




Learn What Is Central Nervous System , Its Functions And Its Importance
CNS full form stands for Central Nervous System, which consists of the brain and spinal cord. It plays a vital role in controlling and coordinating all bodily functions.
Learn and get simple and clear explanation of the CNS, including its structure, functions, and significance in maintaining overall body function.
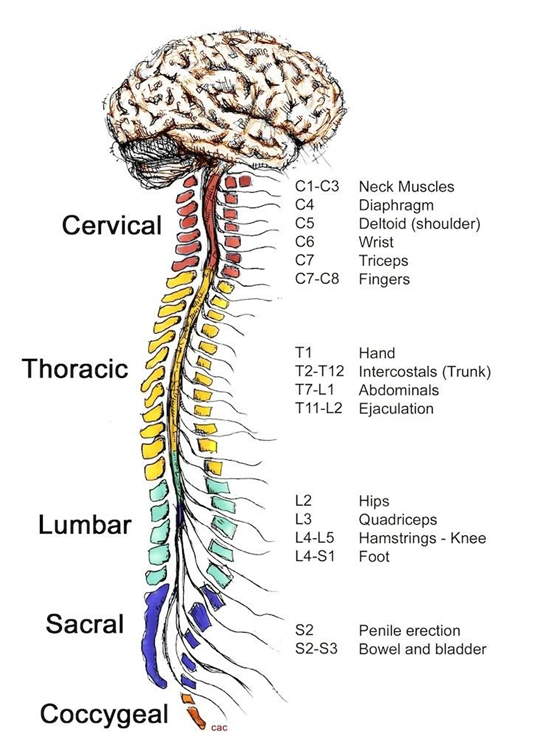
Understanding the Central Nervous System (CNS)
The CNS is integral to coordination, processing information, and responding to the body’s internal and external environments. The brain processes information and sends commands, while the spinal cord transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
Key functions of the CNS include processing sensory information, controlling motor functions, and maintaining homeostasis by regulating vital bodily processes like heart rate and respiration.
Grey and White Matter in the CNS
The CNS is composed of grey and white matter, which are essential for processing and transmitting information.
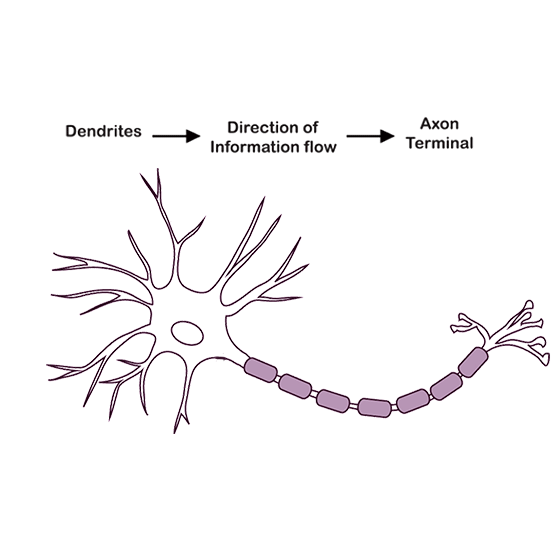
Grey Matter contains neurons' cell bodies, dendrites, and synapses. It plays a significant role in processing information and controlling voluntary muscle movements.
White Matter consists of nerve fibers (axons) covered by myelin. It facilitates the transmission of signals between the brain and spinal cord, ensuring efficient communication.
Understanding the function of both types of matter is vital to understanding how the CNS operates and how signals are processed.
The Brain: Control Center of the CNS
The brain is the most complex organ in the body, managing all higher-level functions, including thinking, emotions, memory, and movement. It is divided into regions such as:
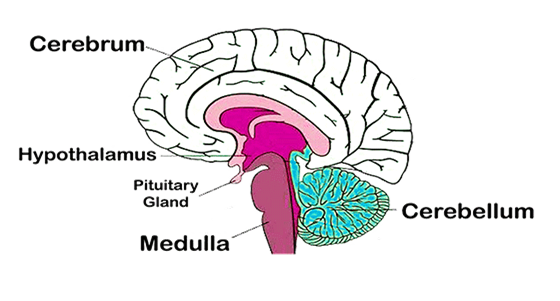
Cerebrum: Responsible for thought, reasoning, and voluntary movement.
Cerebellum: Controls balance, coordination, and fine motor skills.
Brainstem: Regulates basic life functions like breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
Hypothalamus: It regulates vital functions such as body temperature, hunger, thirst, and hormonal control by influencing the endocrine system.
Medulla : It controls essential autonomic functions, including heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure.
Each part of the brain works in unison to ensure smooth coordination of bodily functions.
Parts of the Brain and Their Functions
The brain can be broken down into several key parts that each serve different functions:
Cerebrum: The largest part of the brain, involved in higher functions like conscious thought, memory, and decision-making.
Cerebellum: Coordinates balance and motor control, ensuring precise movements.
Brainstem: Controls involuntary actions like heartbeat, digestion, and respiration, and serves as the communication pathway between the brain and the spinal cord.
Each part is essential for life-sustaining functions and higher cognitive processes.
Spinal Cord: The Communication Highway
The spinal cord connects the brain to the rest of the body, allowing for the transmission of signals between the CNS and peripheral nervous system (PNS). It is responsible for reflex actions and communicates sensory input from the body to the brain and vice versa.
The spinal cord is divided into regions that correspond to different body parts and play a critical role in motor control and sensation.
Diseases and Disorders Affecting the CNS
Several neurological disorders can affect the CNS, impairing function and quality of life. Some common diseases include:
Alzheimer's Disease: A neurodegenerative condition that affects memory and cognition.
Parkinson's Disease: A movement disorder that impairs motor control.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS): An autoimmune disease that damages the nerve fibers in the CNS, affecting motor and sensory functions.
Stroke: A blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, causing brain cell death and impairing motor and cognitive abilities.
Early detection and treatment are crucial for managing these conditions.
Signs of Nervous System Damage
Damage to the CNS can manifest through several symptoms, including:
Numbness or tingling in specific body parts.
Muscle weakness or lack of coordination.
Difficulty with speech or swallowing.
Loss of reflexes or abnormal responses.
Chronic pain, especially shooting or burning sensations.
Prompt medical attention is important to prevent further damage and to help with rehabilitation.
Conclusion
The Central Nervous System (CNS) is crucial for coordinating body functions, processing sensory input, and ensuring that the body responds appropriately to environmental stimuli. Understanding the structure, functions, and common disorders affecting the CNS is vital to maintaining overall health and treating neurological conditions effectively. Keeping the CNS healthy is essential for optimal brain and spinal cord function, which in turn supports every aspect of human life.
FAQs on CNS Full Form: Central Nervous System
1. What is the full form of CNS?
CNS stands for Central Nervous System, which includes the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing information and controlling body functions.
2. What is the main function of the CNS?
The CNS processes sensory information, coordinates movement, regulates bodily functions, and enables cognitive activities like thinking, memory, and emotions.
3. What are the two main parts of the CNS?
The two main parts of the CNS are the brain and the spinal cord, both playing crucial roles in controlling the body’s functions and responses.
4. What is grey matter and white matter in the CNS?
Grey matter consists of neurons' cell bodies, while white matter is composed of nerve fibers (axons) covered by myelin, responsible for transmitting signals.
5. How does the brain control the body?
The brain processes sensory data, sends commands to muscles and organs, and regulates involuntary functions like breathing, heartbeat, and digestion.
6. What are the common diseases affecting the CNS?
Common CNS diseases include Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, stroke, and epilepsy, which can impair cognitive, motor, or sensory functions.
7. What are some signs of CNS damage?
Signs of CNS damage may include numbness, muscle weakness, loss of coordination, memory problems, and chronic pain.
8. What is the role of the spinal cord in the CNS?
The spinal cord connects the brain to the body, transmitting signals for movement, sensation, and reflex actions between the brain and peripheral nervous system.
9. How can I keep my CNS healthy?
Maintaining CNS health involves regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, getting adequate sleep, managing stress, and avoiding substance abuse.
10. What happens if the CNS is damaged?
CNS damage can result in paralysis, cognitive impairment, or sensory loss, and can have long-term effects depending on the severity and location of the injury.























