




Understand the Importance of Biomolecules in Living Organisms
Every living being, from kingdom Plantae to Animalia, is built up of small building components called cells. They are the smallest fundamental units in our body, made up of a range of inorganic and organic substances. Biomolecules are all carbon-containing compounds present in living things.
Biomolecules chapter is an important part of the NEET Chemistry Syllabus. In these biomolecules notes, we have covered all of the major topics of biomolecules, including what biomolecules are, types of biomolecules, the structure of biomolecules, previous years’ questions, practise questions, etc. This comprehensive biomolecules NEET note will give you a leg up on the competition.
What are Biomolecules?
Biomolecules are organic chemicals that make up the very backbone of a cell in living creatures. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins, for example, could all be present in various quantities. All of these biomolecules serve important functions in the body and are produced there. Some examples of biomolecules are DNA, RNA, cellulose, and glucose.
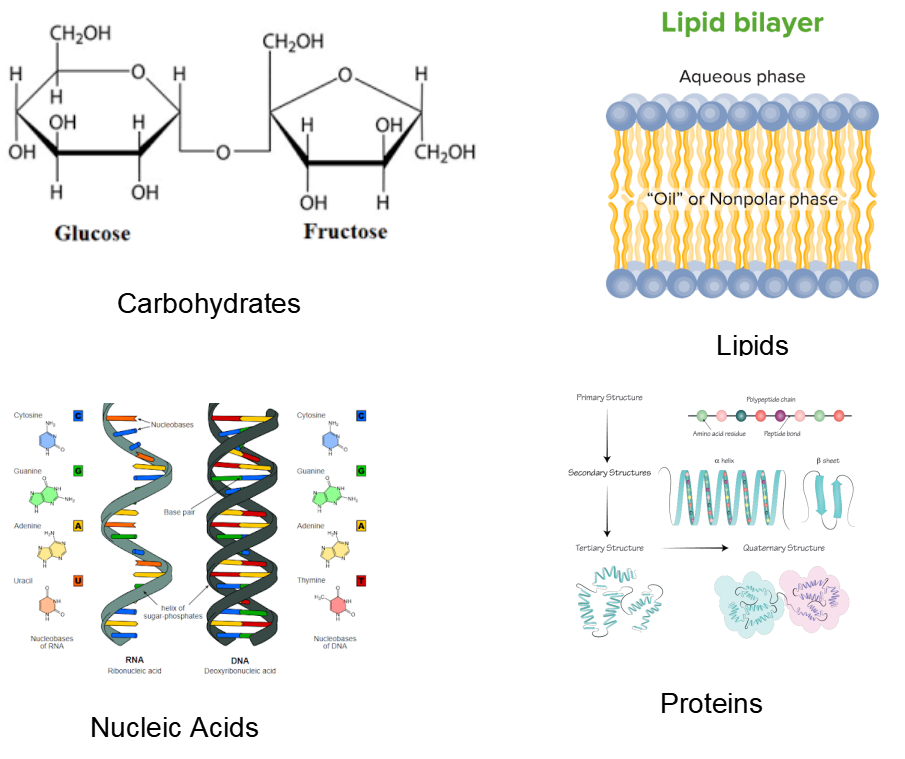
While organic molecules can be made up of straight-chain carbons, they can also be made up of cyclic rings, branched chains, or a combination of these. They differ in terms of characteristics, chemical properties, and structures, which leads to differences in physical attributes like boiling and melting points, as well as water solubility. Biomolecules can be classified as hydrophilic or hydrophobic depending on their affinity for water.
Major Structural Elements of Biomolecules
The majority of biomolecules are organic compounds made up of only four components. The major structural elements of biomolecules are oxygen, carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen. They account for 96 percent of the mass of the human body. However, several additional elements, such as biometals, are present in trace levels.
Biomolecules Flowchart
Biomolecules chart is discussed below.

Classification of Biomolecules
Make sure you understand organic compounds and their properties before moving on to the next section of the biomolecules NEET notes. This will make it easier for you to comprehend the next things. The biomolecules lists are discussed here.
Carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four main types of biomolecules. Among these, the most abundant biomolecule on earth is carbohydrates.
1. Carbohydrates- Carbohydrates are polysaccharides that are the end products of the majority of our body's metabolic processes. They are the foundations of our metabolic apparatus, and their molecular structure is made up of several monosaccharides stacked on top of one another. Carbohydrates are abundant in most living cells, and it is safe to claim that these biomolecules represent the origin of life on our planet.
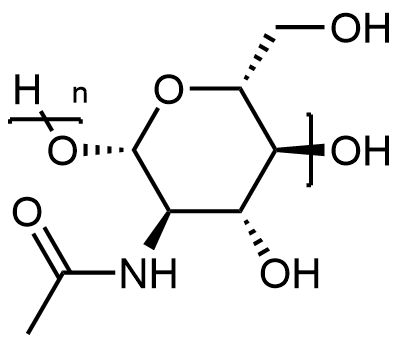
For example, cellulose is an essential component of plant cells, and it is normally stored as starch. Glucose, on the other hand, is the end product of photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into food. Monosaccharides, disaccharides, and oligosaccharides are the three main types of saccharides. They're divided into groups based on the number of sugar molecules they contain. Sucrose, cellulose, fructose, glucose and dextrose are some of the most common sugars we encounter regularly.
You'll also learn about the three fundamental types of sugar-containing carbohydrates, namely monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, and disaccharides, in these biomolecules class 12 notes.
Monosaccharides- They are the most basic carbohydrates and cannot be further hydrolysed. They are present in the general chemical formulae of (CH2O)n. Ribose and glucose are examples of monosaccharides.
Oligosaccharides- These are complicated carbohydrates that break down into two to ten monosaccharide subunits. They are then subdivided into other categories. Stachyose and raffinose are two examples.
Disaccharides- Disaccharides are carbohydrates that break down into two monosaccharide molecules when hydrolysed. Sucrose, for example, produces fructose and glucose. Maltose, on the other hand, releases two molecules of glucose when hydrolysed.
2. Proteins- Proteins are organic substances that are abundant in our meals and are made up of amino acids. They are made up of long-chain monomers joined together by polypeptide bonds. As a result, proteins are also known as polypeptides.
Protein Structure
Protein is a complex chain made up of amino acids. In a linear protein molecule, amino acids are connected by peptide bonds. Proteins are also referred to as polypeptides.
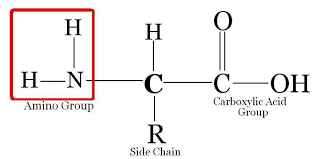
Amino acids are organic compounds and are substituted amines.
The α-carbon has various substituents, making them also known as α-amino acids.
The α-carbon is attached to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable R group.
There are 20 amino acids in proteins, determined by the nature of the R group.
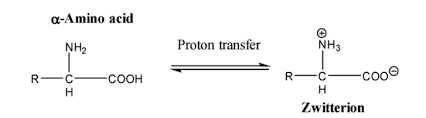
Amino acids can exist in a zwitterionic form, which changes with pH
NH3+ at low pH
COO– at high pH.
3. Lipids- Fats, oils, steroids, phospholipids and glycerol are all examples of hydrophobic substances. Lipids can have a variety of structures and properties depending on the ingredients. Fatty acids, for example, are composed of a single carboxyl group attached to a variable group or R. Saturated or unsaturated fatty acids can be found in these foods.
Furthermore, some lipids may contain phosphorus groups that are linked to the organic groups. Phospholipids are another name for them. Phospholipids are the fundamental components of a cell's plasma membrane.
4. Nucleic Acids- The smallest fundamental pieces of our genetic information, often known as genes, are made up of DNA and RNA building blocks. These are a combination of nitrogenous bases, sugar molecules, and a phosphate group that make up our bodies' genetic material.
Purines and pyrimidines are examples of heterocyclic compounds. Xanthine, caffeine, and nitrogenous bases like guanine and adenine are examples of purines. The product of nitrogenous bases forming chemical bonds with sugar molecules is known as a nucleoside. Nucleotides are formed when these molecules interact with phosphate groups (RNA, DNA).
Is Lecithin a Heteropolymer?
Phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylserine and phosphatidic acid are all glycerophospholipids found in lecithins.
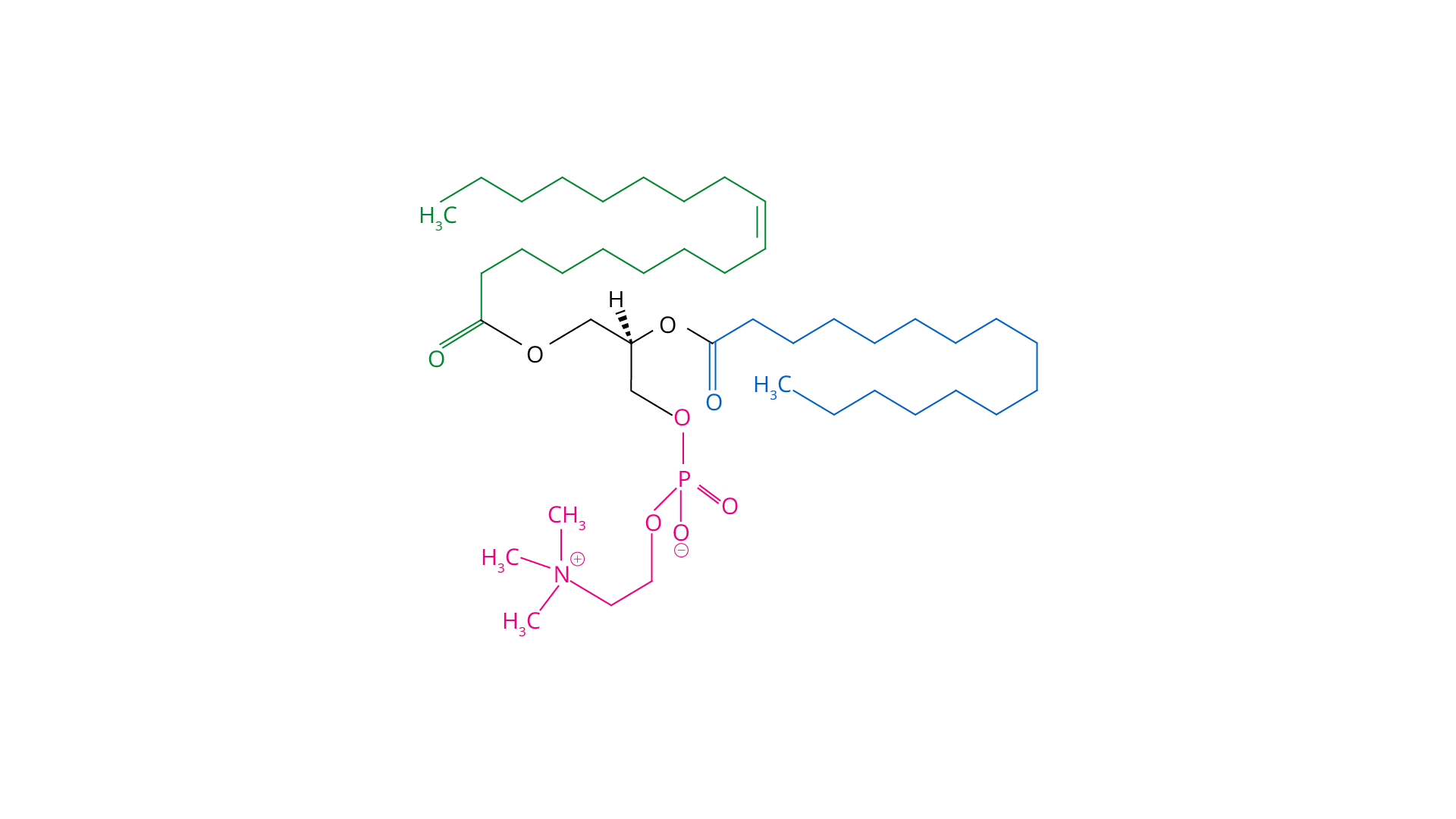
A Linear Polymeric Biomolecules with Reducing and Nonreducing Group
Sugars with an accessible OH group are known as reducing sugars. Starch is made up of 1,4 bonds between two glucose components that are broken down during digestion. Amylose and amylopectin are two different types of amylose. Amylose is a linear poly-D-glucose with alpha 1, 4 linkages connecting the monosaccharides. The OH group on one edge of the amylose is accessible, making it a diminishing end, whereas the OH group on the other edge forms the glycosidic bond, making it a non-reducing end.
Importance of Biomolecules
Biomolecules are essential for life since they assist organisms in growing, living, and reproducing. They aid the development of organisms ranging from single cells to sophisticated living beings such as humans by interacting with one another. Because of their shape and structure, they can be used for a variety of purposes.
Solved Examples from the Chapter- Biomolecules
1. How do you explain the absence of the aldehyde group in the pentaacetate of D-glucose?
Due to the lack of a free OH group at C-1, glucose pentaacetate cannot be hydrolysed in an aqueous solution to produce the open-chain aldehydic form, and so glucose pentaacetate does not react with NH2OH to make glucose oxime. This demonstrates that glucose pentaacetate lacks an aldehyde group.
Key Points- Hydroxyl group (OH) undergoes hydrolysis reaction while carbonyl group does not.
2. The melting points and solubility in water of amino acids are generally higher than that of the corresponding halo acids. Explain.
Amino acids, like ionic substances, have a strong electrostatic attraction in the zwitterion. As a result, their melting point and solubility are higher than those of the comparable haloacids.
Key Points- Melting point and solubility depend upon the type of attraction or bond present in the molecule. These parameters (melting points and solubility) are proportional to the polarity of the molecule.
Solved Problems of Previous Years’ Question from the Chapter - Biomolecules
1. The RBC deficiency is a deficiency disease of
(1) Vitamin B12
(2) Vitamin B6
(3) Vitamin B1
(4) Vitamin B2
The correct answer is option (1). The deficiency of vitamin B12 leads to the formation of unusually large, abnormal, immature megaloblasts from bone marrow.
Tricks- Vitamin B 12 deficiency causes Pernicious anemia/Megaloblastic anemia.
2. Sucrose on hydrolysis gives
(1) β-D-Glucose+α-D-Fructose
(2) α-D-Glucose+β-D-Glucose
(3) α-D-Glucose+β-D-Fructose
(4) α-D-Fructose+β-D-Fructose
The correct answer is option (1).
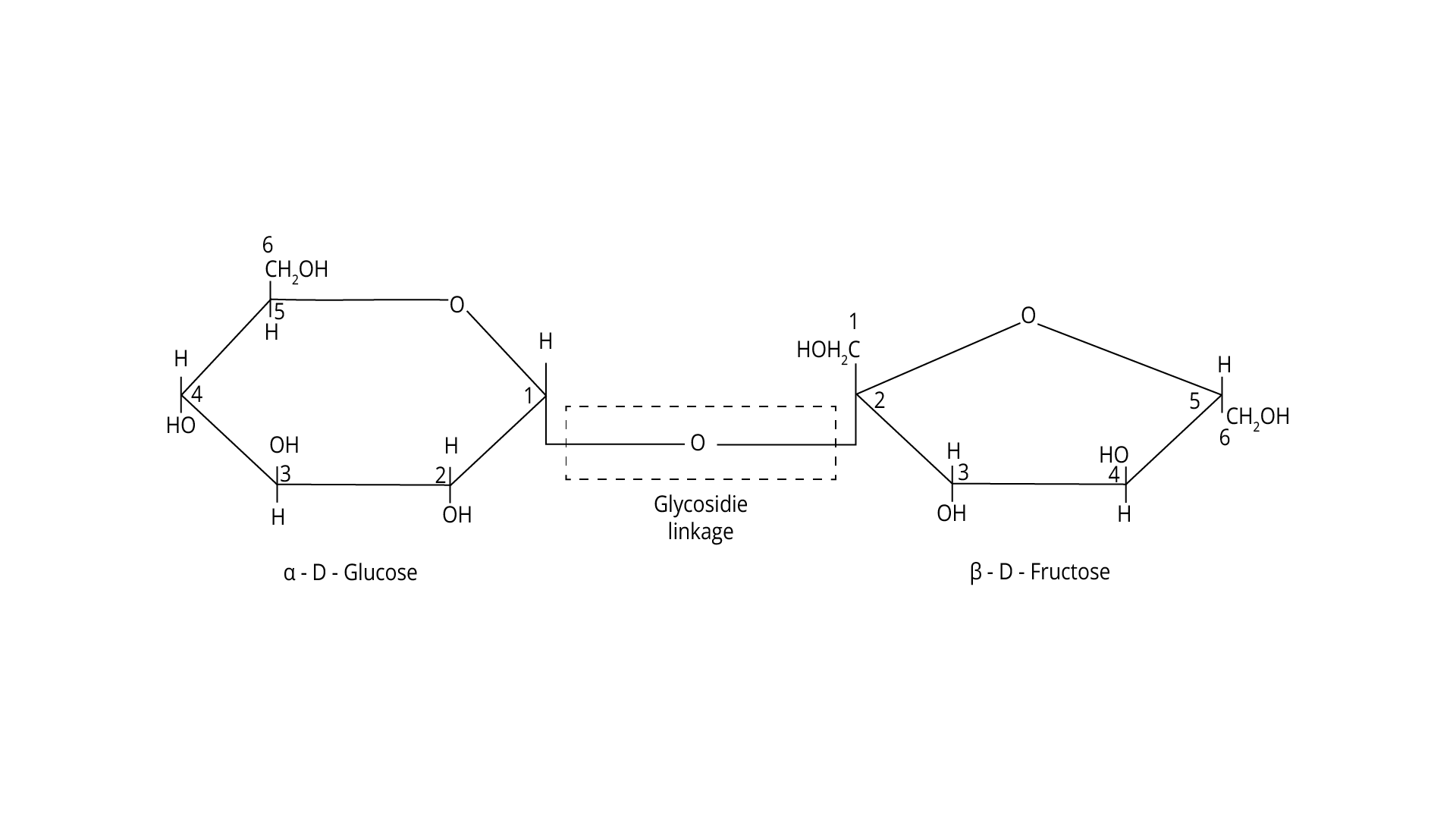
Trick- These two monosaccharides are held together by a glycosidic linkage between C1 of α-D-glucose and C2 of β-D-fructose.
3. The non-essential amino acid among the following is
(1) Valine
(2) Leucine
(3) Alanine
(4) Lysine
The correct answer is option (1). Alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine and tyrosine are non-essential amino acids.
Trick- This amino acid is synthesised and stored in our body.
Practise Questions
1. Why cannot vitamin C be stored in our body?
(Because it is water-soluble)
2. What is the difference between DNA and RNA nitrogenous bases?
DNA contain thymine while RNA contain uracil
Conclusion
Studying these biomolecules notes for NEET as well as for JEE exam will help you to go a long way toward ensuring you get the best rank. Students can get well-structured and accurate study notes on the Vedantu Website for free.
Essential Study Materials for NEET UG Success
Biomolecules - Building Blocks of Life

 Share
ShareFAQs on Biomolecules - Building Blocks of Life
1. What are biomolecules?
Biomolecules are molecules made by living things. They are essential for life and help in important processes like growth and energy production. The main types of biomolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids (fats), and nucleic acids (DNA & RNA). Small molecules like vitamins and hormones also play important roles in the body.
2. What are the four main types of biomolecules?
The four main types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. These are essential for life, helping with energy, structure, and genetic information in living things.
3. What type of biomolecule is ATP?
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) is a type of nucleic acid. It is a nucleotide made of a sugar, a nitrogen base, and phosphate groups.
4. Is DNA a protein or an acid?
DNA is an acid, not a protein. It is a type of nucleic acid, just like RNA. Along with proteins, fats (lipids), and carbohydrates, nucleic acids are one of the four main molecules essential for life.
5. What kind of biomolecule is an enzyme?
Enzymes are proteins that help speed up chemical reactions in the body.
6. What kind of biomolecule is glucose?
Glucose is a type of carbohydrate. It is a simple sugar (monosaccharide) with six carbon atoms. The body quickly breaks it down to produce energy.
7. What is a biological catalyst?
A biological catalyst is something that helps speed up chemical reactions in living things without being used up. Enzymes, which are mostly proteins, are the most common biological catalysts.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video


