
3-phosphoglyceric acid as the first ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ fixation product in algal photosynthesis was discovered by
(a) Priestly
(b) Ingenhousz
(c) Calvin
(d) Sachs
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: To study photosynthetic activity in algae, radioactive sources are used which leads to the discovery of a three-carbon compound. This biosynthetic pathway is named after the scientist which is also called dark reaction.
Complete answer:
In algae and green plants, sugar is synthesized by the Calvin pathway. It has three steps namely carboxylation, reduction, and regeneration. In the carboxylation step fixation of carbon dioxide into a stable intermediate takes place.
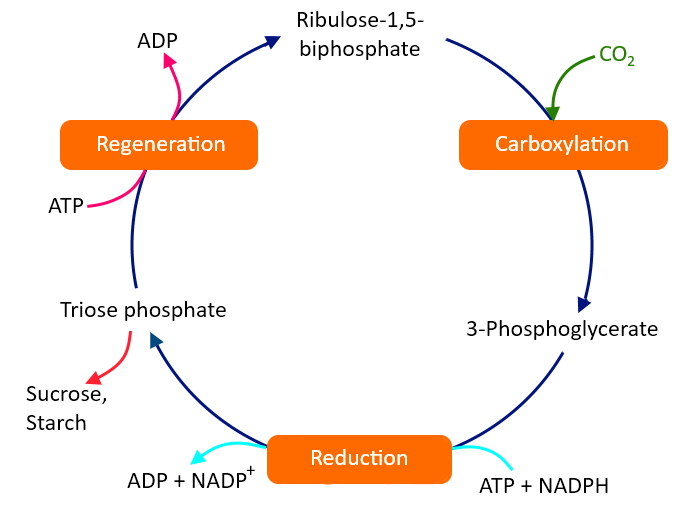
It is the most crucial step in the Calvin cycle discovered by Calvin. The first product formed in the fixation of carbon dioxide in algal and plant photosynthesis is 3-phosphoglyceric acid.
Additional information:
- In carboxylation ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ is utilized for the carboxylation of RuBP. RuBP carboxylase is the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction resulting in the formation of two molecules of 3-phosphoglyceric acid. This enzyme has an activity of oxygenation, so it is also called RuBP carboxylase-oxygenase (RuBisCO).
- Reduction is a two-step reaction resulting in the formation of trioses. For a molecule of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$, this step utilizes 2 molecules of ATP for phosphorylation and two NADPH for reduction. The fixation of six molecules of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$, 6 turns of the cycle is required for the removal of one glucose molecule.
- In order to continue the cycle uninterrupted, regeneration of the ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ acceptor molecule is crucial.
So, the correct answer is ‘(c) Calvin’.
Note: Oxygen was discovered by the series of experiments on green plants conducted by Joseph Priestly in 1774. Jan Ingenhousz discovered that sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis. During the growth of the plants, glucose was produced, this was discovered by Julius Von Sachs.
Complete answer:
In algae and green plants, sugar is synthesized by the Calvin pathway. It has three steps namely carboxylation, reduction, and regeneration. In the carboxylation step fixation of carbon dioxide into a stable intermediate takes place.

It is the most crucial step in the Calvin cycle discovered by Calvin. The first product formed in the fixation of carbon dioxide in algal and plant photosynthesis is 3-phosphoglyceric acid.
Additional information:
- In carboxylation ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ is utilized for the carboxylation of RuBP. RuBP carboxylase is the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction resulting in the formation of two molecules of 3-phosphoglyceric acid. This enzyme has an activity of oxygenation, so it is also called RuBP carboxylase-oxygenase (RuBisCO).
- Reduction is a two-step reaction resulting in the formation of trioses. For a molecule of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$, this step utilizes 2 molecules of ATP for phosphorylation and two NADPH for reduction. The fixation of six molecules of ${ CO }_{ 2 }$, 6 turns of the cycle is required for the removal of one glucose molecule.
- In order to continue the cycle uninterrupted, regeneration of the ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ acceptor molecule is crucial.
So, the correct answer is ‘(c) Calvin’.
Note: Oxygen was discovered by the series of experiments on green plants conducted by Joseph Priestly in 1774. Jan Ingenhousz discovered that sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis. During the growth of the plants, glucose was produced, this was discovered by Julius Von Sachs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




