




Biological Classification
This article is created by keeping NEET aspirants in mind. It contains notes and important questions from the chapter Biological Classification. This article will be served for last-minute quick revision notes as well as for clarifying concepts in short related to the chapter.
It covers all the important concepts such as the characteristic features of living beings, the basic unit of biological classification, rules of binomial nomenclature, and the difference between taxonomy and systematics. Biological classification notes include all the concepts in short and crisp language. Along with this, it contains generic FAQs regarding the NEET Exam.
Important Topics of The Living World
Kingdom Monera, Protista and Fungi
Artificial system of classification
Natural system of classification
Five Kingdom Classification
Viruses, Viroids and Prions
Lichens
Important Concepts
Need for Biological Classification
It is impossible to identify any organism without classification.
It is not possible to research each and every organism. The study of one or two species from a group provides enough knowledge about that group's essential characteristics.
Without an appropriate classification system, it is impossible to study prehistoric organisms.
Classification aids in understanding the relationships between various categories of species.
Evolutionary trends can be determined based on relationships and the simplicity or complexity of members of distinct taxa.
Artificial System of Classification
It is a classification system that groups organisms based on one or two morphological features.
Aristotle categorized animals into two types: enaima (with red blood) and anaima (without red blood).
Pliny divided animals into two categories: flight and non-flight ones.
Natural System of Classification
It is a classification method that considers a comparative examination of a number of traits in order to reveal natural similarities and differences, and thus natural connections, among species.
Characters that are relatively constant are used in the system.
Morphological, anatomical, and cytological characteristics, physiology, ontogeny or development, reproduction, cytochemistry and biochemistry, and experimental taxonomy, are among them.
Difference between Artificial System and Natural System
Phylogenetic System of Classification
In this system, the classification of organisms is based on their evolutionary relationships.
Difference between Natural System and Phylogenetic System
Two Kingdoms of Classification
It was proposed by Linnaeus.
He divided the living things into two kingdoms: Plantae and Animalia.
Difference Between Plant and Animal Kingdom on the basis of Two Kingdoms of Classification
Drawbacks of Two Kingdoms of Classification
Some organisms show both features of plants and animals. Eg., Euglena like plants are autotrophs and like animals are motile.
Sponges like plants are fixed, having an irregularly branched body.
Fungi resemble plants in having cell walls but lack chlorophyll.
Bacteria and cyanobacteria are prokaryotic in nature.
Three Kingdoms of Classification
It was proposed by Ernst Haeckel.
He divided the living organisms into three kingdoms: Plantae, Animalia and Protista.
Difference between Plant and Animal Kingdom and Protista on the basis of Three Kingdoms of Classification
Drawbacks of Three Kingdom of Classification
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are not separated.
Protista includes both unicellular and multicellular organisms.
Four Kingdoms of Classification
It was proposed by Copland.
He added a new kingdom known as Monera.
He divided all the living organisms on the basis of cell organization and mode of nutrition.
Drawbacks of Four Kingdoms of Classification
Copland was not able to place fungi in any of the kingdoms.
Five Kingdom of Classification
It was proposed by R.H. Whittaker.
He added the new kingdom Fungi.
This classification is based on cell structure, thallus organization, mode of nutrition, reproduction and phylogenetic relationships.
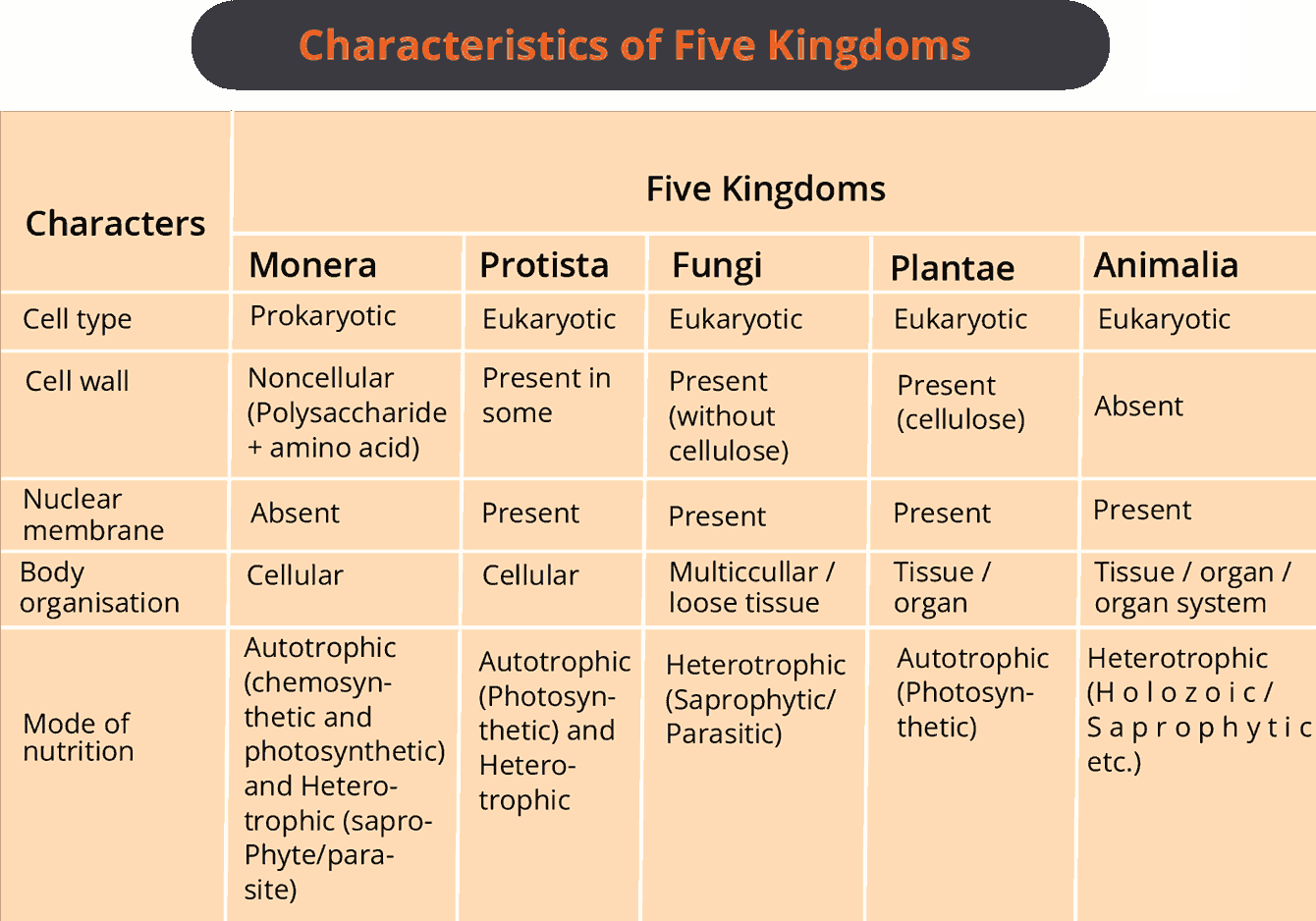
Difference between Monera and Protista
Viruses
Dmitri Ivanowsky discovered the virus for the first time on tobacco leaves causing mosaic disease of tobacco.
M.W. Beijerinek named it "virus"
Virus is an obligate parasite. It is inert outside the host cell (virion).
Biosynthetic machinery is absent.
It does not grow, divide or reproduce like other organisms.
A virus consists of two parts; nucleoid (genome) and capsid, and envelope (present only in a few viruses).
In nucleic acid, only DNA or RNA is present but never both.
Viral Diseases
Viroids
It was discovered by Diener.
They are the smallest self-replicating particles.
They are infectious RNA particles and lack protein coats.
They are obligate parasites.
They can multiply by both RNA dependent and DNA dependent replication.
They are known to cause diseases in plants only.
For example: Potato spindle tuber, chrysanthemum stunt.
Prions
They are highly resistant small-sized glycoprotein particles (which function as infectious agents).
They also act as a catalyst, therefore, converts normal protein into a prion state.
Diseases Caused by Prions
Accumulates in nervous tissue and brings about its degeneration.
Scrapie of sheep
Mad cow disease
Cruetzfeldt-Jakob disease
Kuru
Difference Between Virus and Viroid
Lichens
They are a symbiotic or mutual relationship between algae and fungi.
The algal component (autotrophic) is called phycobiont and the fungal component is known as mycobiont (heterotrophic).
Algae prepare food and fungi provide shelter and absorb mineral nutrients.
They are good pollution indicators, as they do not grow in the areas which are polluted.
Solved Example/Problems from Chapter
1. State two economic importance of
heterotrophic bacteria
archaebacteria
Ans:
Heterotrophic bacteria- (i) Vitamins, medicines, cheese, and curd are all made using them. (ii) They aid in nitrogen fixation.
Archaebacteria- (i) They are employed in the manufacture of biogas. (ii) They're employed in mine bioleaching.
Key Point to Remember:
Heterotrophic Bacteria- Cannot synthesize their own food.
Archaebacteria- They can tolerate high temperatures.
2. What are the properties of diatom cell walls?
Ans: Cell walls in diatoms are encrusted with silica, which creates distinct patterns on the walls. These diatoms leave a lot of cell wall deposits in their habitat, which eventually turns into diatomaceous earth.
Key Point to remember: Cell wall is indestructible
Solved Problems of Previous Year Questions
1. Which of the following statements is correct?
Organisms that depend on living plants are called saprophytes.
In specialized cells known as sheath cells, several species can fix atmospheric nitrogen.
The fusion of two cells is called Karyogamy
Fusion of protoplasms between two motile or non-motile gametes is called plasmogamy.
Ans: (d) The fusion of protoplasms between two motile or non-motile gametes is known as plasmogamy.
2. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
The infective constituent in viruses is the protein coat.
Viruses are obligate parasites.
Prions consist of abnormally folded proteins.
Viroids lack a protein coat.
Ans: (a) The Infective constituent in viruses is the protein coat.
Viruses are nucleoprotein entities that can use the synthesis machinery of another organism's live-cell for multiplication rather than growth and division.
Trick to remember: Virus body is made up of Nucleic acid + Protein = Nucleoprotein.
Practice Questions (Biological Classification MCQs for NEET)
1. Which system of classification was given by Bentham and Hooker?
Phylogenetic
Natural
Numerical
Artificial
Ans: (b) Natural
It is a classifying method that considers a comparative examination of a number of traits in order to describe natural similarities and differences, and thus natural connections, among species.
Key point to remember: Employs several morphological characters for grouping of organism
2. Archaea and Nitrogen-fixing organisms are classified among which of the following kingdoms?
Protista
Monera
Fungi
Plantae
Ans: (b) Monera
Monera is the kingdom of prokaryotes. It is divided into two major groups; archaebacteria and eubacteria. Eubacteria is further divided into two types, i.e., bacteria and cyanobacteria (nitrogen-fixing bacteria).
Key point to remember: Monera - Unicellular prokaryotes
Conclusion
This article covers all of the major concepts such as the need for biological classification, natural and artificial systems of classification, viruses, viroids, prions, etc. and also provides clear explanations which make it ideal for quick and successful revision. It covers key ideas, concepts given in Biology NCERT and problems from previous year's NEET question papers, as well as NEET practice tests which makes it excellent for the last time revision.
NEET Important Chapter - Biological Classification

 Share
ShareFAQs on NEET Important Chapter - Biological Classification
1. Is the chapter on biological classification important for NEET?
Biological classification is an important and high-scoring topic in biology that helps you understand living species by comparing and contrasting their similarities and differences.
2. What is the number of questions that are asked from the NCERT book?
More than 80-85 percent of questions (asked directly or indirectly) in NEET come from NCERT, on average.
3. How do I find out if my NEET application has been rejected?
You must log in to the registration window using the credentials to check that your NEET 2022 Application Form has been rejected. If you are unable to proceed through the confirmation page, or if you are unable to locate your admission card after it has been released, this could indicate that your application has been rejected.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video


