




Structural Organisation in Animals
This article covers the concepts of the chapter Structural Organisation in Animals as per the NEET 2022 syllabus for biology. This article will help out the students who are preparing for NEET 2022 as it includes the main and important topics for the last-minute revision.
The following document contains all of the important topics and provides an insight into the exam pattern. By studying this article, one can find out all the answers to the important questions related to the chapter, such as what are animal tissues, definitions and explanation of epithelial tissues, connective tissues, what are muscle tissue and neural tissue, organ and organ systems of organisms, anatomy and morphology of earthworm, anatomy and morphology of cockroach, anatomy and morphology of frog, etc.
Important Topics of Structural Organisation in Animals
Animal tissues
Organ and organ system
Earthworm - morphology and anatomy
Cockroach - Morphology and anatomy
Frogs - Morphology and anatomy
Important Concepts
Animal Tissues
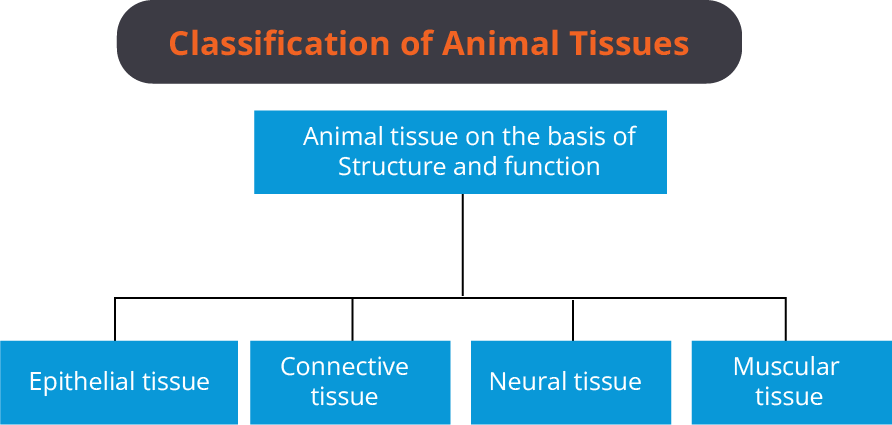
(I) Epithelial Tissue: They are densely packed cells with little intercellular matrix and one surface of this tissue is exposed to air or internal fluid.
1) Simple Epithelium:
a) Squamous Epithelium
b) Cuboidal Epithelium
c) Columnar Epithelium
d) Ciliated Epithelium
e) Glandular Epithelium
2) Compound Epithelium
Junctions
They are specialised structures that connect individual cells structurally and functionally.
They are classified as tight, adhering, and gap junctions.
1. Tight Junctions: These are the specialised structures that prevent substances
from leaking across a tissue.
2. Adhering Junctions: A specialised structure that connects neighbouring cells.
3. Gap Junctions: These are the specialised structures that allow cells to communicate with one another. They connect the cytoplasm of neighbouring cells, allowing for the rapid transfer of ions, small molecules, and large molecules.
(II) Connective Tissue: Connective tissue is the basic tissue of the body. It includes fat, cartilage, bone, and blood. It provides support, helps in filling the spaces between organs, protecting organs, and also helps in the transportation of materials around the body.
(i). Loose Connective Tissue:
a) Areolar Tissue
b) Adipose Tissue
(ii). Dense Connective Tissue:
a) Dense Regular Connective Tissue
b) Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
(iii). Specialised Connective Tissue:
a) Bone
b) Cartilage
c) Blood
(III) Muscle Tissue: Muscle tissues are made up of protein filaments of myosin and actin that slide past each other and produce expanding and contracting movements of muscles. This kind of movement changes both the shape and length of the muscle cells. Muscles function in humans by producing motion and force. They help in the circulation of blood, changing and maintaining body pressure, movement of internal organs like the movement of food down the digestive tract, and locomotion.
Skeletal Muscle
Striated Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
(IV) Neural Tissue: The primary tissue of our nervous system is the nervous or nerve tissue. It monitors and controls the body's functions. Nervous tissue consists of two cells: neurons or nerve cells and glial cells, which help to transmit nerve impulses and also provide nutrients to neurons.
Organ and Organ System
The body's basic tissue types organise in various ways to form organs. In multicellular organisms, a group of such organs will then associate with one another to form organ systems. The organisation of the body into tissues, organs, and organ systems is necessary for the body to function more efficiently. It also aids in the better coordination of the activities of the millions of cells that comprise an organism. Every organ in our bodies is made up of one or more types of tissues. For example, our heart is made up of all four types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscular, and neural. The complexity of organs and organ systems exhibits a discernible trend, which is referred to as an evolutionary trend.
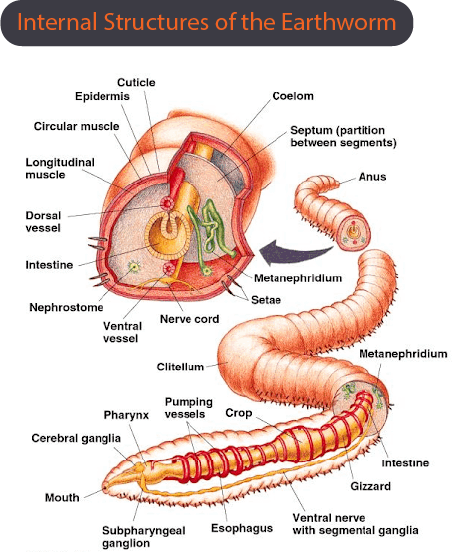
Earthworms
These survive in the upper moist layer of the soil which are reddish-brown in colour and are terrestrial invertebrates. These are called farmer’s friends as they increase the fertility of the soil by increasing the amount of air and water that gets into the soil
Morphology
The study of the external features of the earthworm is the morphology of earthworms. Earthworms have a reddish-brown coloured body. The body is divided into small segments. The dark line of body vessels is the dorsal side characteristics and the genital opening is the characteristics of the ventral side.

Anatomy
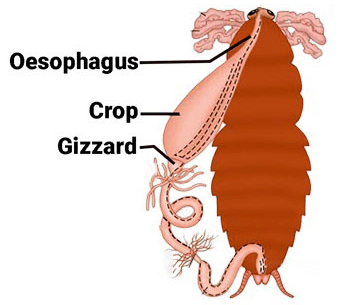
The study of the internal structures of an organism is called anatomy. Earthworms are tube-like organisms with a tube-like body plan. The body of these organisms is fully segmented and there are about 100-150 segments on a single earthworm body and these are helpful in movements.
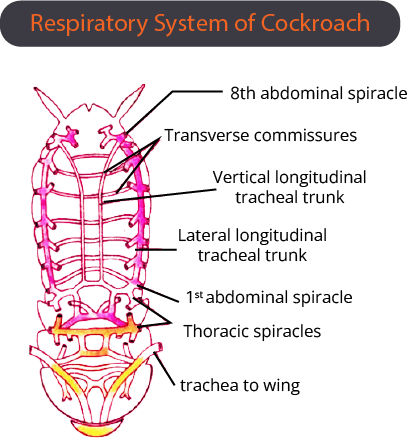
Cockroach
These belong to the class Insecta of phylum Arthropoda, which have brown or black coloured bodies.
Morphology
The cockroaches are the Arthropods. Their body is divided into 3 parts namely the head, thorax and abdomen. The body is covered with the hardest exoskeleton in plate-like structures which are called scleritis and are brown in colour.

Anatomy
The study of the internal structures of an organism is called anatomy. The anatomy of cockroaches possesses the digestive system, nervous system, and respiratory system.

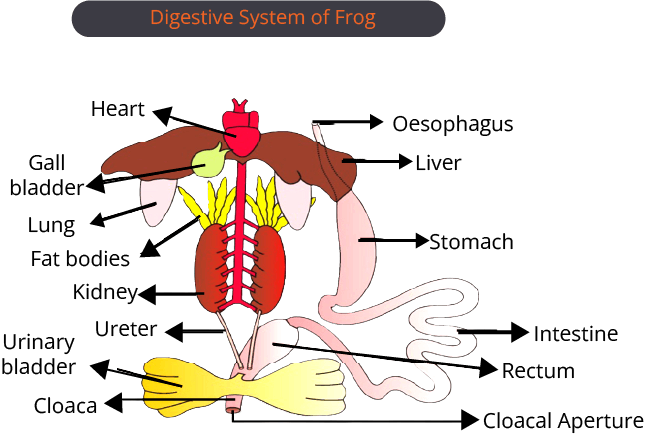
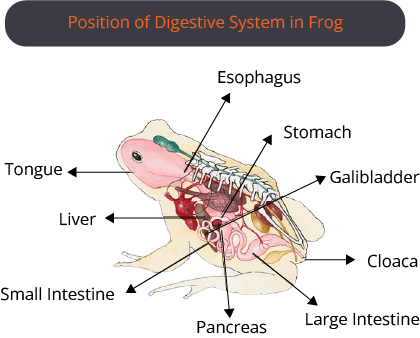
Frog
These are the members of chordates and class amphibians, so they are called vertebrate amphibians. They survive on both land and water.
Morphology
The frogs have 2 lifecycle stages one is tadpole and the adult stage. Morphology is different in both stages. In the tadpole stage, they possess tails and resemble small fishes in the water. Adult ones are tailless and the stout-like body is divided into head, short neck and trunk. In the adult stage, they possess webbed limbs, wet and slippery skin, a pair of nostrils, protruding eyes and a tympanum.
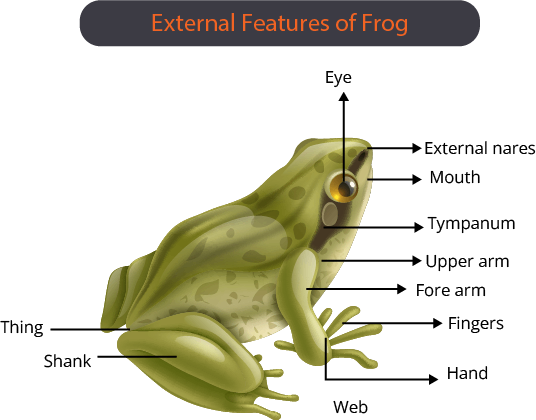

Anatomy
The body of the frog is divided into a head, a small neck and a trunk. Brain, ears, nose, eyes and mouth are present on the flathead. Limited head movement is allowed by the small neck. The trunk is large.
Solved Examples/Problems
1. Which one of the following types of cell is involved in making of the inner walls of blood vessels?
a) Cuboidal epithelium
b) Columnar epithelium
c) Squamous epithelium
d) Stratified epithelium
Ans: Squamous epithelium
Simple squamous epithelium lines the inner walls of blood vessels. It is composed of large flat cells which rest on a thin basement membrane.
2. To which one of the following categories does adipose tissue belong?
a) Epithelial tissue
b) Connective tissue
c) Muscular tissue
d) Neural tissue
Ans: Connective tissue
Adipose tissue is a type of loose connective tissue which comes under the class of connective tissue.
Solved Problems of Previous Year Question
1. The terga sterna and pleura of the cockroach body are joined by
a) Cementing glue
b) Muscular issue
c) Arthrodial membrane
d) Cartilage
Ans: Arthrodial membrane
There are three segments into which the cockroach body is divided. These segments are the head, abdomen, and thorax. Each segment is further divided into four plates called terga, sterna, and two lateral pleura. These divisions are joined together by the Arthrodial membrane.
2. Choose the correctly matched pair.
a) Tendon-Specialised connective tissue
b) Adipose tissue-Dense connective tissue
c) Areolar tissue-Loose connective tissue
d) Cartilage-Loose connective tissue
Ans: Areolar tissue-Loose connective tissue
Areolar Tissue: It is present under the skin and supports the epithelium. It possesses randomly distributed fibres, fibroblasts, mast cells, and macrophages. It makes a support system in the organs present in the abdominal cavity, fills the space between muscle fibres, and wraps around blood and lymph vessels.
Adipose Tissue: They are present under the skin and they usually store fat. It acts as a shock absorber and helps in maintaining body temperature in colder environments. They are also loose connective tissue. White adipose tissues protect kidneys and are also found at the back of the eye, in the hump of camels, blubber of whales, etc.
Tendon Ligaments are dense connective tissue.
3. What external changes are visible after the last moult of a cockroach nymph?
a) Mandible become harder
b) Anal cerci develop
c) Both forewings and hind wings develop
d) Labium develops
Ans: Both forewings and hind wings develop
As they grow, nymphs undergo a process of development known as moulting. They moult thirteen times, and after each moult, they appear more and more like adults. The second last nymphal stage develops wings. Before the last moult stage, wing pads develop.
Practice Questions
1. Large amoeboid cells, which are a part of our innate immune system, found in the areolar tissue are called
a) Macrophages
b) Mast cells
c) Fibroblasts
d) Adipocytes
Ans: Mast cells
Mast cells are also called melanocytes. These are large, rounded or oval cells that secrete the matrix of connective tissue. These are very similar in structure and function to the basophil cells which are a type of white blood cell. These are part of our innate immune system which are large amoeboid cells and present in areolar tissue.
2. The cells that release heparin and histamines in the blood are:
a) Basophils
b) Mast cells
c) Eosinophils
c) Neutrophils
Ans: Basophils
Histamine, serotonin, and heparin are secreted by the mast cells during inflammation and allergic reactions. A type of granular basophil cell consists of mast cells. Basophils are granulocytes that contain large cytoplasmic granules in the nucleus of the cell. Basophils store histamine which is a vasodilator and also contains anticoagulant heparin and serotonin that induces inflammation.
Conclusion
This article contains all the important information required for NEET 2022 aspirants and can be really helpful for a quick and effective revision. It includes all the important concepts and topics, and questions from the previous year's NEET 2022 question papers. Make sure to try the practice question on your own to test your learnings.
NEET Important Chapter - Structural Organisation in Animals

 Share
ShareFAQs on NEET Important Chapter - Structural Organisation in Animals
1. How many questions are asked from structural organisations in animals?
According to the previous year's papers review this chapter has a weightage of 5 marks and so 1- 3 questions may be asked from this chapter
2. What is the importance of the chapter - Structural Organisation in animals in NEET 2022?
About 4-5 marks questions can be expected in this chapter according to the previous year's NEET 2022 question papers analysis. So if the student needs to score more marks in the NEET 2022 exam this chapter is very important to cover.
3. How are organisms organised?
The organisms are organised on the basis of the level of organisation. For example molecular level, cellular level, tissue level and organ level




















 Watch Video
Watch Video


