
$ 1\mu $ is
(A) $ {10^{ - 6}}m $
(B) $ {10^{ - 9}}m $
(C) $ {10^{ - 10}}m $
(D) $ {10^{ - 3}}m $
Answer
487.2k+ views
Hint: To measure the quantities we define a unit for them. Meter is a unit of length. We use scientific notations to write very small or very large numbers. Scientific notation is used when a number between $ 1 $ to $ 10 $ is multiplied by a power of $ 10 $ . Here, we will discuss these scientific notations, particularly, metric prefixes. They make calculations easy and error-free.
Complete answer:
We have a whole table of standard notations shown below in the picture.
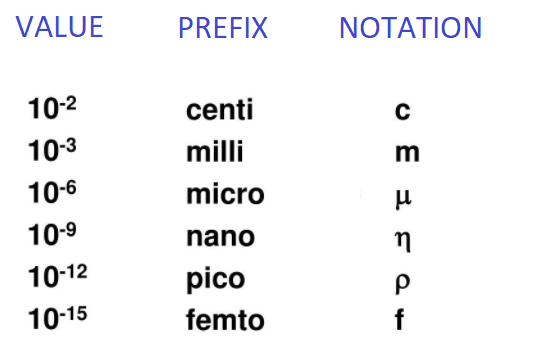
A metric prefix is a unit that precedes a basic unit of measurement to indicate a multiple of the unit. All the metric prefixes used are decadic and each prefix has a unique symbol. They are very helpful, to write very large and very small measurements.
From the table, we can see that $ 1\mu $ is a metric prefix $ {10^{ - 6}} $ .
Hence, the correct option is (A) $ {10^{ - 6}}m $ .
Note:
Very common metric prefixes are centi $ \left( c \right) $ , milli $ \left( m \right) $ , micro $ \left( \mu \right) $ , nano $ \left( n \right) $ , pico $ \left( p \right) $ , Giga $ \left( G \right) $ , mega $ \left( M \right) $ , kilo $ \left( k \right) $ , hecto $ \left( h \right) $ .
A metric prefix is always followed by a SI unit.
To write the numbers in scientific notation, there are some rules.
-It is always written in base $ 10 $ and the power of $ 10 $ carries either positive or negative signs.
-The value of the coefficient is (either positive or negative) of $ 10 $ is less than $ 10 $ and equal to or greater than $ 1 $ .
-When we move the decimal to the left the power of $ 10 $ increases. Similarly, when we move the decimal to the right, the power of $ 10 $ decreases.
Complete answer:
We have a whole table of standard notations shown below in the picture.

A metric prefix is a unit that precedes a basic unit of measurement to indicate a multiple of the unit. All the metric prefixes used are decadic and each prefix has a unique symbol. They are very helpful, to write very large and very small measurements.
From the table, we can see that $ 1\mu $ is a metric prefix $ {10^{ - 6}} $ .
Hence, the correct option is (A) $ {10^{ - 6}}m $ .
Note:
Very common metric prefixes are centi $ \left( c \right) $ , milli $ \left( m \right) $ , micro $ \left( \mu \right) $ , nano $ \left( n \right) $ , pico $ \left( p \right) $ , Giga $ \left( G \right) $ , mega $ \left( M \right) $ , kilo $ \left( k \right) $ , hecto $ \left( h \right) $ .
A metric prefix is always followed by a SI unit.
To write the numbers in scientific notation, there are some rules.
-It is always written in base $ 10 $ and the power of $ 10 $ carries either positive or negative signs.
-The value of the coefficient is (either positive or negative) of $ 10 $ is less than $ 10 $ and equal to or greater than $ 1 $ .
-When we move the decimal to the left the power of $ 10 $ increases. Similarly, when we move the decimal to the right, the power of $ 10 $ decreases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




