
A $ 0\cdot 2\text{ kg} $ ball is suspended by a thread of length $ 1\text{ }m $ . It is pulled a side until the thread makes an angle of $ 30{}^\circ $ with a vertical. How much work is done against gravity? The ball is now released. Find the velocity at the lowest point. Ignore air resistance and take $ g=10\text{ }m{{s}^{-2}} $ .
Answer
553.8k+ views
Hint: When a ball is suspended by a thread, it acts like a pendulum. When the particle is at a mean position, its potential energy is zero, kinetic energy is maximum , but kinetic energy is zero. Work done by a ball is due to work done by gravity which is given by potential energy.
Use the work energy theorem, according to which change in kinetic energy is equal to work done and work done is equal to potential energy. It means change in potential energy is equal to change in kinetic energy.
And we can calculate velocity at the lowest point.
Formula used: Work done due to gravity $ =mg\text{ }h $
By work energy theorem $ \vartriangle K.E=\text{ work done} $
$ \begin{align}
& {{\left( K.E \right)}_{A}}-{{\left( K.E \right)}_{B}}=-{{\left( P.E \right)}_{A}}+{{\left( P.E \right)}_{B}} \\
& {{\left( K.E \right)}_{A}}={{\left( P.E \right)}_{B}} \\
\end{align} $
Here $ A $ is a mean position.
$ B $ is an extreme position.
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=mg\text{ }h \\
& {{v}^{2}}=2\dfrac{mg\text{ }h}{h} \\
& v=\sqrt{\dfrac{2mg\text{ }h}{m}} \\
\end{align} $ .
Complete step by step solution
We have a blue suspended by a thread. $ A $ is the mean position and $ B $ is the extreme position.
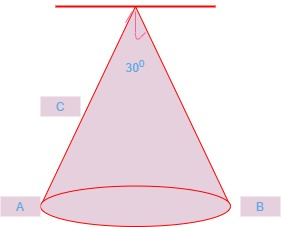
Mass of ball is given by $ m=0\cdot 2\text{ }kg $ this is the length of thread.
$ \angle AOB=\theta $ = $ 30{}^\circ $
Since $ BC\text{ is perpendicular to }DA $
$ \begin{align}
& \text{Take a perpendicular }\vartriangle BOX,\text{ }Cos\theta =\dfrac{OC}{OB} \\
& \text{ }OC=OB\cos \theta \\
& \text{ }OC=1\times \cos \theta \\
\end{align} $
Here, thread is at
$ \begin{align}
& 30{}^\circ \text{ angle} \\
& \text{cos}\theta \text{=cos 30}{}^\circ \text{=}\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
& \\
\end{align} $
$ \begin{align}
& Oc=1\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=\dfrac{1\cdot 73205}{2} \\
& OC=0\cdot 866 \\
& OA=1\text{ }cm \\
\end{align} $ $ $
Height through which ball is raised,
$ \begin{align}
& h=AC=AO-OC \\
& h=1-0\cdot 866=0\cdot 134\text{ }m \\
\end{align} $
Work done due to gravity is given by
$ \begin{align}
& =mg\text{ }h \\
& =0\cdot 2\times 10\times 0\cdot 134\text{ }m \\
& \text{ work done }=0\cdot 268\text{ }J \\
\end{align} $
By work energy theorem,
According to this, the work done by all forces acting on a particle equals change in the K.E of the particle.
$ \begin{align}
& \vartriangle K.E=\text{Work done} \\
& \vartriangle K.E=-\vartriangle P.E\text{ }[\text{because , in this case work done due to gravity }\!\!]\!\!\text{ } \\
& {{\left( K.E \right)}_{A}}-{{\left( K.E \right)}_{_{B}}}=-{{\left( P.E \right)}_{A}}+{{\left( P.E \right)}_{B}} \\
& {{\left( K.E \right)}_{B}}=0,\text{ at extreme position kinetic energy is zero} \\
& {{\left( P.E \right)}_{A}}=0,\text{ at mean position potential energy is zero}\text{.} \\
\end{align} $
$ \begin{align}
& {{\left( K.C \right)}_{A}}={{\left( P.E \right)}_{B}} \\
& \dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=mg\text{ }h \\
& \dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=0\cdot 268\text{ }J \\
& {{v}^{2}}=\dfrac{2}{m}\times 0\cdot 268 \\
& \text{ }=\dfrac{2}{0\cdot 2}\times 0\cdot 268 \\
& \text{ }=10\times 0\cdot 268 \\
& {{v}^{2}}=268 \\
& v=1\cdot 63\text{ }m{{s}^{-1}}[\text{Ans }\!\!]\!\!\text{ } \\
\end{align} $
Hence work done by ball is $ 0\cdot 268\text{ }J $
And velocity at lowest point is $ 1\cdot 63\text{ }m{{s}^{-1}} $
Note
Work energy theorem: The work done by the net force on a particle is equal to the change in the particle's kinetic energy.
$ W=\vartriangle K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}_{{{f}^{2}}}}-\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}} $
The work energy theorem can be derived from Newton's second law: kinetic energy is directly proportional to the mass of the object and to the square of its velocity.
Potential energy is energy an object has because of its position relative to the same other object.
The formula of potential energy depends on the force acting on two objects.
Use the work energy theorem, according to which change in kinetic energy is equal to work done and work done is equal to potential energy. It means change in potential energy is equal to change in kinetic energy.
And we can calculate velocity at the lowest point.
Formula used: Work done due to gravity $ =mg\text{ }h $
By work energy theorem $ \vartriangle K.E=\text{ work done} $
$ \begin{align}
& {{\left( K.E \right)}_{A}}-{{\left( K.E \right)}_{B}}=-{{\left( P.E \right)}_{A}}+{{\left( P.E \right)}_{B}} \\
& {{\left( K.E \right)}_{A}}={{\left( P.E \right)}_{B}} \\
\end{align} $
Here $ A $ is a mean position.
$ B $ is an extreme position.
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=mg\text{ }h \\
& {{v}^{2}}=2\dfrac{mg\text{ }h}{h} \\
& v=\sqrt{\dfrac{2mg\text{ }h}{m}} \\
\end{align} $ .
Complete step by step solution
We have a blue suspended by a thread. $ A $ is the mean position and $ B $ is the extreme position.

Mass of ball is given by $ m=0\cdot 2\text{ }kg $ this is the length of thread.
$ \angle AOB=\theta $ = $ 30{}^\circ $
Since $ BC\text{ is perpendicular to }DA $
$ \begin{align}
& \text{Take a perpendicular }\vartriangle BOX,\text{ }Cos\theta =\dfrac{OC}{OB} \\
& \text{ }OC=OB\cos \theta \\
& \text{ }OC=1\times \cos \theta \\
\end{align} $
Here, thread is at
$ \begin{align}
& 30{}^\circ \text{ angle} \\
& \text{cos}\theta \text{=cos 30}{}^\circ \text{=}\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
& \\
\end{align} $
$ \begin{align}
& Oc=1\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=\dfrac{1\cdot 73205}{2} \\
& OC=0\cdot 866 \\
& OA=1\text{ }cm \\
\end{align} $ $ $
Height through which ball is raised,
$ \begin{align}
& h=AC=AO-OC \\
& h=1-0\cdot 866=0\cdot 134\text{ }m \\
\end{align} $
Work done due to gravity is given by
$ \begin{align}
& =mg\text{ }h \\
& =0\cdot 2\times 10\times 0\cdot 134\text{ }m \\
& \text{ work done }=0\cdot 268\text{ }J \\
\end{align} $
By work energy theorem,
According to this, the work done by all forces acting on a particle equals change in the K.E of the particle.
$ \begin{align}
& \vartriangle K.E=\text{Work done} \\
& \vartriangle K.E=-\vartriangle P.E\text{ }[\text{because , in this case work done due to gravity }\!\!]\!\!\text{ } \\
& {{\left( K.E \right)}_{A}}-{{\left( K.E \right)}_{_{B}}}=-{{\left( P.E \right)}_{A}}+{{\left( P.E \right)}_{B}} \\
& {{\left( K.E \right)}_{B}}=0,\text{ at extreme position kinetic energy is zero} \\
& {{\left( P.E \right)}_{A}}=0,\text{ at mean position potential energy is zero}\text{.} \\
\end{align} $
$ \begin{align}
& {{\left( K.C \right)}_{A}}={{\left( P.E \right)}_{B}} \\
& \dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=mg\text{ }h \\
& \dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=0\cdot 268\text{ }J \\
& {{v}^{2}}=\dfrac{2}{m}\times 0\cdot 268 \\
& \text{ }=\dfrac{2}{0\cdot 2}\times 0\cdot 268 \\
& \text{ }=10\times 0\cdot 268 \\
& {{v}^{2}}=268 \\
& v=1\cdot 63\text{ }m{{s}^{-1}}[\text{Ans }\!\!]\!\!\text{ } \\
\end{align} $
Hence work done by ball is $ 0\cdot 268\text{ }J $
And velocity at lowest point is $ 1\cdot 63\text{ }m{{s}^{-1}} $
Note
Work energy theorem: The work done by the net force on a particle is equal to the change in the particle's kinetic energy.
$ W=\vartriangle K.E=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}_{{{f}^{2}}}}-\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}} $
The work energy theorem can be derived from Newton's second law: kinetic energy is directly proportional to the mass of the object and to the square of its velocity.
Potential energy is energy an object has because of its position relative to the same other object.
The formula of potential energy depends on the force acting on two objects.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




