




Plant Kingdom
Introduction
This article is created by keeping NEET aspirants in mind. It contains notes and important questions related to the plant kingdom and it will be great for last-minute revision.
It covers all the important concepts such as the difference between classes of Thallophyta, Haplontic, diplontic, haplo-diplontic life cycle, gametophyte, sporophyte, etc. and these concepts are short and crisp. Along with this, it contains FAQs regarding the NEET exam.
Important Topics of Plant Kingdom
Plant Kingdom & Its classification
Sporophyte
Gametophyte
Triple fusion
Plant Life Cycle/Alternation of generation
Double fertilisation
Important Concepts
Cryptogamae
Plants without seeds and sex organs are invisible. For example, Thallophyta, Bryophyta, and Pteridophyta.
Phanerogamae
Plants with seeds and sex organs are visible. For example, Gymnosperm, Angiosperm.
1. Thallophyta/Algae
They are chlorophyll-containing simple plants.
Embryonic stages are absent and non-jacketed gametangia are present in which all the cells are fertile.
It shows a haplontic life cycle.
Difference Between Classes of Thallophyta
The Economic Importance of Algae: Food (Porphyra, Laminaria), food supplements (Spirulina), Antibiotics (Polysiphonia), sewage oxidation (Chlamydomonas, Chlorella), and phycocolloids (agar, carrageenin).
Difference Between Sporophyte and Gametophyte
2. Bryophyta
They are called amphibians of the plant kingdom because for surviving they need water on the soil surface as water helps them in dehiscence of antheridia and archegonia, swimming of male gametes to archegonia, protection from transpiration, and supply of water to all parts through capillarity (as vascular tissues are absent).
It shows a haplo-diplontic life cycle.
Gametophyte (haploid) is the dominant phase in the life cycle. It is photosynthetic and independent.
Sporophyte (diploid) is dependent on gametophyte and it is short-lived.
Difference Between Classes of Bryophyta
Economic Importance of Bryophytes:
Prevent soil erosion (ecological importance)
Soil formation (by plant succession)
Peat
Used as a packaging material because of their water holding capacity (fruits and vegetables are wrapped for keeping them fresh for a long time), etc.
3. Pteridophyta
Seedless vascular plant.
Sporophyte is the dominant phase of the life cycle and gametophyte is inconspicuous.
It shows a haplo-diplontic life cycle.
Sporophyte (diploid) is the dominant phase and it is independent and free living.
Gametophyte (haploid) is short-lived and independent.
Difference Between Classes of Pteridophyta
Economic Importance of Pteridophytes: Food (starch is obtained from sporocarp of Marsilea), Soil binding, Scouring (cleaning of utensils), Nitrogen fixation, Medicines, Ornamental.
4. Gymnosperm
Plant with naked seed.
Microsporophylls are aggregated to form male cones and megasporophylls are aggregated to form female cones.
The male gametophyte produces only two male gametes (only one of them is functional).
It shows a diplontic life cycle.
Sporophyte is the dominant phase of the life cycle.
Economic Importance of Gymnosperms: Edible seeds, Timber, Paper, Fibre boards (which are used in making packing cases), Linoleum, Turpentine oil, Rosin (used in waterproofing, sealing joints, preparation of writing paper), and Ephedrine (used in curing respiratory disorders).
5. Angiosperm
These are the seed plants in which seeds are formed inside fruits and the sporophylls are organised into flowers. This is the reason they are called flowering plants.
Microsporophylls (stamen) and megasporophylls (carpel) are specialised. Microsporophyll consists of a filament and an anther. Megasporophyll forms stigma, style, and ovary which contains an ovule.
There is double fertilisation, during this process, one male gamete fuses with the egg cell to form a zygote called syngamy (generative fertilisation) whereas the second male gametes fuse with the diploid secondary nucleus to form a triploid primary endosperm nucleus (PEN) (vegetative fertilisation).
Generative fertilisation and vegetative fertilisation are inclusively called triple fusion.
Within ovules, embryo sacs are present.
The embryo sac is 7-celled and 8-nucleate (1 egg cell-haploid, 3 antipodal cell-haploid, 2 synergids-haploid, 1 central cell with 2 polar nuclei).
Sporophyte is the dominant phase of the life cycle.
It shows a diplontic life cycle.
Difference Between Classes of Angiosperm
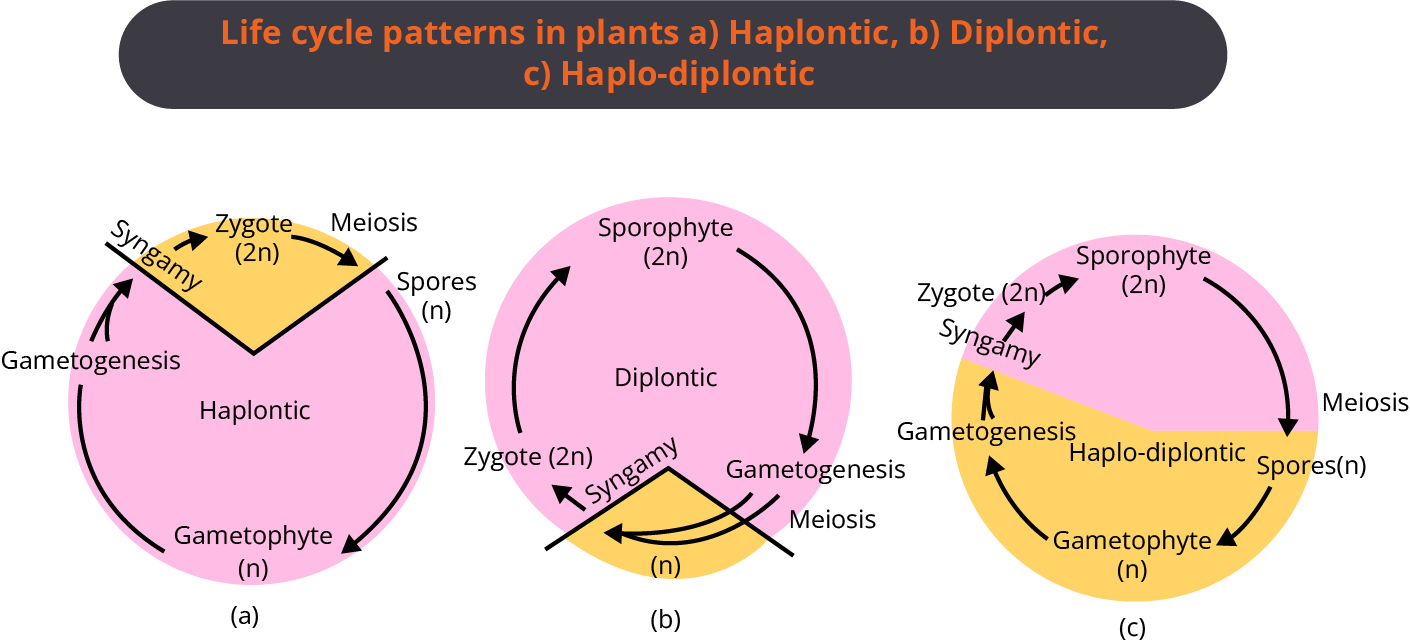
Alternation of Generation
Different plant groups complete their life cycles in different patterns. Sexually reproducing plants alternate between the haploid and diploid stages. This is referred to as generational alternation.
Haplontic
There is a single vegetative phase called gametophyte which is haploid.
It can be unicellular, colonial, and multicellular.
Gametophyte (haploid) undergoes mitosis and produces haploid gametes.
The gametes fuse and produce a diploid zygote.
In the zygote, meiosis occurs at the time of germination and gives rise to a new plant.
Alternation of generation is absent.
Diplontic
There is a single vegetative phase called sporophyte which is diploid.
It undergoes meiosis and produces gametes which is the only haploid structure during its life cycle.
Gametes fuse to form diploid zygotes which grow into diploid individuals.
Alternation of generation is absent.
Haplodiplontic
It involves sequential recurrence of haploid (gametophyte) and diploid (sporophyte) phase.
The sporophyte produces haploid spores through meiosis.
The haploid spores germinate to produce haploid gametophyte.
The gametophyte produces gametes (haploid) which fuse to form zygote (diploid).
The zygote develops into the sporophytic thallus of the progeny.
There is a clear alternation of generation.
Solved Examples From the Chapter
1. Why do we call mosses and ferns as amphibians?
Ans: Mosses and ferns belong to bryophyta. Bryophyta are called amphibians of the plant kingdom because they survive on land but require water for fertilisation.
2. Distinguish between antheridia and archegonia.
Ans:
Key Point to Remember: Antheridia- male organ; Archegonia- female organ
3. What is heterospory? Briefly comment on its significance. Give two examples.
Ans: Heterospory is the phenomenon in which two different sizes and sex of spores are formed by the sporophyte of land plants. The small size of a spore is called a microspore and the large size of a spore is called a megaspore.
Heterospory is considered an important step in evolution because it is a precursor to seed habit.
Megaspores and microspores, respectively, germinate and produce female and male gametophytes. The male gametophyte is produced by the microspore whereas the female gametophyte is produced by the megaspore. This occurrence is a precursor to the seed habit, which is thought to be an essential evolutionary step.
Two examples of heterospory are Selaginella and Salvinia.
Key Point to Remember: Hetero means different. Heterospory- different types of spores.
Solved Problems of Previous Year Question From the Chapter
1. The endosperm of a gymnosperm develops ___________ fertilisation whereas the endosperm of an angiosperm develops __________ fertilisation.
after, before
after, after
before, after
before, before
Ans: The correct answer is option (c) before, after.
The seed of gymnosperm contains the endosperm which is also called food-laden. It is haploid in nature and developed before fertilisation.
The endosperm of angiosperm is formed after fertilisation by triple fusion (when another male gamete fuses with two polar nuclei).
Trick to Remember: Endosperm provides nutrition to the developing embryo.
2. Identify the incorrectly matched pair:
Chlamydomonas - microscopic unicellular algae
Volvox - Colonial algae
Ulothrix - Filamentous algae
Fucus - Isogamous algae
Ans: The correct answer is option (d) Fucus - Isogamous algae.
Fucus shows oogamy. Oogamy is a type of anisogamy in which the female gamete is larger than the male gamete and female gametes are non-motile; however, male gametes are motile.
Trick to Remember: anisogamy- dissimilar gamete
Practice Questions
1. Double fertilisation is the characteristic of
Pteridophytes
Gymnosperms
Angiosperms
Chordata
Ans: The correct answer is option (c) Angiosperms.
Double fertilisation is the characteristic of angiosperms in which one male gamete is fertilised with an egg cell and another male gamete fuses with a central cell which has two polar nuclei.
Key Point to Remember: During double fertilization triple fusion is also seen. Fusion of nucleus of one male gamete with the nucleus of egg and fusion of nucleus of another male gamete with two polar nuclei.
2. Agar is commercially obtained from
Cyanobacteria
Rhodophyceae
Phaeophyceae
Chlorophyceae
Ans: The correct answer is option (b) Rhodophyceae.
Agar is a type of phycocolloids. It is obtained from Gelidium and Gracilaria. It is used in solidifying laboratory culture media and is added as stabiliser and thickener in the preparation of jellies, puddings, creams, etc.
Conclusion
This article covers all of the main points in detail and with simple explanations, making it ideal for quick and successful revision as it is made by keeping in focus the NEET aspirants. It contains key concepts, topics, and questions from past NEET exam papers, NEET sample tests, and Biology NCERT. Make sure to test your understanding by attempting the Practice question on your own.
NEET Important Chapter - Plant Kingdom

 Share
ShareFAQs on NEET Important Chapter - Plant Kingdom
1. Is the plant kingdom important for NEET?
This chapter is equally important as other chapters of biology. Students should clear all the topics of this chapter to solve maximum questions in the minimum time possible.
2. What are the number of questions that will come from the plant kingdom in NEET?
The chapter Plant Kingdom carries 12% of the weightage in NEET.
3. How many questions come in NEET from the plant kingdom?
The number of questions that are asked in NEET from the chapter Plant Kingdom is 6.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video


