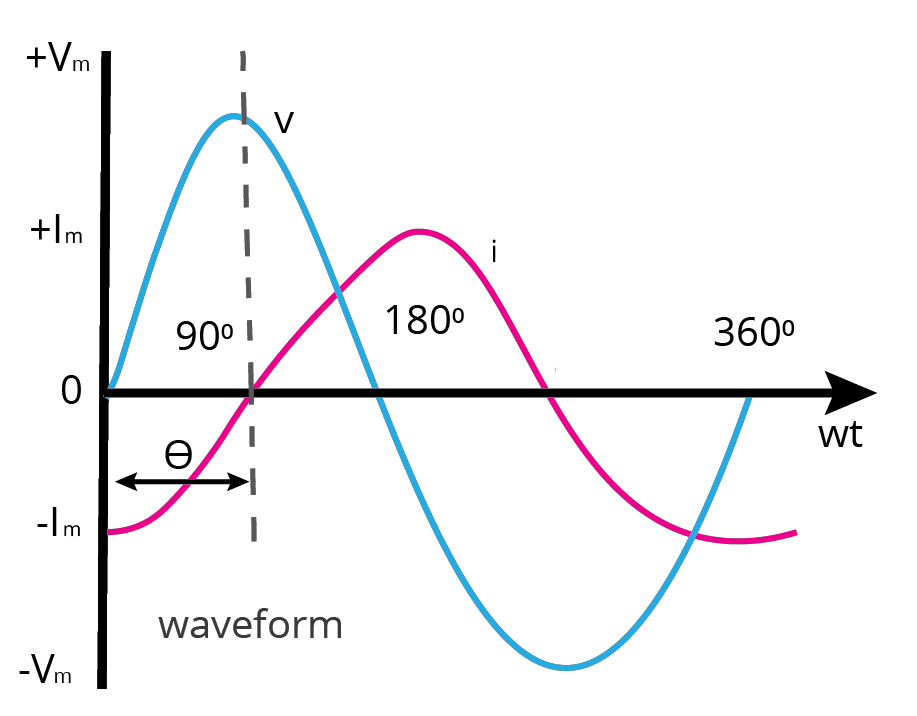
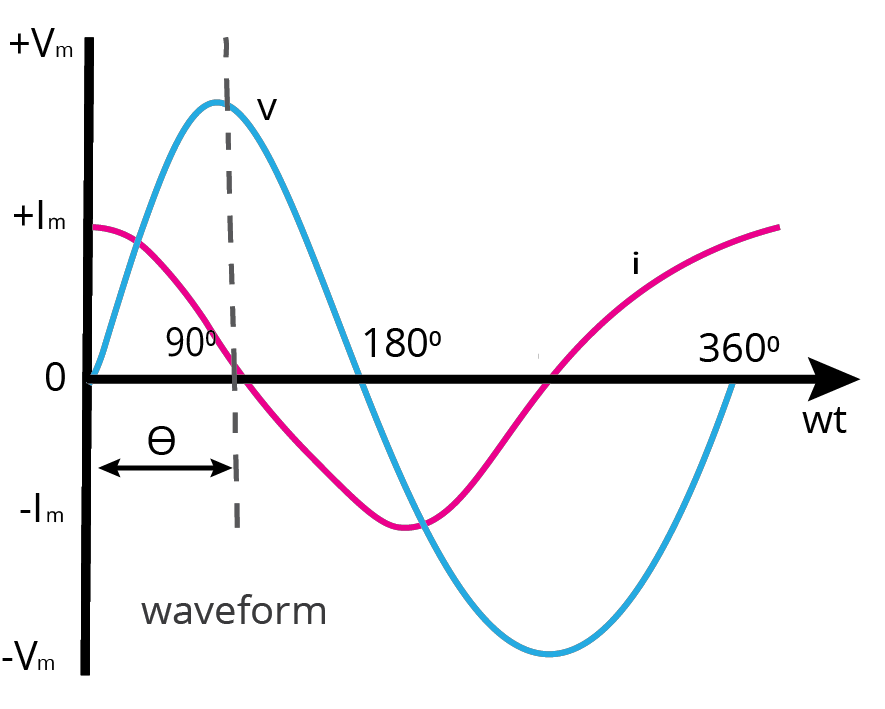
Impedance
Average and RMS value of AC
Admittance
Reactance
Resonance
Power Factor
L. C. Oscillations
Transformer
Important Concepts of Alternating Current
List of Important Formulae
Solved Examples of Alternating Current
1. The current in an inductive circuit is given by 0.3 sin (200t – 40°) A. Write the equation for the voltage across it if the inductance is 40 mH.
Sol:
Given, i = 0.3 sin (200t – 40°) A, L = 40mH =$40 \times 10^{-3} H $
$X_{L}$ = ${\omega L}$ = $200\times 400 \times 10^{-3}$ = 8Ω
$V_{m}$ = $I_{m}\times X_{L}$ = $ 0.3 \times 8$ =2.4V
In an inductive circuit, the voltage leads the current by 90^{\circ}.
Therefore,
V = $V_{m}sin(\omega\times t + 90^{\circ})$
V = $2.4 sin(200t - 40 ^{\circ} + 90^{\circ})$
V = $2.4 sin(200t + 50^{\circ})$.
Key point: The ques here focuses mainly on the phase difference between current and voltage in an inductive circuit.
2. The output of a step-down transformer is measured to be 24 V when connected to a 12 W light bulb. The value of the peak current is
$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$
$\sqrt{2}A$
$2A$
$2 \sqrt{2}A$
Sol:
Given:
Output of Secondary Voltage = $V_{s}$ = 24V
Power associated with Secondary $P_{s}$ = 12W
$I_{s}$ = $\dfrac{P_{s}}{V_{s}}$ = $\dfrac{12}{24}$ = 0.5A
Amplitude of the current in the secondary winding:
$ I_{\circ}$ = $I_{\circ}$ = $I_{s}\sqrt{2}$
= 0.5(1.414) = 0.707 = $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$A.
Hence, Option (a) is Correct.
Key Point: Here, in the case of a step-down transformer, the output voltage decreases and the output current increases.
Previous Year Questions of Alternating Current
1. An inductor 20 mH, a capacitor 50μF and a resistor 40Ω are connected in series across a source of emf V=10 sin 340t. The power loss in A.C. circuit is (NEET - 2016)
0.51 W
0.67 W
0.76 W
0.89 W
Sol:
Given:
V=10 sin 340t = $V_{rms} = \dfrac{10}{\sqrt{2}}$
L = 20mH = $20 \times 10^{-3} H $
C = 50μF = $50 \times 10^{-6} F $
R = 40Ω and V=10 sin 340t
$X_{C}$ =$\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$ = $X_{C}$ = $\dfrac{1}{340\times 50 \times 10^{-6}}$ = 58.8Ω
$X_{L} = {\omega L}$ = ${340\times 20 \times 10^{-3} }$ = 6.8Ω
$Z = \sqrt{R^{2} + (X_{L}- X_{C})^{2}}$ = $Z = \sqrt{40^{2} + (58.8- 6.8)^{2}}$ = $\sqrt{4304}$Ω
Hence P = $i_{rms}^{2}\times R$
Or P = $(\dfrac{V_{rms}}{Z})^{2}\times R$
=$(\dfrac{50}{4304}) \times 40$ = 0.47W
Correct solution is 0.47W and the closest option is (a).
Trick: Here the formulae of capacitive, inductive reactance and impedance play a major role in ans along with the power.
3. A series LCR circuit is connected to an AC voltage source. When L is removed from the circuit, the phase difference between current and voltage is $\dfrac{\pi} {3}$. If instead C is removed from the circuit, the phase difference is again $\dfrac{\pi} {3}$ between current and voltage. The power factor of the circuit is (NEET 2020)
0.51W
0.67W
0.76W
0.89 W
Sol:
Given:
When L is removed,
Phase = $\tan\phi$= $\dfrac{ X_{C}}{R}$ = $\tan\dfrac{\pi}{3}$ = $\dfrac{\ X_{C}}{R}$
When C is removed,
Phase=$\tan\phi$ = $\dfrac{X_{L}}{R}$ = $\tan\dfrac{\pi}{3}$ = $\dfrac{\ X_{L}}{R}$
From both above-mentioned equations, we have $X_{C} = X_{L}$
Hence, the circuit is in resonance and Z = R
So, power factor = $\cos\phi=\dfrac{R}{Z} $
The correct answer is 1 and option is b.
Trick: Formula of phase is given as = $\tan\phi = \dfrac{X_{L} - X_{C}}{R}$
Practice Questions
1. A 100 mH inductor, a 25 μF capacitor and a 15 Ω resistor are connected in series to a 120 V, 50 Hz a.c. source. Calculate
(a) impedance of the circuit at resonance.
(b) current at resonance.
(c) Resonant frequency.
(Ans (a) 15 Ω (b) 8 A (c) 100.7 Hz)
2. The inductance of a choke-coil is 0.2 Henry and its resistance is 0.50 Ω . If a current of 2.0 ampere (rms value) and frequency 50Hz is passed through it, what will be the potential difference across its ends ?
(Ans: 125.6 V)
Conclusion
In conclusion we can say that the chapter Alternating Current has covered all the important formulae and concepts like Power factor, Impedance, Reactance offered by different electrical circuits, etc. which will help in boosting your confidence to score high marks in the NEET 2026 exam. Students can have hands-on experience of the exam by practising the numericals.
NEET Important Chapter - Alternating Current

 Share
ShareFAQs on NEET Important Chapter - Alternating Current
1. What is the weightage of the Alternating Current in NEET?
Nearly 1-2 questions appear in the exam from this chapter, covering about 10 marks which makes about 2% of the total marks.
2. What are the key points that need to be practised for solving questions from Alternating Current ?
Students should practice enough numericals and learn formulae for solving the questions from the Alternating Current .
3. Are previous year questions enough for NEET ?
Aspirants should know that revision is the key factor to any preparation for NEET. Candidates can easily evaluate their NEET preparation and work on the portion they need to and try to overcome lackings. As famously said, practice is the key to success so more practice = 600+ marks in the exam.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video