




A Detailed Overview of Euglena and Its Features
Is the topic of Euglena – Overview, Classification, Structure and Functions for NEET Biology giving you a hard time? If yes, then how about Vedantu making it easy for you? Vedantu has brought this as well as many other topics of NEET Exams for you in an easier and more understandable format. All these are available for free and made available to you by Vedantu’s experts in biology. For this particular topic, let’s start by understanding what Euglena is.
Euglena comes under the category of eukaryotes, meaning it has a nucleus within its cell membrane. Unlike the prokaryotes, one of the prominent Euglena characteristics is that these organisms are bigger by almost ten times. However, both types have other organelles inside the plasma membrane.
Herein, you will find Euglena structure and classification explained in detail for your fundamental understanding. Make sure you go through each section thoroughly to Ace the Exam with flying colours.
Like every other living organism, scientists have categorically defined Euglena for a universal understanding. Here is the table for the relevant data. Ensure that you remember each category distinctively to avoid confusion in the Exam.
Classification of Euglena
Many times questions based on an organism's place in biological classification have appeared in the NEET Examination. Therefore we have discussed the classification of Euglena in a tabular format, this will help you in remembering it easily.
From the table, you can see Euglena is categorised under eight heads. Remember, every classification has a reason behind it, which has made the Euglena fall into a specific class or order or phylum. For instance, one of the Euglena characteristics is that it has chlorophyll, hence it is put under phylum Euglenozoa.
Structure of Euglena
To understand the fundamental structure, here is a Euglena diagram to help you. Carefully look at the picture, which shows how the plasma membrane has enclosed all the organelles inside it. Also, note the nucleus is represented with red color.
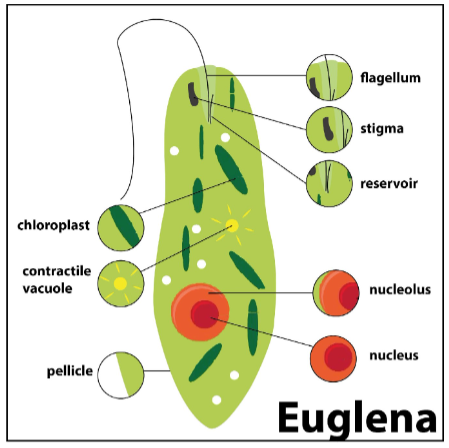
For your convenience, each organelle is well-labelled. Also, you should note here that their properties remain the same, similar to any other eukaryotic cell. To help you understand, here is a short description of some of the essential constituents of Euglena.
1. Stigma- It is an area that is sensitive to light. Therefore, the stigma helps it to move towards a light source to conduct photosynthesis.
2. Flagellum- It is a long thread-like structure that works as a navigator or a steering wheel in a car. The thin filament helps Euglena to move forward in any direction it desires.
3. Chloroplast- It is the organelle present inside the plasma membrane that helps in conducting photosynthesis.
4. Vacuole- This helps in expelling excess water inside the membrane into the reservoir. This excess water, if not expelled, will burst the cell entirely.
5. Pellicle- It is a thick membrane that is present on the other side of the filament-like structure. This also helps in moving forward when Euglena is wriggling.
6. Nucleus- It is the central organelle of Euglena that contains a nucleolus and DNA. The nucleus is responsible for conducting cellular activities.
You are now aware of the cell constituents and their functions. Make sure you get through them all in detail for an in-depth clarification. Also, refer to the diagram as you study the Euglena characteristics.
Functions of Euglena
By now, you might have known Euglena is capable of moving and also reproducing. Hereunder, we will dig deeper into these two concepts for a better hold on this topic.
1. Reproduction- The Euglena undergoes asexual reproduction. That being said, Euglenas divide themselves longitudinally into two halves and produce offspring. Their entire life is spent in a swimming stage where they float freely and survive in a non-motile stage.
Here in the Euglena reproduction, they have a thick wall that protects them from external injuries. In some other instances, most Euglenas come together and form a mass by leaving their flagella. They come together into a soft substance that is mostly gelatinous.
Binary fission occurs, and the Euglenas produce their daughter cells. These cells then grow their respective flagella and become Euglenas again. Then they come out of the mass, which is termed as the palmelloid stage.
2. Locomotion- The Euglena structure facilitates it to perform locomotion. As already discussed, it has light receptors like features called the stigma, it helps in moving. The stigma navigates or guides the Euglena towards the light to undergo photosynthesis. This is called phototaxis movement.
3. Nutrition - Euglena has chloroplasts with chlorophyll, which come from green algae through a symbiotic relationship. These chloroplasts help Euglena perform photosynthesis, but they also need other nutrients, like vitamin B12, to survive. Some Euglena species lose their chlorophyll in the dark and get nutrients by absorbing organic matter. Other species of Euglena are heterotrophs, meaning they absorb organic compounds or engulf bacteria and small organisms for food. Euglena also produces paramylon, a type of glucose stored for energy when there's no light. Some species release a toxic substance called euglenophycin that can kill fish. Euglena is grown in some countries, like Japan, to produce paramylon, and certain species contain vitamin E and astaxanthin.
In another instance, there might be more than one flagellum to help the Euglena in locomotion. In case, there are more than one flagella, both differ in size. The longer one protrudes out of the cell to help in swimming and move forward. Whereas, the shorter one remains inside the cell.
Hence, now you know how Euglena moves and spends their entire lifetime. Although this topic does not end right here, there is always scope for more learning. Here is a short guide to help you make the most of your time available before NEET.
Get Hold of the Basics and Excel Your Exams
High scores are mandatory now, considering the fierce competition or securing a decent career. Since your journey in the medical field is only about to begin, it is better to be cautious right from your first step. To start with, study all your lessons, including Euglena's characteristics and others and revise them.
Also, do not forget to check the Euglena diagram. It will build a more robust understanding and help you retain information longer. Besides, get adequate sleep and ensure a balanced diet while you prepare. Indulging yoga or meditation can also help you in keeping calm and motivated.
Essential Study Materials for NEET UG Success
Conclusion
This much information about Euglena will put you in a position where you will be able to answer all the questions related to it in the Exam hall of the NEET Examination. It will also help you in other medical entrance Exams as well such as JIPMER, AIIMS, and IPU NEET.
FAQs on Euglena- Overview, Classification, Structure and Functions for NEET
1. What do you understand by euglena?
Euglena is an eukaryotic cell that has a plasma membrane covering all its organelles. It belongs to kingdom Protista and phylum euglenoza.
2. What are the fundamental characteristics of euglena?
The fundamental euglena characteristics include containing chlorophyll and performing locomotion with a pellicle. Both these features resemble plant-like and animal-like characteristics.
3. What is the basic anatomy of euglena?
The basic anatomy of euglena is that it has a nucleus and a cell membrane. Its nucleus controls the cellular activities, and the membrane encloses all the organelles, thereby protecting the innerds
4. How is the locomotion of euglena like?
For locomotion, euglenas use their filament-like structure called a flagellum. They also possess a pellicle that is the thick membrane, which helps them in movement.
5. Is Vedantu helpful in understanding the topic of Euglena – Overview, Classification, Structure and Functions for NEET Biology?
Vedantu has supplied a lot of study material for students preparing for the NEET Examination for years now. Students themselves have testified how helpful these free study materials are. The same has been applied while preparing Euglena – Overview, Classification, Structure and Functions for NEET Biology for you. Reading this will help you cover the topic in its entirety. After reading this you will be in a position to answer all the questions related to Euglena not just in NEET biology Exams but also in other medical entrance Exams.
6. What are the 7 levels of classification for Euglena?
Euglena is classified into 7 levels based on shared traits-
Domain – Eukaryota (has a nucleus)
Kingdom – Protista (not a plant, animal, or fungus)
Phylum – Euglenozoa
Class – Euglenophyceae
Order – Euglenales
Family – Euglenaceae
Genus – Euglena
7. What harms Euglena?
Tips to control Euglena in ponds
To control Euglena, some effective treatments include Copper Sulfate, Copper Chelated Complexes, and Alkylamine salts of Endothall. Copper Sulfate and Copper Chelated Complexes work very well, while Alkylamine salts of Endothall are also helpful.
8. Are Euglena and Leishmania the same?
No, Euglena and Leishmania are not the same. Both belong to the same group called Euglenozoa, but they are different types of organisms. Euglena is a single-celled algae, while Leishmania is a type of parasite.
9. What are the 5 features of Euglena?
Here are five key features of Euglena-
Single-celled- Euglena is made up of just one cell.
Green colour- They appear green because of the chlorophyll inside.
Flagellum- They have a tail-like structure called a flagellum that helps them swim.
Contractile vacuole- This part of Euglena helps get rid of extra water from the cell.
Eyespot- Euglena has a red-coloured spot that helps them sense light.























