




Reproductive Health
This article is created keeping the NEET aspirants in mind. It contains notes and important questions related to the reproductive health of human beings and it will be of great help for thorough preparation as well as last-minute revision.
It covers all important concepts such as the importance of reproductive health, the prevention of sexually transmitted diseases, methods of birth control, and various infertility treatments. These concepts are short and crisp and will help you grasp the chapter easily. Along with this, the article contains FAQs regarding the NEET exam.
Important Topics of Reproductive Health
Reproductive Health
Contraceptive methods
Medical termination of Pregnancy
Sexually transmitted infections
Infertility
Important Concepts
Reproduction Health - The term reproductive health refers to the healthy reproductive organs with normal functions. In other words, reproductive health means the physical, emotional, social, and behavioural well-being of an individual with respect to reproduction.
Reproductive Health- Problem and Strategies
Overpopulation is the main problem in India. The rapid increase in population over a relatively short period is defined as a population explosion.
After independence, our population, which was around 350 million, reached close to the billion mark by 2000 and crossed 1.2 billion in 2011.
Factors Responsible for Population Explosion
A rapid decrease in death rate, both maternal mortality rate, and infant death rate, and the increased birth rate is the major cause of the population explosion.
The increase in the average span of life.
It is very important to control population explosion. Because the population explosion leads to overpopulation which causes the migration of people from rural areas to the urban areas causing the growth of slum areas. Forcing people to live in the most unhygienic and insanitary conditions. Unemployment and poverty lead to frustration and anger among the educated youth.
Programs for Population Control
To control population explosion, various programs have been initiated by governmental and non-governmental organisations. Some of them are as follows.
Reproductive and Child Health Care (RCH) programs were initiated to create awareness among people about various reproduction-related aspects and provide facilities and support for building up a reproductively healthy society.
Reproductive age group people should be educated by the advantage of a small family. Advertisements on Social media platforms and posters in public places, showing a happy couple with two children with the slogan Hum Do Hamare Do (we two, our two) also should be displayed. Many people are also adopting the one-child policy.
Providing sex education in schools.
Provides information on many birth control measures which can check the birth rate.
Raising the marriageable age is more effective to control the population.
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a procedure used for the detection of certain genetic disorders, such as down syndrome, sickle-cell anaemia, haemophilia, etc.
However, some medical practitioners use amniocentesis for sex determination of the child by taking the amniotic fluid of the developing fetus.
It increases the menace of female foeticides; thus a statutory ban is put on amniocentesis by the Government of India.
Birth Control or Contraception
Contraception is defined as the methods that are used to avoid pregnancy with side effects, also called birth control. This can be categorised into two groups.
1. Natural Methods
Periodic abstinence(When male and female avoid having sexual intercourse) from the 10th to the 17th day of the menstrual cycle during the fertile period.
To avoid insemination, withdrawal or coitus interruptus is used.
After parturition, lactational amenorrhea occurs when there is no menstruation or ovulation for six months. Lack of ovulation during breastfeeding causes lactation amenorrhea.
2. Barrier Methods
Barrier methods are used to block the entry of sperm and prevent pregnancy. It includes cervical caps, diaphragms, and condoms. It includes the following.

Intrauterine Devices ( IUDs) - These are inserted through the vagina in the uterus and work by suppressing the sperm motility, fertilising capacity, and enhancing phagocytosis of sperms.
Some of the most widely used contraceptive methods are given below.
List of Intrauterine Devices

Oral Contraceptives
They are commonly referred to as pills. They must be taken for 21 days, from the beginning on the 5th day of the menstrual cycle. One must continue the course after a 7-day break to prevent pregnancy.
Oral contraceptives have a progesterone-oestrogen or progestogen-progestin combination to prevent ovulation. They also thicken the cervical mucus, which prevents implantation and sperm entry.
CDRI Lucknow created Saheli, a non-steroidal oral contraceptive tablet. It is only necessary to take it once a week. It has been found to be quite efficient with few negative effects.
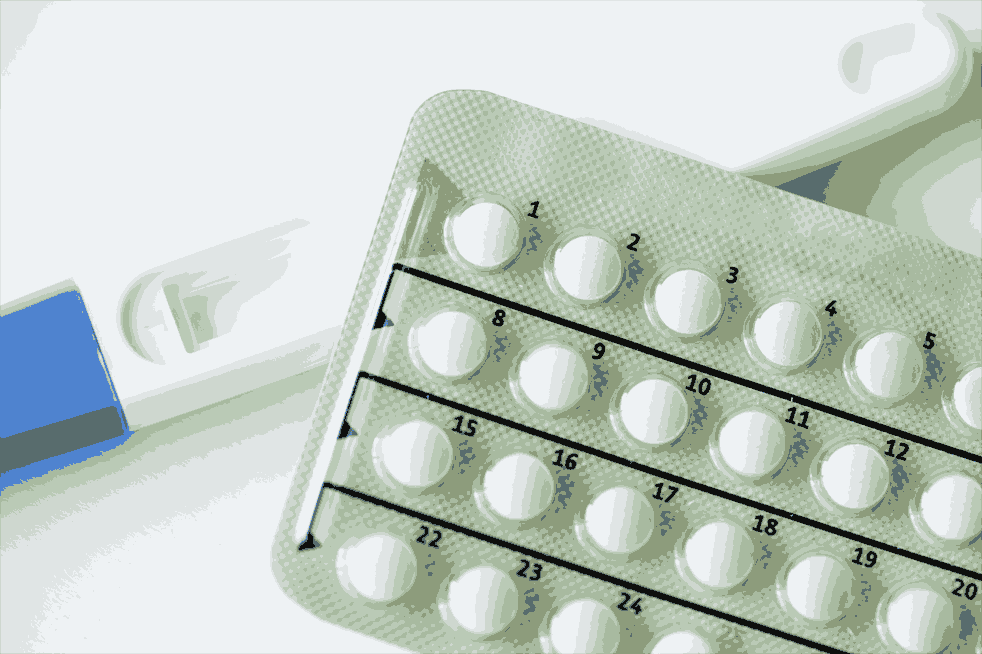
Injectable and Implants - These are effective emergency contraceptive measures, to be taken within 72 hrs of unprotected sexual intercourse to avoid implantation. Implants are made of progesterone or its combination with an oestrogen is implanted under the skin.
Surgical Methods - It is the final method of birth control that is highly effective but reversing them is difficult. It can be performed in both males and females.
Vasectomy is a male sterilisation procedure in which a piece of the vas deferens is tied and cut.
Tubectomy is a female sterilisation procedure that involves tying and cutting a tiny section of the fallopian tubes.
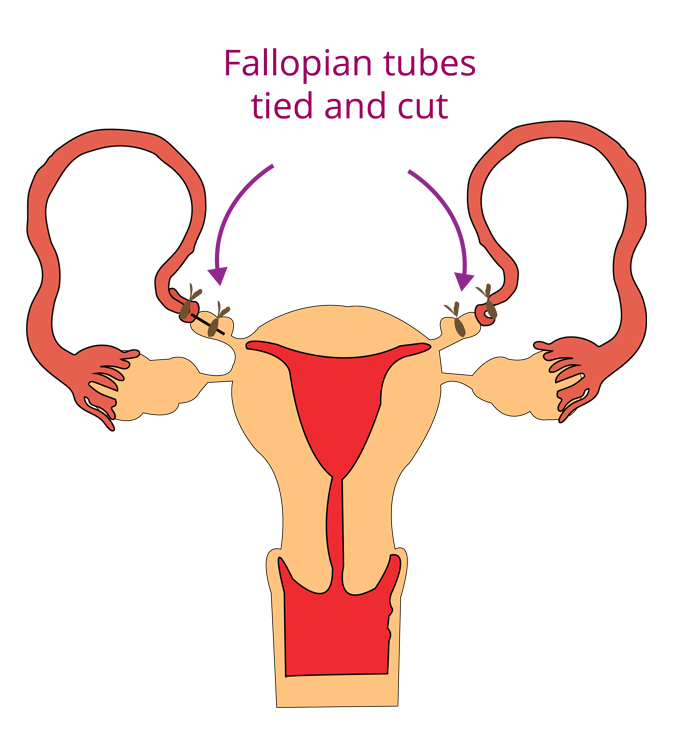
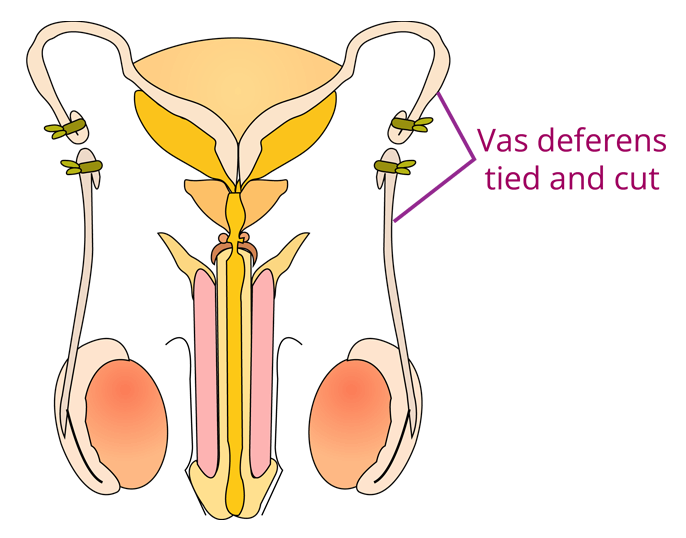
Please Note: All contraceptive methods add significant contributions to population control.
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP)
Medical termination of pregnancy or abortion is a method to avoid unwanted pregnancy. It refers to a voluntary action taken by medical experts with the consent of individuals. In India, MTP was legalised in 1971. MTP is safe up to the first trimester or 12 weeks of pregnancy because the foetus is not attached to maternal tissue during this period of time.
In 2017, The MTP Amendment Act was enacted by the Government of India. Under this act, abortion of more than 12 weeks of pregnancy is illegal. If it is to be done, the opinion of two registered medical practitioners is required.
Mtp Between 12 to 24 Weeks can Only be Legalised Under Two Circumstances -
If the continuation of the pregnancy would involve a risk to the life of the mother
If there is a substantial risk that the child would bear physical or mental abnormalities.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases/Infections (STDs/STIs)
Various diseases are transmitted due to unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected person. These are termed Sexually Transmitted Diseases/Infections (STDs/STIs), reproductive tract infections (RTIs), or venereal diseases (VD).
List of Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Vaccines have been developed for the treatment of Hepatitis-B and HPV. Genital herpes and hepatitis B and other infections are curable if detected at an early stage except for AIDS.
Prevention of STIs
Individuals should avoid sex with unknown partners or multiple partners.
Avoid unprotected sex, which means one should always use condoms during sex.
If the individual feels discomfort or is in doubt, one should consult a doctor. When STI is detected, one should get treatment on an early basis.
Infertility
Infertility is defined as the inability to produce young ones after one or more years of unprotected sexual intercourse or coitus. Infertility can be treated with the help of various methods such as Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART).
IVF or In-Vitro Fertilisation
It involves the fusion of gametes outside the body of the female. The embryo is formed outside the body and transferred to the uterus, called embryo transfer (ET).
It is also called a test-tube baby.
When the zygote is allowed to be divided up to 8 blastomeres and transferred into the fallopian tube, it is called zygote intrafallopian transfer (ZIFT).
In-Vivo Fertilisation- Embryos are formed by the fusion of gametes within the female; it can also be used for such transfer to assist those females who cannot conceive.
Intrauterine Transfer (IUT)- When a zygote is divided into more than 8 blastomeres and directly transferred into the uterus, it is called Intrauterine Transfer.
Artificial Insemination (AI)- The sperm is collected either from the husband or a healthy donor and inseminated into the female vagina or uterus. It is also called intrauterine insemination.
Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer (GIFT)- The ovum is collected from a donor female and transferred to another female who can not produce the ovum but can provide the optimum environment for the development of the embryo.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)- When sperm is directly injected into the ovum for the formation of an embryo in the laboratory.
The last option for infertile couples who desire a child is a legal adoption.
Solved Examples/Problems from the Chapter
1. Cu-T, LNG-20, and Cu-7 are examples of
Contraceptive pills
Surgical methods of sterilisation
Assisted reproductive technology
Intrauterine Devices
Ans: Intrauterine Devices.
Intrauterine Devices are inserted through the vagina in the uterus and work by suppressing the sperm motility, fertilising capacity, and enhancing phagocytosis of sperms.
Key Point to Remember- Cu-T, LNG-20, and Cu-7 are intrauterine devices that play a major role in population control. Intrauterine devices are a type of Barrier contraceptive.
2. Embryo with more than 16 blastomeres formed due to in vitro fertilisation is transferred into
Cervix
Uterus
Fimbriae
Fallopian tube
Ans: Uterus
Embryo with more than 16 blastomeres is called the morula. It is present in the form of a solid ball inside Zona Pellucida. Morula is implanted in the uterus.
Key Point to Remember- When Embryo with more than 16 blastomeres formed due to in vitro fertilisation is transferred into the fallopian tube. It is called ZIFT.
Solved Problems of Previous Year Questions
1. In the case of a couple where the male is having a very low sperm count, which technique will be suitable for fertilisation
Artificial insemination
Intrauterine transfer
Gamete intracytoplasmic fallopian transfer
None of the above
Ans: Artificial insemination
In the case of a couple where the male is having a very low sperm count, the sperm is collected either from the husband or a healthy donor and inseminated into the female vagina or uterus. It is also called intrauterine insemination or artificial insemination.
2. Which of the following is a hormone-releasing IUD?
Lippes Loop
Multiload 375
Cu-7
LNG 20
Ans: Multiload 375
Multiload 375 releases a hormone called progesterone which makes the uterus unsuitable for the sperms and kills them to prevent pregnancy.
Practice Questions
1. According to WHO, reproductive health means total well-being in all aspects of reproduction like
Physical, Emotional, Behavioural, Social
Physical, Mental, Health, Sexual Habits, Healthy body
Physical, Mental, Behavioral, Development of sexual organs
Physical, Mental, Emotional, Social
Ans: Physical, Emotional, Behavioural, Social
According to WHO, reproductive health means the physical, emotional, social, and behavioural well-being of an individual in the aspect of reproduction.
2. What do you mean by induced abortion?
Voluntary termination of pregnancy after the foetus becomes viable
Voluntary termination of pregnancy before the foetus becomes viable
Foetus removed at incomplete gestation months
Accidently foetus is lost
Ans: Voluntary termination of pregnancy after the foetus becomes viable
Medical termination of pregnancy or abortion is a method to avoid unwanted pregnancy after the fetus becomes viable. It refers to a voluntary action taken by medical experts with the consent of individuals.
Conclusion
This article has been made to help NEET aspirants prepare well and score the maximum in the exam. It contains all the important topics with easy explanations which are helpful for quick and effective revision. It includes important concepts, topics, and questions from previous year's NEET question papers, NEET mock test, and NCERT Biology. Make sure to try the practice question by yourself to test your understanding.
NEET Important Chapter - Reproductive Health

 Share
ShareFAQs on NEET Important Chapter - Reproductive Health
1. Is reproductive health important for NEET?
The chapter Reproductive Health is equally important as other chapters of Biology. Students should have a clear understanding of all the topics of this chapter to solve maximum questions in the minimum time possible.
2. What are the number of questions that are likely to appear from Reproductive Health in NEET?
The chapter Reproductive Health carries 10% weightage in the syllabus and exam of NEET. Hence, more focus and emphasis are required to secure full marks in this section of the paper.
3. How does this chapter help in spreading awareness about STDs in people?
There are a number of topics which help in spreading awareness about STDs in people by providing information regarding causing agents and how they spread for example- AIDS. AIDS is caused by HIV which spreads due to unprotected intercourse, illicit injection drug use or sharing needles, contact with infected blood, or from mother to child during pregnancy, etc.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video


