
1-phenyl-2-chloropropane on treating with alc. KOH gives mainly.
A. 1-phenyl propene
B. 2-phenyl propene
C. 1-phenylpropan-2-ol
D. 1-phenyl-propan-1-ol
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: In the given reaction, dehydrohalogenation is taking place which means the chloride ion is removed which further acts as a nucleophile and attacks the metal cation to form salt. In this reaction the alcoholic potassium hydroxide acts as a base. The main product formed will be an unsaturated hydrocarbon compound.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given reaction, a dehydrohalogenation reaction is taking place. In this reaction, the alcoholic KOH is acting as a base where potassium carries a positive charge and the hydroxyl group carries the negative charge. The hydroxyl anion will abstract the hydrogen present at the alpha position of 1-phenyl-2-chloropropane to eliminate water. After the removal of the hydrogen the charge will shift to form a double bond and chlorine will be removed as chloride anion. The chloride anion will further act as a nucleophile and will attack the positive charged potassium to form potassium chloride. The resulting main product which will be formed is 1-phenyl propene
The reaction between 1-phenyl-2-chloropropane with alc. KOH is shown below.
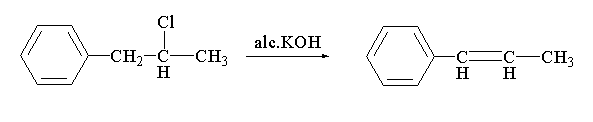
In this reaction, 1-phenyl-2-chloropropane reacts with alcoholic potassium hydroxide to form 1-phenyl propene.
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note: The reaction is a type of elimination reaction, as a saturated compound is converted to an unsaturated compound. If in place of alcoholic potassium hydroxide, aqueous potassium hydroxide solution was used, the resulting product which will be formed is alcohol.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given reaction, a dehydrohalogenation reaction is taking place. In this reaction, the alcoholic KOH is acting as a base where potassium carries a positive charge and the hydroxyl group carries the negative charge. The hydroxyl anion will abstract the hydrogen present at the alpha position of 1-phenyl-2-chloropropane to eliminate water. After the removal of the hydrogen the charge will shift to form a double bond and chlorine will be removed as chloride anion. The chloride anion will further act as a nucleophile and will attack the positive charged potassium to form potassium chloride. The resulting main product which will be formed is 1-phenyl propene
The reaction between 1-phenyl-2-chloropropane with alc. KOH is shown below.

In this reaction, 1-phenyl-2-chloropropane reacts with alcoholic potassium hydroxide to form 1-phenyl propene.
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note: The reaction is a type of elimination reaction, as a saturated compound is converted to an unsaturated compound. If in place of alcoholic potassium hydroxide, aqueous potassium hydroxide solution was used, the resulting product which will be formed is alcohol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




