
When \[3-methylbutan-2-ol\] is treated with \[HBr\], the following reaction takes place:
Give a mechanism for this reaction.

Answer
523.2k+ views
Hint: We know that the secondary carbocation formed in step II rearranges to a more stable tertiary carbocation by a hydride ion shift from 3rd carbon atom. Reaction of hydrogen halide with alcohol gives the alkyl halide and water as products and it is a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Complete answer:
The reaction takes place with the formation of the carbocation as an intermediate. Here, halide ion is acting as nucleophile attacks on the electropositive center that is carbocation formed as intermediates in the reaction. Here, the stability of the carbocation formed decides the nature of the product.
In a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction, since the attack of nucleophile and the departure of leaving group take place at the same time, attack from the front side by incoming nucleophile is hindered due to the leaving nucleophile. Thus, the nucleophile attacks the carbon from the back side. In this case, the parent alkyl part is a cyclohexane ring. Thus, a backside attack on the carbon atom is hindered. As a result, we can say that the reaction proceeds through the unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
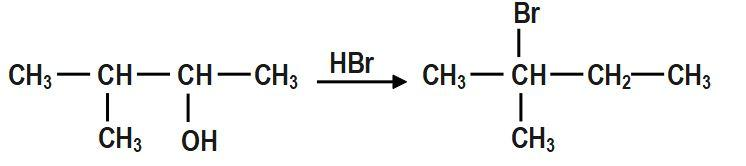
The mechanism for the reaction between \[3-methylbutan-2-ol\] and \[HBr\]is shown above.
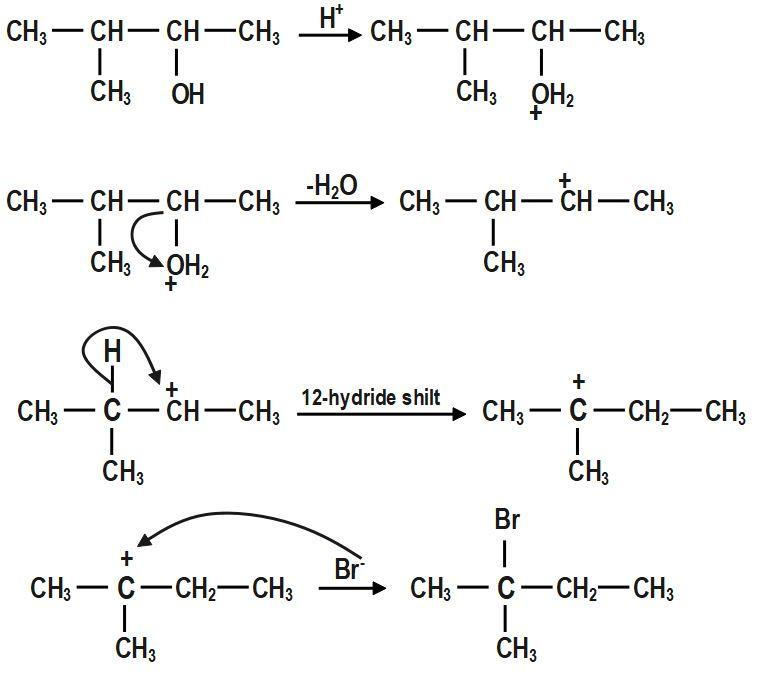
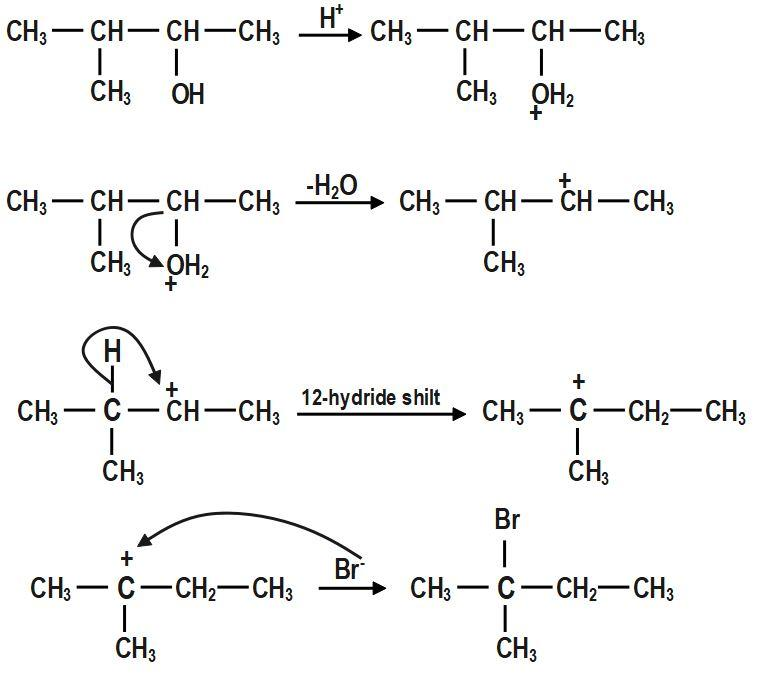
In the first step, \[-OH~\] group is protonated. In the second step, a molecule of water is lost to form secondary carbocation. Third step is the rearrangement of less stable secondary carbocation to more stable tertiary carbocation through \[1,2-\]hydride shift. Final step is the nucleophilic attack of bromide ion on tertiary carbocation to form \[2-bromo-2-methylbutane.\]
Note:
Remember that the rates of reactivity of alcohols towards reaction mechanisms are as follows: Tertiary alcohol \[~>\] Secondary alcohol \[~>\] Primary alcohol Primary alcohols do not undergo reaction as primary carbocation is not stable.
Complete answer:
The reaction takes place with the formation of the carbocation as an intermediate. Here, halide ion is acting as nucleophile attacks on the electropositive center that is carbocation formed as intermediates in the reaction. Here, the stability of the carbocation formed decides the nature of the product.
In a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction, since the attack of nucleophile and the departure of leaving group take place at the same time, attack from the front side by incoming nucleophile is hindered due to the leaving nucleophile. Thus, the nucleophile attacks the carbon from the back side. In this case, the parent alkyl part is a cyclohexane ring. Thus, a backside attack on the carbon atom is hindered. As a result, we can say that the reaction proceeds through the unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The mechanism for the reaction between \[3-methylbutan-2-ol\] and \[HBr\]is shown above.
In the first step, \[-OH~\] group is protonated. In the second step, a molecule of water is lost to form secondary carbocation. Third step is the rearrangement of less stable secondary carbocation to more stable tertiary carbocation through \[1,2-\]hydride shift. Final step is the nucleophilic attack of bromide ion on tertiary carbocation to form \[2-bromo-2-methylbutane.\]


Note:
Remember that the rates of reactivity of alcohols towards reaction mechanisms are as follows: Tertiary alcohol \[~>\] Secondary alcohol \[~>\] Primary alcohol Primary alcohols do not undergo reaction as primary carbocation is not stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




