




Morphology of Flowering Plants
Introduction
This document contains the chapter named morphology in flowering plants as per the NEET syllabus for biology. It will be fruitful for NEET aspirants who are looking for the last minute revision notes.
The following document contains all of the important topics and provides insight of the exam pattern. By going through this document, one can find out all the answers to the important questions related to the chapter such as what is morphology, what are the different parts of the plants, their modifications & their functions, different plant families & their characteristics, etc.
Important Topics of Morphology of Flowering Plants
Different parts of the plant
Root & its modification
Stem & its modifications
Leaf & its modifications
Flower & its different parts
Fruit
Seed: Monocot & Dicot seeds
Different plant families & their description
Important Concepts
Definition of Morphology
The branch of science that concerns the study of form, size, colour, and relative positions of different parts of the organism is called morphology.
Different Parts of the Plant
Roots and Their Modifications
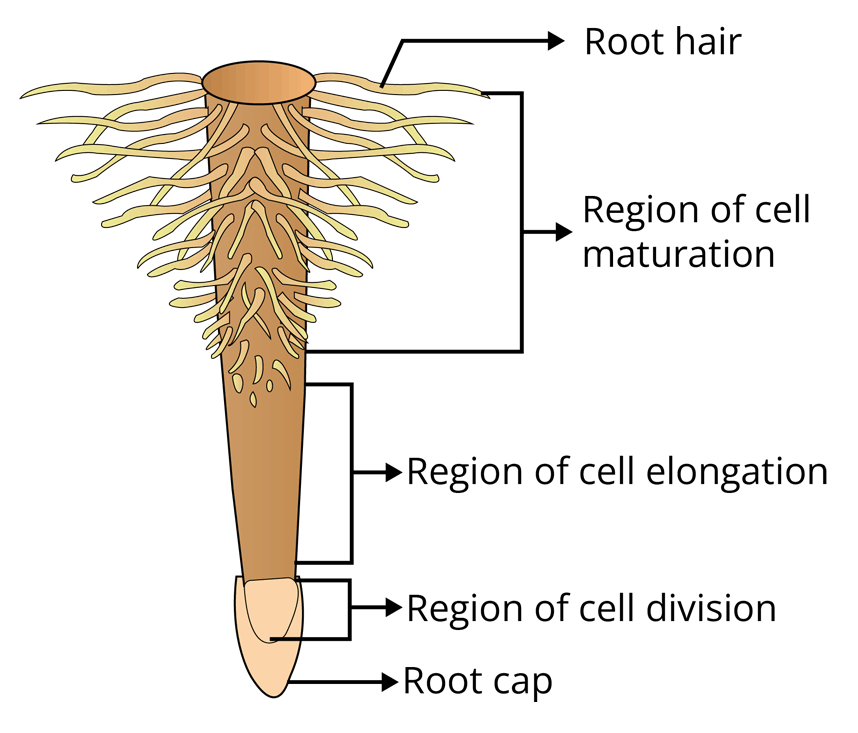
Modification of Roots
1. Tap-roots
2. Adventitious Roots
Stem and Its Modifications
1. Underground Stem Modifications
2. Sub-aerial Stem Modifications
3. Aerial Stem Modifications
Leaf and Its Modifications
Flower
It is the reproductive organ of the plant that gives rise to the seeds. It carries male and female reproductive parts. If both the reproductive parts are present together in the single flower, then such flower is termed as bisexual flower. If the reproductive organs of males and females are present separately, then in such a case, the flower is termed as uni-sexual flower. There are mainly four parts of the flower that are sepals, petals, stamen, and pistil.

Fruit
It is the seed bearing structure found in flowering plants. After the ripening, the ovary gets converted into fruit which protects the seeds and plays an important role in the seed dispersal. The parts of the fruit are given in the diagram below.
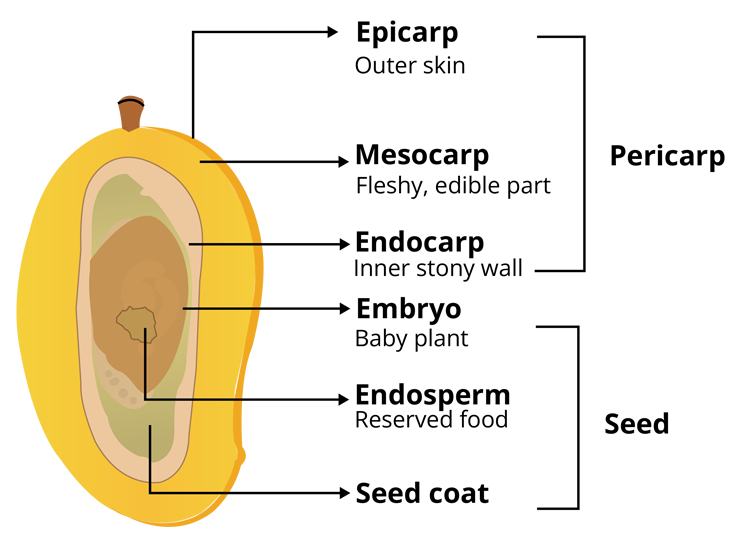
Seeds
It is the product of sexual reproduction in flowering plants that give rise to new plant after the germination. The differences between monocot and dicot seeds are given below:
Plant Families
The comparative description of different plant families is given below:
Solved Examples From the Chapter
1. Differentiate between the roots of aquatic plants and terrestrial plants.
Ans:
2. “Flower is a modified shoot.” justify the statement.
Ans: This is because in the case of flowers, the internodes are highly condensed; therefore, the number of appendages such as sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels are generally large.
3. Write a note on the symmetry of a flower.
Ans: On the basis of the symmetry, flower can be:
(a) Actinomorphic: Such kind of symmetry in which a flower can be divided into two equal halves whenever any radial plane passes through the centre. The example includes mustard, datura, chilli, etc.
(b) Zygomorphic: Such kind of symmetry in which a flower can be divided into two similar halves only in one particular vertical plane. The example includes pea, bean, gulmohar, etc.
Solved Problems of Previous Year’s Questions from the Chapter
1. In Bougainvillea, thorns are the modifications of ?
A. stipules
B. leaf
C. stem
D. adventitious root
Ans: The correct answer is option “C”.
In the case of Bougainvillea, thorns are curved. They play an important role in the climbing.
2. This is correctly matched with its three characteristics?
A. Maize: C3 pathway, closed vascular bundles, scutellum
B. Onion: bulb, imbricate aestivation, axile placentation
C. Tomato: twisted aestivation, axile placentation, berry
D. Pea: C3 pathway, endospermic seed, vexillary aestivation
Ans: The correct answer is option “B”.
Onion is the modification of the stem. The aestivation is imbricate type (if the margins of sepal and petals overlap one another but not in any particular direction). The placentation (arrangement of ovules in the ovary) is axile kind.
Tomatoes have valvate aestivation. Maize shows C4 pathway. The vascular bundle is open type. Pea plants show the C3 pathway. The seeds are non-endospermic and the aestivation is valvate or imbricate type.
3. Root plays an insignificant role in the absorption of water in?
A. Pea
B. Wheat
C. Sunflower
D. Pistia
Ans: The correct answer is option “D”.
Pistia is commonly known as water lettuce. It is the hydrophyte which floats on the surface of the water and its roots are hanging submerged beneath the floating leaves. So, its roots have an insignificant role in water absorption.
Practice Questions
1. Veins of the leaves are useful for
A. Mechanical support
B. Transport of water and minerals
C. Transport of organic nutrients
D. All of the above
Ans: The correct answer is option “D”.
Veins in leaves are made up of xylem and phloem. It performs varieties of functions such as mechanical support, transport of water, minerals, and organic nutrients.
2. In a pitcher plant, the pitchers are modified
A. fruits
B. branches
C. petioles
D. leaves
Ans: The correct answer is option “D”.
Pitcher plant is the type of carnivorous plant where pitchers are used to trap the insects and later digest them. They do so to fulfil their nitrogen requirements.
Conclusion
This article contains all the important information as per the requirement of students who are preparing for the NEET and can be really helpful for a quick and effective revision. It includes all the important concepts and topics, questions from the previous year’s NEET exam, NEET mock test as well as the Biology NCERT. Make sure to try the practice questions on your own to test your knowledge and to get desired outputs.
NEET Important Chapter - Morphology of Flowering Plants

 Share
ShareFAQs on NEET Important Chapter - Morphology of Flowering Plants
1. Is the morphology of flowering plants important for NEET?
Yes it is important for the NEET exam because it covers most of the important topics and the concepts that are useful for the exam.
2. Does the morphology of flowering plants come under the difficult chapter?
No, it comes under the moderate category. The most difficult part of this chapter is to learn the floral formula of the three families - Fabaceae, Liliaceae, and Solanaceae.
3. Is NCERT enough for preparing for the NEET exam?
Yes, it is enough. One can score very well by going through it again and again because every time a person receives new information which is very important in terms of exams.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video


