Anatomy of Flowering Plants
Introduction
This article is created by keeping NEET aspirants in mind. It contains notes and important questions related to the plant kingdom and it will be great for last-minute revision.
It covers all the important concepts such as the difference between monocot and dicot root, simple and permanent tissues, etc. and these concepts are short and crisp. Along with this, it contains FAQs regarding the NEET exam.
Important Topics of Anatomy of Flowering Plants
Meristematic tissue
Permanent tissue
Vascular Tissue System
Leaf
Important Concepts
Tissue
A tissue is a collection of cells with a common origin that collaborate to perform a common function.
Plant Tissue
1. Meristematic Tissue
It is a type of simple tissue that consists of a group of similar and immature cells (meristematic cells) which can divide and form new cells.
Apical Meristem – present at the tip of root and shoot and results in the formation of primary tissues such as dermal, vascular, and ground tissues.
Intercalary Meristem – They are meristematic regions derived from the apical meristems. It helps in the elongation of the organs and allows fallen stems of cereals to become erect.
Lateral Meristem – It is present on the sides and helps in increasing the girth of the plant.
2. Permanent Tissue
Due to morphological, biochemical, and physiological differentiation, cells in these tissues have lost their ability to divide and have taken on a permanent shape, size, and function.
(a) Simple Permanent Tissue: The tissue is made up of similar permanent cells that carry out the same function. It is further divided into three types:
(b) Complex Permanent Tissue: They contain more than one type of cells and all the types of cells work together as a unit.
Difference Between Meristematic Tissue and Permanent Tissue
Tissue Systems
It is a tissue or a group of tissues that are derived from a portion of meristem which performs a similar function.
On the basis of their location and structure, there is three tissue system in plants.
1. Epidermal Tissue System
This system forms the outermost covering of the plant body.
It consists of the epidermis (made up of epidermal cells and stomata), and epidermal appendages such as root hairs, and trichomes.
2. Ground Tissue System
It forms most of the tissues between the epidermis and vascular tissues. For example, Cortex, Pericycle, Pith.
The tissues present in this region are simple tissues.
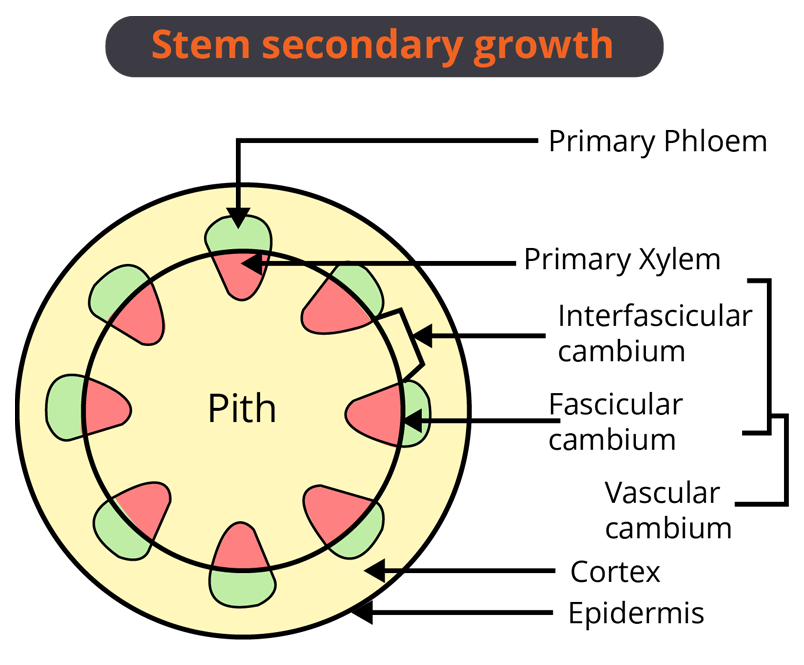
3. Vascular Tissue System
It forms a strand of vascular tissues called a vascular strand.
In gymnosperm and flowering plants, the vascular tissues occur as distinct patches called vascular bundles.
In roots, vascular bundles are radial and in stems it is conjoint.
Difference between Open and Closed Vascular Bundles
Difference between Xylem and Phloem
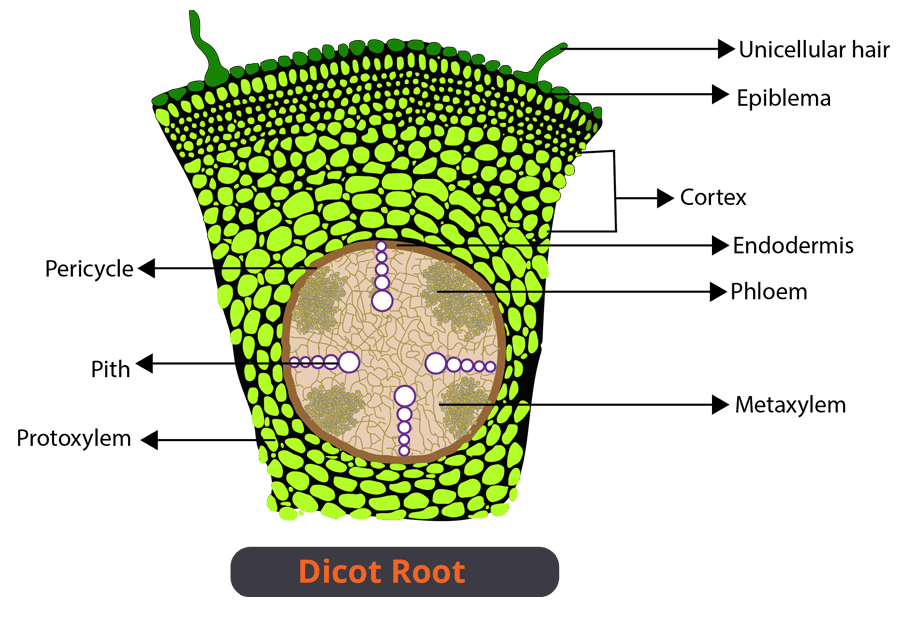
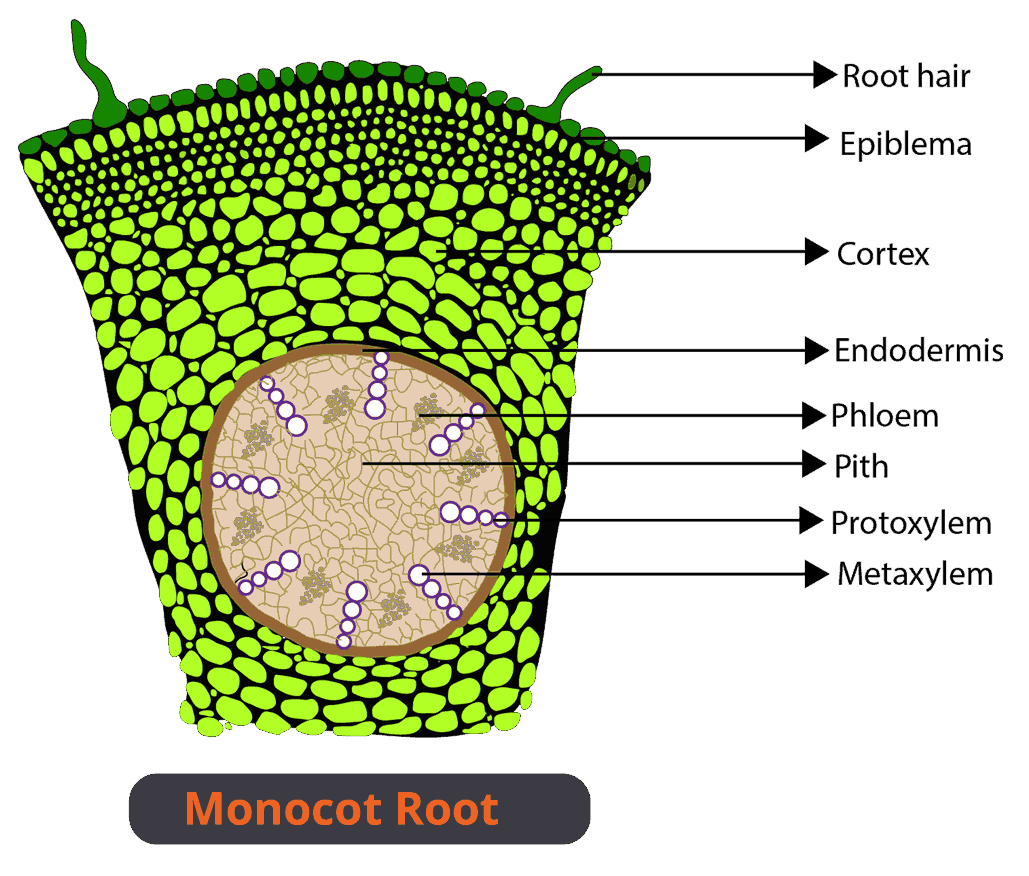
Difference Between Dicot and Monocot Root
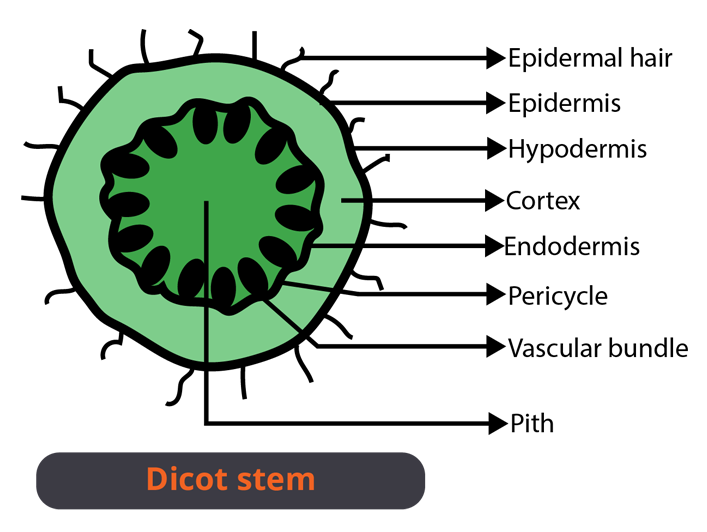
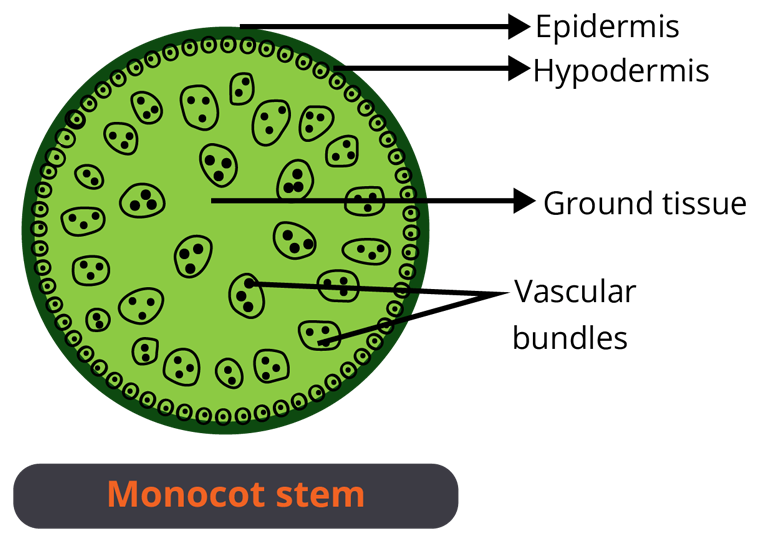
Difference between Dicot and Monocot Stem
Difference between Fascicular and Interfascicular Cambium
Leaf
Difference Between Dicot and Monocot Leaf
Solved Problems Example From Chapter
1. Why xylem and phloem are known as complex tissues?
Ans: Xylem and phloem are known as complex tissues because they are made up of more than one type of cells and these cells work in coordination to perform various activities.
Key Point to Remember:
Xylem- Tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma, xylem fibres
Phloem- Sieve tube, companion cells, Phloem parenchyma, phloem fibres
2. How do tree trunks get their growth rings? What is its significance of it?
Ans: Concentric rings are formed by secondary growth. The action of meristematic tissue, cambium, causes secondary growth. The age of the tree can be determined by counting these rings.
Key Point to Remember: Concentric rings also known as annual rings and growth rings.
Solved Problems of Previous Year Question from the Chapter
1. The vascular cambium typically gives rise to one of the following anatomical structures?
a. Phelloderm
b. Secondary xylem
c. Periderm
d. Primary phloem
Ans: b. Secondary xylem.
The ring of vascular cambium produces secondary xylem on the inner side and secondary phloem on the outside. Both are in the form of rings.
Trick to Remember: Secondary xylem commonly known as wood
2. There is one old piece of dicot stem and one piece of dicot root. So, which of the following anatomical structures will be used to distinguish between the two?
a. Cortex
b. Primary xylem
c. Secondary phloem
d. Protoxylem
Ans: d. Protoxylem.
The position of the protoxylem distinguishes the old dicot root from the dicot stem. Protoxylem is oriented toward the pith (endarch xylem) in the stem and toward the periphery in the root (exarch xylem).
Trick to Remember: First formed xylem
Practice Questions
1. In plants, healing of wounds takes place by the activity of
a. Apical meristem
b. Secondary meristem
c. Parenchyma
d. Intercalary meristem
Ans: b. Secondary meristem.
It is a type of lateral meristem. Here, some of the permanent cells acquire the power of division (called dedifferentiation). This meristem gives rise to secondary tissues such as vascular cambium of the root, interfascicular vascular cambium of stem, cork cambium or phellogen, and wound cambium (from the cells surrounding an area of injury or wound).
Key to Remember: Secondary meristem responsible for growth in girth
2. The vascular cambium, on one side, produces xylem and on another side produces phloem due to its
a. Interfascicular position
b. Differential action of hormones
c. Gravitational force
d. Rapid division of cells
Ans: b. Differential action of hormones.
Intra and interfascicular cambium unite to form a ring of cambium known as vascular cambium in the stems of dicotyledonous plants, producing secondary xylem on the inner side and secondary phloem on the outer side. Hormonal influences play a role in this.
Conclusion
This post is written keeping in focus the NEET aspirants in mind. It covers all of the major concepts and provides clear explanations, making it ideal for quick and successful revision. It covers key ideas, concepts, and problems from previous year's NEET question papers, as well as NEET practice tests and Biology NCERT. Make sure to test your understanding by attempting the Practice question on your own.
NEET Important Chapter - Anatomy of Flowering Plants

 Share
ShareFAQs on NEET Important Chapter - Anatomy of Flowering Plants
1. What is the weightage of the chapter Anatomy of Flowering Plants?
The chapter Anatomy of Flowering Plants carries 6% of the weightage in NEET.
2. What is the number of questions that are asked from Anatomy of Flowering Plants in NEET?
The number of questions that come from this chapter is 3.
3. How do I find out if my NEET application has been rejected?
You must log in to the registration window using the credentials to check that your NEET 2020 Application Form has been rejected. If you are unable to proceed through the confirmation page, or if you are unable to locate your admission card after it has been released, this could indicate that your application has been rejected.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video