




What Causes Magnets to Attract or Repel Each Other?
Depending on which way the magnetic poles are facing one another, magnets will either attract or repel one another. Magnets' repulsion and attraction When magnets' identical poles, such as their N-N or S-S poles, are held close to one another, repulsion results. When the magnets' opposing poles (N-S or S-N) are kept closer to one another, attraction happens. There is always a force that draws magnets with different poles together and repels them when their poles are similar. Both the attraction and the repulsion of magnets drastically diminish as the distance between them rises. The attraction between two uneven poles is 5-10% larger than the repulsion of equal poles when two equal magnets are in contact with one another.
Attraction and Repulsion Between Magnets
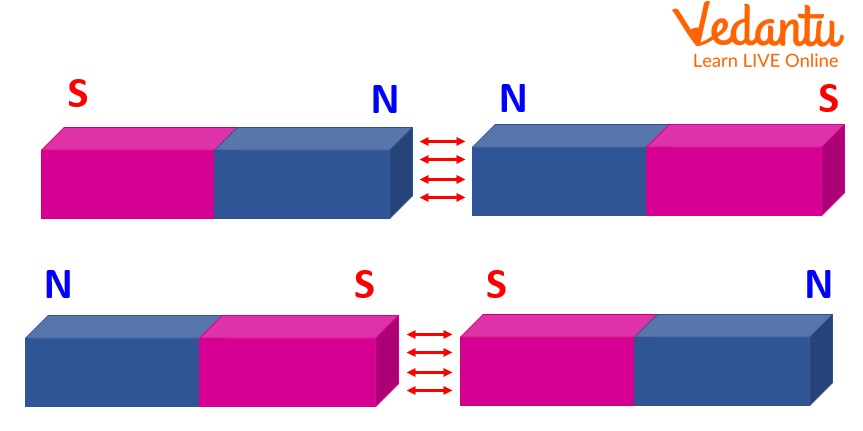
All magnets have two poles. When magnets come in contact, a north pole attracts a south pole, while pairs of the same or like poles repel each other. Due to this property, a magnetic material can turn into a temporary magnet of the opposite polarity, eventually attracting each other. In a magnet, domains are the small magnetic regions found in metals such as steel or iron.
Attraction between opposite poles of a magnet.
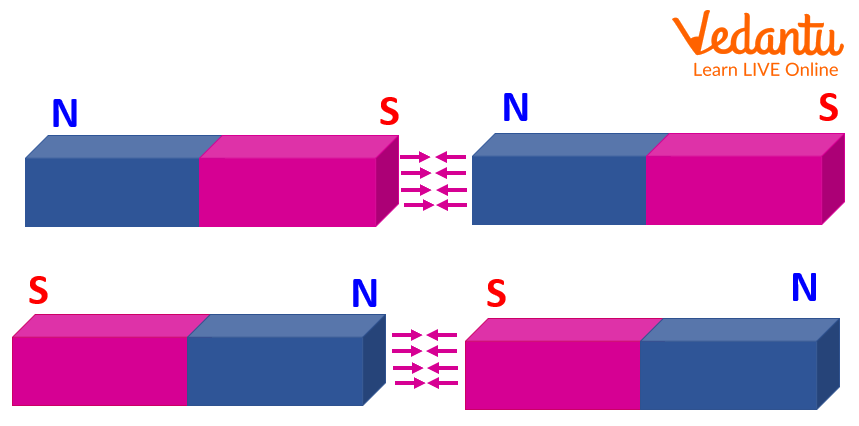
Repulsion
Repulsion is a force between two charges that are similar or the same. During the repulsion process between two magnets, one magnet disrupts the parallel alignment of the molecular magnets in the other magnet. This makes both magnets a little weaker. The repulsion between magnets is weaker than the attraction.
Repulsion between like poles of a magnet.
Bar Magnet
A bar magnet is a rectangular object piece completely made of iron, steel, or any other substance with ferromagnetic properties. Ferromagnetism composites or substances show natural permanent magnetic properties.
Every bar magnet has north and south poles at each end. Even if the magnet gets broken from the middle, it will still have the same properties. No matter how often it gets broken or cut, they will still have north and south poles. The magnetic force of this magnet is weaker at its middle point and stronger on its poles. If two bar magnets are kept together closely, their similar poles repel each other while their opposite poles attract one another.
Magnetic Poles
The ends of a magnet are known as magnetic poles. The exterior field is powerful. Also, the north and south pole are the two sides of magnetite. It is the property of the attraction mechanism behind this. Moreover, the same side of the magnets lead them far from each other.
Pole Strength Unit
According to the pole strength formula, the ratio of magnetic moment to its effective length is the pole strength of a magnet (Called the magnetic length). A-m is the unit of pole strength.
Magnet Attracts
All magnets have two poles. When magnets are brought together, a north pole always attracts a south pole or a south pole always attracts a north pole. This is called the attraction of two magnets.
Circular Magnet
A circular magnet is an electromagnet with a straightforward and durable structure used to lift ferromagnetic materials, not a permanent magnet. Typically, the centre is the strongest attraction point in a circular magnet. Where there are no great precision requirements, circular magnets are used: it is the case of scrap lifting.
What are the Properties of Magnets?
Magnets have attractive properties; they attract other magnetic substances.
Magnets have repulsive properties, like magnetic poles repel each other.
Magnets have directive property; a freely suspended magnet always points north-south.
Interesting Facts
Earth is the biggest magnet.
A magnet bar always has two poles, even if it breaks many times.
A circular magnet is not a permanent magnet.
Key Features of Magnet
There is always a force of repulsion between similar poles and a force of attraction between two magnets of different poles.
Magnets can be used to transfer heavy objects using magnetic cranes and also can be used as magnetic data recorders.
The magnet's attraction property can be utilised to separate the magnetic and non-magnetic waste.
List of Related Articles
FAQs on Attraction and Repulsion Between Magnets: Key Concepts Made Simple
1. Poles are not marked in a bar magnet. How will you find its poles?
We will take another bar magnet with known poles to find out the poles. We will bring one of the poles of the given magnet close to the north pole of the magnet. If it attracts the pole, it is the south pole. If it repels, it is the North pole.
2. Which side of a magnet has the strongest force?
The magnetic field generated by any magnet is always strongest at either pole. The magnetic force is equally as strong at the north and south poles.
3. How do magnets repel each other?
We are given two magnets with the N pole of one approaching the N pole of the other. Since both poles are the same, the magnets will repel each other. We are given two magnets with the N pole approaching the S pole of the other.























