
A \[1Kg\] stationary bomb exploded in three parts having mass ratio \[1:1:3\]. Parts having same mass move in perpendicular directions with velocity \[30m/s\], then the velocity of bigger part will be,
\[A.10\sqrt{2}m/s\]
\[B.\dfrac{10}{\sqrt{2}}m/s\]
\[C.15\sqrt{2}m/s\]
\[D.\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{2}}m/s\]
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: In a closed system total momentum before an event is same as that of total momentum after the event. Conservation of momentum is applied only to an isolated system of particles. Explosions and collisions can be used as an example for conservation of momentum.
Here a stationary bomb is exploded; hence conservation of momentum can be applied. Mass of particles and velocity are given in the question. We need to find the velocity of bigger parts. We have the equation which relates velocity and mass i.e., momentum \[p=mv\]
Formula used:
\[p=mv\]
\[\text{Magnitude of resultant vector=}\sqrt{{{\text{x}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2xy\cos \theta }\]
\[\text{Total momentum before the explosion,}{{\text{p}}_{i}}\text{= Total momentum after the explosion, }{{\text{p}}_{f}}\]
Complete answer:
Complete step by step solution:
Given that masses of three parts are in the ratio\[1:1:3\].
i.e.
\[m+m+3m=1Kg\]
\[5m=1\]
\[m=0.2Kg\]
\[3m=0.6Kg\]
Given,
\[Velocity, v=30m/s\]
Here parts with the same mass travel perpendicular to the velocity.
Let’s draw the vector diagram of the particles with the same mass.
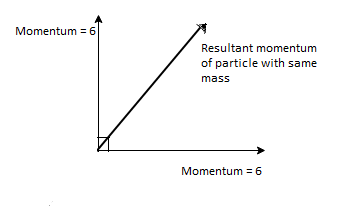
The momentum of particles with same mass, \[p=mv\]
\[{{p}_{s}}=0.2\times 30=6Kgm/{{s}^{2}}\]
Angle between the two momentum vectors is 90$^\circ$
Here we can apply the law of conservation of linear momentum.
\[\text{Total momentum before the explosion,}{{\text{p}}_{i}}\text{= Total momentum after the explosion, }{{\text{p}}_{f}}\]
Here the bomb is stationary. Hence,
\[\text{Initial momentum before the explosion, }{{\text{p}}_{i}}\text{ }=0\]
Since the total momentum is conserved here.
\[\text{momentum after the explosion, }{{\text{p}}_{f}}\text{ }=0\]
Here the momentum is zero. Hence, momentum of particles with bigger mass should be opposite to the above resultant momentum of other two particles.
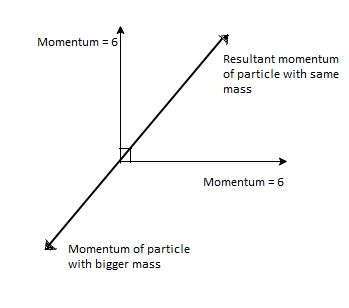
Momentum of particle with bigger mass, \[{{p}_{b}}=0.6\times v\]
Let’s find the magnitude of the above resultant momentum.
We have,
\[\text{Magnitude of resultant vector=}\sqrt{{{\text{x}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2xy\cos \theta }\]
Applying the above formula to find the magnitude of momentum vector of particle with same mass,
\[\left| {{p}_{s}} \right|=\sqrt{{{6}^{2}}+{{6}^{2}}+2\times 6\times 6\cos 90}\]
Where, \[\left| {{p}_{s}} \right|=\text{ Magnitude of linear momentum of the particles with same mass}\]
This should be equal to momentum of particle with bigger mass, \[\left| {{p}_{b}} \right|\].
Where, \[\left| {{p}_{b}} \right|=\text{ Magnitude of linear momentum of the particle with bigger mass}\]
\[\left| {{p}_{b}} \right|=\left| {{p}_{s}} \right|=\sqrt{{{6}^{2}}+{{6}^{2}}+2\times 6\times 6\cos 90}\]
\[0.6\times v=\sqrt{{{6}^{2}}+{{6}^{2}}+2\times 6\times 6\cos 90}\]
\[\operatorname{Cos}90=0\]
\[0.6\times v=\sqrt{{{6}^{2}}+{{6}^{2}}}\]
\[0.6\times v=6\sqrt{2}\]
\[v=10\sqrt{2}m/s\]
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Alternate method to solve the question
Given that masses of three parts are in the ratio \[1:1:3\].
\[\text{Total momentum before the explosion,}{{\text{p}}_{i}}\text{= Total momentum after the explosion, }{{\text{p}}_{f}}\]
Here the bomb was stationary. Hence,
\[\text{Initial momentum before the explosion, }{{\text{p}}_{i}}\text{ }=0\]
By applying law of conservation of momentum,
\[\text{momentum after the explosion, }{{\text{p}}_{f}}\text{ }=0\]
Then, \[0=\dfrac{m}{5}{{\vec{v}}_{1}}\hat{i}+\dfrac{m}{5}{{\vec{v}}_{2}}\hat{j}+\dfrac{3m}{5}{{\vec{v}}_{3}}\]
\[\dfrac{3m}{5}{{\vec{v}}_{3}}=-\dfrac{m}{5}\left[ {{{\vec{v}}}_{1}}\hat{i}+{{{\vec{v}}}_{2}}\hat{j} \right]\]
\[3{{\vec{v}}_{3}}=-\left[ {{{\vec{v}}}_{1}}\hat{i}+{{{\vec{v}}}_{2}}\hat{j} \right]\]
\[{{\vec{v}}_{3}}=-\left[ \dfrac{{{{\vec{v}}}_{1}}}{3}\hat{i}+\dfrac{{{{\vec{v}}}_{2}}}{3}\hat{j} \right]\]
Given, \[{{v}_{1}}={{v}_{2}}=30m/s\]
Then,
\[{{\vec{v}}_{3}}=-\dfrac{30}{3}\hat{i}-\dfrac{30}{3}\hat{j}\]
\[{{\vec{v}}_{3}}=-10\hat{i}-10\hat{j}\]
We have, \[\text{Magnitude of resultant vector=}\sqrt{{{\text{x}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2xy\cos \theta }\]
Then,\[\left| {{{\vec{v}}}_{3}} \right|=\sqrt{{{10}^{2}}+{{10}^{2}}+2\times 10\times 10\cos 90}\]
\[\left| {{{\vec{v}}}_{3}} \right|=10\sqrt{2}m/s\]
Here a stationary bomb is exploded; hence conservation of momentum can be applied. Mass of particles and velocity are given in the question. We need to find the velocity of bigger parts. We have the equation which relates velocity and mass i.e., momentum \[p=mv\]
Formula used:
\[p=mv\]
\[\text{Magnitude of resultant vector=}\sqrt{{{\text{x}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2xy\cos \theta }\]
\[\text{Total momentum before the explosion,}{{\text{p}}_{i}}\text{= Total momentum after the explosion, }{{\text{p}}_{f}}\]
Complete answer:
Complete step by step solution:
Given that masses of three parts are in the ratio\[1:1:3\].
i.e.
\[m+m+3m=1Kg\]
\[5m=1\]
\[m=0.2Kg\]
\[3m=0.6Kg\]
Given,
\[Velocity, v=30m/s\]
Here parts with the same mass travel perpendicular to the velocity.
Let’s draw the vector diagram of the particles with the same mass.

The momentum of particles with same mass, \[p=mv\]
\[{{p}_{s}}=0.2\times 30=6Kgm/{{s}^{2}}\]
Angle between the two momentum vectors is 90$^\circ$
Here we can apply the law of conservation of linear momentum.
\[\text{Total momentum before the explosion,}{{\text{p}}_{i}}\text{= Total momentum after the explosion, }{{\text{p}}_{f}}\]
Here the bomb is stationary. Hence,
\[\text{Initial momentum before the explosion, }{{\text{p}}_{i}}\text{ }=0\]
Since the total momentum is conserved here.
\[\text{momentum after the explosion, }{{\text{p}}_{f}}\text{ }=0\]
Here the momentum is zero. Hence, momentum of particles with bigger mass should be opposite to the above resultant momentum of other two particles.

Momentum of particle with bigger mass, \[{{p}_{b}}=0.6\times v\]
Let’s find the magnitude of the above resultant momentum.
We have,
\[\text{Magnitude of resultant vector=}\sqrt{{{\text{x}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2xy\cos \theta }\]
Applying the above formula to find the magnitude of momentum vector of particle with same mass,
\[\left| {{p}_{s}} \right|=\sqrt{{{6}^{2}}+{{6}^{2}}+2\times 6\times 6\cos 90}\]
Where, \[\left| {{p}_{s}} \right|=\text{ Magnitude of linear momentum of the particles with same mass}\]
This should be equal to momentum of particle with bigger mass, \[\left| {{p}_{b}} \right|\].
Where, \[\left| {{p}_{b}} \right|=\text{ Magnitude of linear momentum of the particle with bigger mass}\]
\[\left| {{p}_{b}} \right|=\left| {{p}_{s}} \right|=\sqrt{{{6}^{2}}+{{6}^{2}}+2\times 6\times 6\cos 90}\]
\[0.6\times v=\sqrt{{{6}^{2}}+{{6}^{2}}+2\times 6\times 6\cos 90}\]
\[\operatorname{Cos}90=0\]
\[0.6\times v=\sqrt{{{6}^{2}}+{{6}^{2}}}\]
\[0.6\times v=6\sqrt{2}\]
\[v=10\sqrt{2}m/s\]
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Alternate method to solve the question
Given that masses of three parts are in the ratio \[1:1:3\].
\[\text{Total momentum before the explosion,}{{\text{p}}_{i}}\text{= Total momentum after the explosion, }{{\text{p}}_{f}}\]
Here the bomb was stationary. Hence,
\[\text{Initial momentum before the explosion, }{{\text{p}}_{i}}\text{ }=0\]
By applying law of conservation of momentum,
\[\text{momentum after the explosion, }{{\text{p}}_{f}}\text{ }=0\]
Then, \[0=\dfrac{m}{5}{{\vec{v}}_{1}}\hat{i}+\dfrac{m}{5}{{\vec{v}}_{2}}\hat{j}+\dfrac{3m}{5}{{\vec{v}}_{3}}\]
\[\dfrac{3m}{5}{{\vec{v}}_{3}}=-\dfrac{m}{5}\left[ {{{\vec{v}}}_{1}}\hat{i}+{{{\vec{v}}}_{2}}\hat{j} \right]\]
\[3{{\vec{v}}_{3}}=-\left[ {{{\vec{v}}}_{1}}\hat{i}+{{{\vec{v}}}_{2}}\hat{j} \right]\]
\[{{\vec{v}}_{3}}=-\left[ \dfrac{{{{\vec{v}}}_{1}}}{3}\hat{i}+\dfrac{{{{\vec{v}}}_{2}}}{3}\hat{j} \right]\]
Given, \[{{v}_{1}}={{v}_{2}}=30m/s\]
Then,
\[{{\vec{v}}_{3}}=-\dfrac{30}{3}\hat{i}-\dfrac{30}{3}\hat{j}\]
\[{{\vec{v}}_{3}}=-10\hat{i}-10\hat{j}\]
We have, \[\text{Magnitude of resultant vector=}\sqrt{{{\text{x}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2xy\cos \theta }\]
Then,\[\left| {{{\vec{v}}}_{3}} \right|=\sqrt{{{10}^{2}}+{{10}^{2}}+2\times 10\times 10\cos 90}\]
\[\left| {{{\vec{v}}}_{3}} \right|=10\sqrt{2}m/s\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




