




Understanding Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Living Beings
Biology is the most important segment in NEET, for it carries the most weightage. In total, 90 questions are asked from biology that carries a total of 360 marks.
There are several topics that are in the syllabus of which reproduction is of utmost importance. Therefore, if you want to excel in the exam, you must prepare important notes of biology for NEET reproduction in organisms.
Detailed reproduction in organism NEET notes will cover the maximum number of questions in biology. Moreover, if you’re aiming to become a doctor in future, this topic will be essential to study the genetic diversity of animals.
Types of Reproduction in Organisms
Reproduction is one of the most vital biological processes by which living organisms give birth to new organisms of the same kind. It helps in maintaining diversity and continuity of life on earth.
Reproduction works through DNA replication, cell divisions, reproduction body formation and developing them into offspring.
The methods of reproduction can be classified into two types- Asexual and sexual reproduction.
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is the form of reproduction that involves a single organism, that creates a copy of itself. The main feature of this process is mitosis. Generally, unicellular organisms and plants practise this method to reproduce.
Following is a list of reproduction in organisms NEET notes that you can prepare
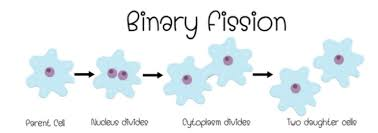
1. Binary Fission – In this process, a cell copies its DNA and splits into two daughter cells. Each of these cells carries a copy of the parent DNA after mitosis. For example, amoeba, bacteria and most single-cellular organisms follow this process.
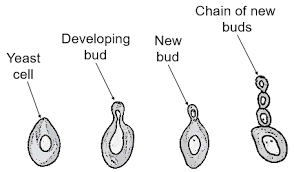
2. Budding – Some organisms split a part of them and form a new organism while staying attached to their parent cell. Once they mature, they separate from it. For example, hydra and yeast.
3. Vegetative Propagation – Many plants propagate through a part of their body known as propagule. Typically leaves, stems, roots are used in vegetative propagation. These parts of that plant come in contact with soil, water and nutrients and start growing as new plants.
Some of the examples are roots- yam, sweet potato, underground stem - lotus, turmeric, bulbs - onion, lilies, tubers-potato, creepers-strawberry, leaves - kalanchoe plant.
Gardeners often use vegetative propagation artificially for economic gain.
4. Fragmentation – Fragmentation happens when the body of an organism breaks into two, and each of them grows into a new organism. Example- spirogyra, flatworm, etc.
5. Sporogenesis – It is the method of producing reproductive cells called spores. Spores generally spread via wind and do not require fertilisation. Example- sporulation occurs in several bacteria and protozoans.
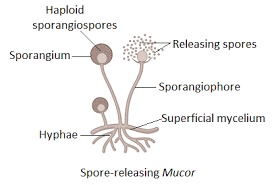
6. Agamenogenesis – This is the process of producing sexual organisms without fertilisation. It happens in different types.
Parthenogenesis occurs when an unfertilised egg develops into a new organism. It possesses only its mother’s genes.
Apomixis takes place when a normal plant reproduces asexually due to lack of male plant to fertilise female gamete.
Nucellar embryony is the process through which an embryo is formed from its parents’ tissue without using reproductive cells or mitosis. Primarily this method happens in citrus fruit.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction takes place when male and female gamete fuse together through fertilisation and give birth to offspring.
The entire process of sexual reproduction takes place in three stages.
Pre-Fertilisation
Gametogenesis takes place in haploid cells.
Homogametes – Male and female gametes look the same. They are seen in some algae.
Heterogametes – In most sexually reproduced organisms, two distinct gametes can be seen. The female gamete is called egg or ovum; the male one is called sperm.
Gamete transfer – In most seed plants pollen grains carry male gametes and ovules carry the eggs. In most plants, pollination occurs when pollen grains are transferred to stigma.
Fertilisation – It involves the fusion of gametes and formation of a diploid zygote.
In most aquatic creatures, fertilisation happens with the help of the medium, means outside of the body. It is called external fertilisation.
In most terrestrial organisms, including mammals, birds, reptiles, it happens inside the body and is called internal fertilisation.
Post-fertilisation
Embryogenesis is the procedure of forming an embryo from a zygote. During this process, zygote undergoes mitosis and cell differentiation.
Oviparous are the animals which lay eggs and the offspring hatch out of it after incubation. Ex - reptiles, birds, etc.
Viviparous animals are mostly mammals, including humans. The zygote forms inside the female body, and after certain stages, the baby is delivered. The chance of survival of these babies is higher due to embryonic protection and parental care.
Reproduction in organisms NEET questions includes a significant part of sexual reproduction. Learn and revise this portion simultaneously so that you don’t miss any concept.
Reproduction in organisms NEET notes also includes a few comparison charts. The difference between sexual and asexual reproduction is one of those.
Difference Between Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
The Importance of Reproduction in Organisms
Reproduction is essential for creating new species, and it ensures that offspring share the same DNA as their parents, allowing species to continue.
Survival is the main goal for all organisms on Earth, and creating new life without existing species is a very complex task.
Complex animals and organisms can't be created easily without already existing species.
Scientists have tried experimenting in labs, but they’ve only been able to create simple organisms like viruses.
These lab-created organisms don't have life-like features, showing how important natural reproduction is for life on Earth.
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Since plants cannot move from place to place, it is unlikely that the sexual mode of reproduction is possible. They release their sperm freely in the wind, water or other modes of transportation for the sake of reproducing. Additionally, the insects and birds also help in the transfer of pollen from plant to plant and aid in plant reproduction.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction
Advantages-
Asexual reproduction can produce a high population when conditions are favourable.
The process is faster than sexual reproduction as no time or energy is spent finding a mate.
Only one parent is involved, allowing for quicker reproduction.
Disadvantages-
In unfavourable conditions, fertilisation might not happen at all.
It depends on external factors like water, wind, and insects for the process to occur.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Sexual Reproduction
Advantages-
Offspring produced are genetically varied, which increases diversity.
Animals are less likely to be affected by diseases due to genetic variation.
Offspring have a better chance of surviving in less-than-ideal conditions.
Disadvantages-
Finding a suitable mate requires time and energy.
It is a slower process compared to asexual reproduction.
Hermaphroditism
Hermaphroditism is when an organism has both male and female reproductive parts in the same body. This is common in many invertebrates, like earthworms and some fish. These organisms don't have separate sexes and can act as either male or female when mating. The opposite of hermaphroditism is gonochoric, where organisms only have male or female reproductive parts.
Advantages of Hermaphroditism-
Hermaphrodites don't need to find a mate to reproduce, as they can self-fertilise.
They have lower chances of extinction since they can reproduce without a mate.
Every hermaphrodite organism can reproduce, unlike those with separate sexes where only one sex can.
Disadvantages of Hermaphroditism-
Hermaphrodites can’t produce large numbers of offspring because they aren't specialised in either sex.
There’s limited genetic diversity because offspring come from just one organism.
Maintaining both male and female reproductive parts requires extra energy.
Allogamy and Autogamy-
Allogamy (Cross-fertilisation)- This is when the sperm of one individual fertilises the egg of another individual. In plants, this is called cross-pollination.
Autogamy (Self-fertilisation)- This is when an organism uses its own sperm and egg to reproduce. In plants, this is known as self-pollination, and it mainly happens in hermaphroditic organisms.
Outbreeding (Outcrossing)-
Outbreeding is the process of fertilising the egg of one individual with the sperm of another individual of a different breed. It is used to increase genetic diversity and produce offspring with varied characteristics.
Essential Study Materials for NEET UG Success
FAQs on Reproduction in Organisms- Important Concepts
1. What are the Animals that Reproduce Asexually?
There are a few animals that reproduce asexually. For example, planarians, several annelid worms like polychaetes, sea stars and various plants and fungi reproduce asexually.
2. Which Male Animals Give Birth?
Male pipefish, sea horses, sea dragons, etc. give birth to their young.
3. Which is the Largest Vertebrate Animal Reproduce Asexually?
A species of lizard, Komodo dragon, is known to be the largest animal that reproduces asexually.
4. What is abiogenesis?
Abiogenesis is the natural process of origin of living from the existing non-living matter. Although, it is still not known exactly how this came to happen. The scientists believe that the process of abiogenesis is not a result of one single process but a combination of various processes like autocatalysis, self-replication and self-assembly that occurred over a long period.
5. What are the different methods of reproduction?
Reproduction can happen in two ways- asexual and sexual. In asexual reproduction, one organism produces offspring that are identical to itself. In sexual reproduction, the genetic material from two organisms combines to create offspring with genetic diversity. Asexual reproduction can happen through processes like fission, budding, and fragmentation.
6. What are the three types of reproduction?
The three main types of reproduction are asexual, sexual, and vegetative reproduction. Asexual reproduction involves one parent, sexual reproduction involves two parents and vegetative reproduction occurs in plants through special structures like roots or stems.
7. What does it mean for organisms to reproduce?
Reproduction is how living things make new life. There are two main ways they do this- asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.























