




The Living World NEET Notes and Important Questions
This article is created by keeping NEET aspirants in mind. It contains important notes and questions related to the chapter ‘The Living World’. Also, this article will be a great help for last-minute quick revision as well as for clarifying any concept related to the chapter.
It covers all the important concepts such as the characteristic features of living beings, rules of binomial nomenclature, and the difference between taxonomy and systematics. These concepts are discussed in a short and crisp way. Along with this, it contains FAQs regarding the NEET exam.
Important Topics of The Living World
Characteristics of living organisms
Binomial nomenclature
Taxonomy Of Biological Classification
Systematics
Taxonomical Aids
Important Concepts of The Living World
Characteristics of Living Beings
Cellular Structure: It is the defining characteristic of all living beings. All the living beings are made up of one or more cells and the cells are made up of living matter which is called living matter.
Metabolism: The sum total of chemical reactions that occur inside the body of living organisms is called metabolism. It is also the defining characteristic of all living things.
Growth: It is an irreversible increase in the mass of an individual. Multicellular organisms increase their mass by cell division. Unicellular organisms also grow through a process of cell division. Cell division is also a means of reproduction in them.
Reproduction: It is the process of the formation of new individuals of a similar kind. It is not required for a person's survival but it is necessary for the continuation of a population.
Consciousness: It involves being aware of one's surroundings and reacting to external stimuli. It is the defining characteristic of all living things.
Organization: The living being is made up of various components that work together to ensure the health of the entire organism.
Terminology
Systematics: It is the branch of science that deals with the diversity of organisms and all their comparative and evolutionary relationships.
Taxonomy: It is the branch of science that deals with the principles and procedures of identification, nomenclature and classification of organisms.
Classification: It is the arrangement of organisms into convenient categories on the basis of their similarities and differences in easily observable and fundamental characters and then the hierarchy of categories is created.
Nomenclature: It is the science of providing unique names to organisms so that they can be easily recognised and differentiated from others.
Identification: It is the process of finding the correct name and place of an organism in a system of classification.
Binomial Nomenclature
Carolus Linnaeus developed the binomial nomenclature. It is the system of providing organisms with appropriate and distinct names consisting of two words, the first is genera and the second is species.
Rules of Binomial Nomenclature
The names are usually written in italics and printed in Latin.
The genus is represented by the first term, while the species is represented by the second term.
When the names are handwritten they are separately underlined and when it is printed they are written in italics.
The genus (first word) starts with a capital letter and the species starts with a small letter. For example; Mangifera indica.
Taxonomic Categories
Hierarchy of categories is the classification of organisms in a definite sequence of categories in descending order from the kingdom and reaching up to species or an ascending order from species to the kingdom is called taxonomic categories.
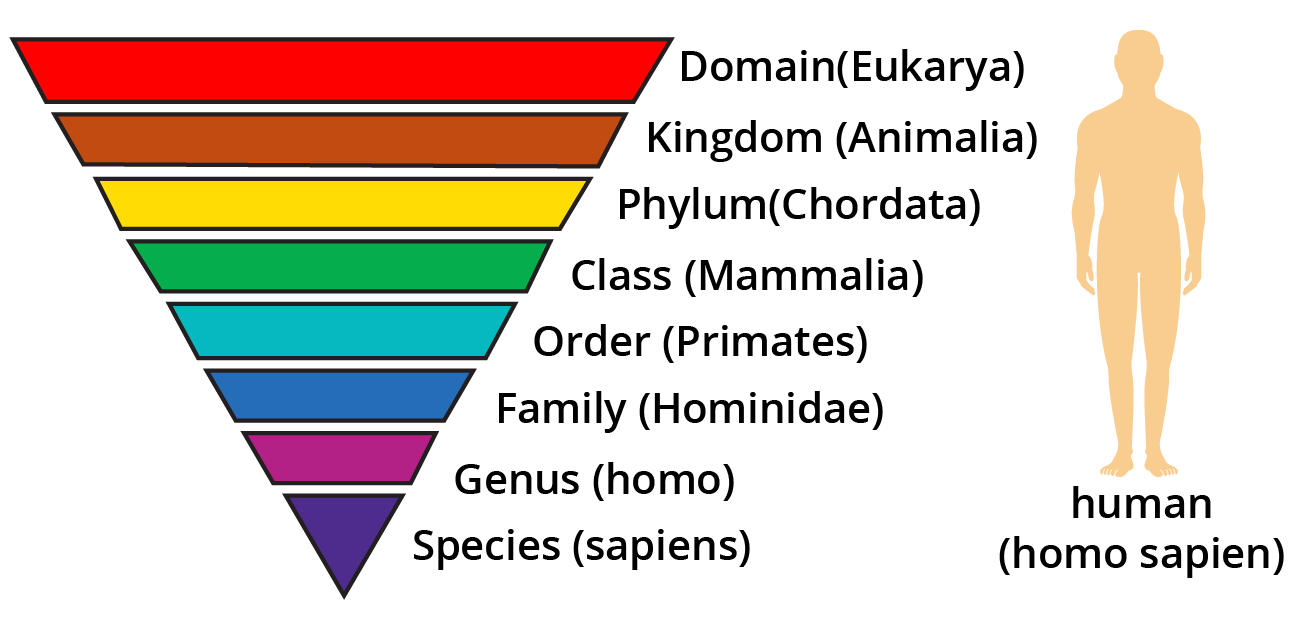
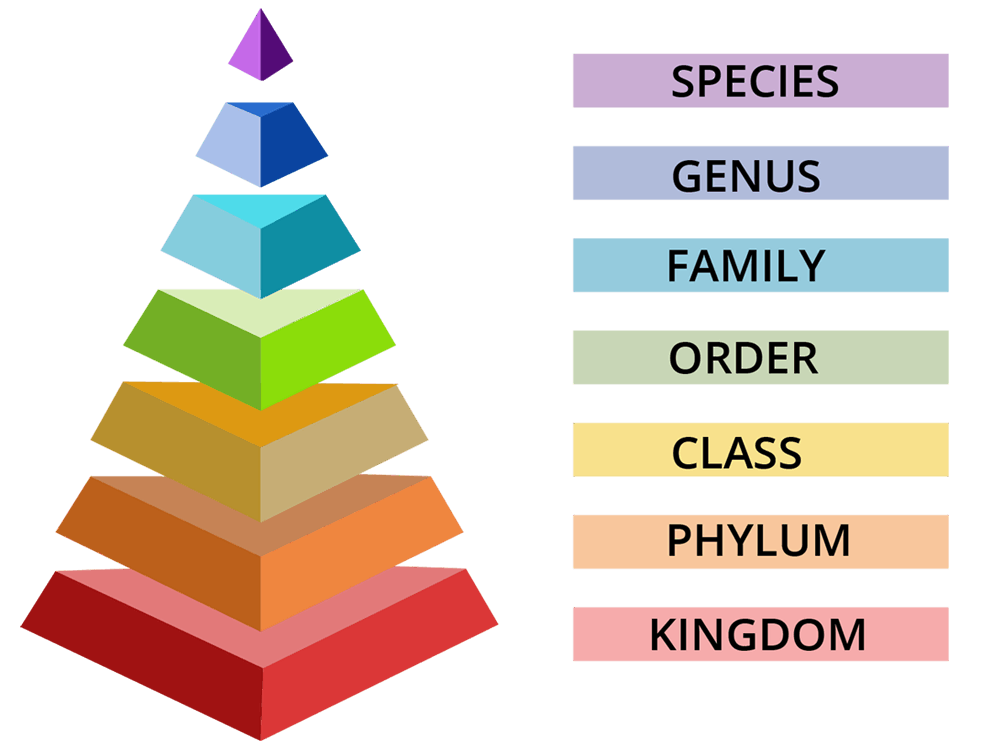

Hierarchy of Biological Classification
Species: It is a natural population of individuals which resemble one another in morphological and reproductive characteristics so that they can easily interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
Genus: It is a group of related species which resemble one another in some characters that are related. For example; Solanum tuberosum (Solanum- genus; tuberosum-species)
Family: It is the taxonomic category that contains one or more related genera. All the genera of a family show common characters. For example; genera of cats (Felis) and leopard (Panthera) are included in the family Felidae.
Order: It contains one or more related families. For example; Solanaceae, convolvulaceae, polemoniaceae are placed in the same order polemoniales.
Class: It contains one or more related orders. For example; Chiroptera, Marsupialia, Rodentia, cetacea, and Carnivora come under the class Mammalia.
Phylum or Division: The term phylum is used for animals and division for plants. Phylum or division contains one or more classes. For example; Class Mammalia, Aves, Reptilia, Amphibia, Cyclostomata, Chondrichthyes, and Osteichthyes are places in the phylum Chordata.
Kingdom: It is the topmost taxonomic category. For example; all the animals belong to the kingdom Animalia.
As the hierarchy increases, lesser similar characters are seen. Species show the maximum similar characters while the kingdom shows the minimum.
Taxonomical Aids
The techniques, procedures and stored information that are useful in the identification and classification of organisms are called taxonomic aids.
Herbarium
It is a place where dried and pressed plant specimens are mounted on sheets and are kept systematically according to a widely accepted system of classification. It is a repository for future use.
Botanical garden
They are large-sized areas where different types of plants are grown for scientific and educational purposes. Example; Kew (England), Indian Botanical Garden, Howrah (India), National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow (India).
Zoological parks
It is commonly known as a zoo. It is the place where different types of living animals are kept in enclosures under human care.
Museum
It is an institution where preserved materials such as plant or animal species are kept for exhibition, study and reference purposes.
Key
It is a booklet that contains a list of characters and their alternates which are helpful in the identification of various taxa.
Catalogue
It is a list that systematically summarises all of the species found in a specific location, generally with a brief description to aid identification.
Monograph
It is a handbook that contains all information regarding a certain taxon, such as a family or genus.
Flora
It is a book that contains information about habitat, climate, seasonal changes, distribution, description, and index of plants in certain areas.
Manual
It's a handbook that details the occurrence, collection, and identification of species present in a specific area.
Difference between Wildlife Sanctuary and National Park
Solved example from Chapter
1. Regeneration is the characteristic feature of living beings. Yes/No.
Ans: Yes, as the organisms that are fragmented regain their lost part of the body. For example; Planaria.
Key point to remember: Regeneration is a type of asexual reproduction.
2. Name the international organization that assigns scientific names to plants.
Ans: The international organization that assigns scientific names to plants is the Botanical Nomenclature International Code (ICBN).
Key point to remember: There are five codes of nomenclature :
International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN)
International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN)
International Code of Bacteriological Nomenclature (IC Bac N)
International Code of Viral Nomenclature (ICVN)
International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants (ICNCP)
Solved Problems from Previous Year Question from the Chapter
1. This aspect is an exclusive characteristic of living things
Increase in mass from inside only
Perception of events happening in the environment and their memory
Isolated metabolic reactions occur in vitro
Increase in mass by the accumulation of material both on the surface as well as internally
Ans: (b) Perception of events happening in the environment and their memory.
The ability to perceive and remember events in the environment is the most unique feature of a living thing. Consciousness or irritation are the terms used to describe a living being’s behaviour.
Trick to remember: Consciousness, Metabolism, and cellular structure are the defining features of living organisms.
2. Biosystematics aims at
Delimiting various taxa of organisms and establishing their relationships
The classification of organisms based on broad morphological characters
The classification of organisms based on their evolutionary history and establishing their phylogeny on the totality of various parameters from all fields of studies
Identification and arrangement of organisms on the basis of their cytological characteristics
Ans: (c) The classification of organisms based on their evolutionary history and establishing their phylogeny on the totality of various parameters from all fields of studies
Biosystematics is the study of the past and present diversification of living forms, as well as the links between living entities over time.
Trick to remember: In biosystematic, evolutionary trees are used to represent relationships.
Practice Questions (The Living World MCQ for NEET)
1. A group of plants and animals with similar features of any rank is
Order
Family
Genus
Taxon
Ans: (d) Taxon
It is a population of organisms that represent any level of grouping based on certain and easily observable characteristics.
Key point to remember: Level of grouping is called hierarchy.
2. Which is the correct sequence?
Species-Genus-Order-Phylum
Kingdom-Phylum-Class-Order
Genus-Order-Species-Kingdom
Kingdom-Species-Order-Phylum
Ans: (b) Kingdom-Phylum-Class-Order
The given sequence is of taxonomic categories. It is the hierarchy of categories in which organisms are classified in a definite sequence of categories in descending order from the kingdom and reaching up to species or an ascending order from species to kingdom.
Key point to remember: Members of the species show maximum similar characters while the kingdom shows the minimum similar characters.
Conclusion
This article covers all of the important ideas and gives concise explanations of The Living World, making it excellent for NEET applicants who want to revise quickly and effectively. It includes fundamental concepts from Biology NCERT, as well as problems from previous year's NEET exam papers and NEET practice tests. Make sure to put your knowledge to the test by doing the Practice question on your own.
NEET Important Chapter - The Living World

 Share
ShareFAQs on NEET Important Chapter - The Living World
1. Is the chapter The Living World important for NEET?
As this chapter introduces you to the core principles of the world of living beings, it is important that you become acquainted with them. So, yes this is an important chapter from the NEET point of view.
2. Is NCERT enough for the preparation of the chapter The Living World?
Yes, NCERT is enough for preparing the chapter The Living World.
3. Do the questions that come in the NEET are from the NCERT?
The NCERT syllabus is primarily covered in NEET. While a large percentage of the question paper is based on NCERT textbooks from grades 11 and 12, a significant portion is also based on sources other than NCERT.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video


