
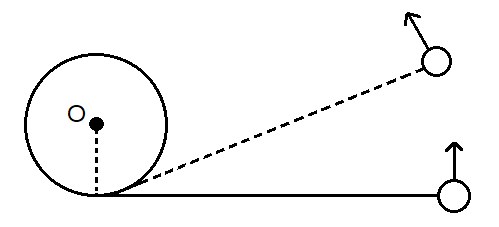
A ball is attached to a string that is attached to a pole. When the ball is hit, the string wraps around the pole and the ball spirals inwards sliding on the frictionless surface. Neglecting air resistance, what happens as the ball swings around the pole?
(A) The mechanical energy and angular momentum are conserved
(B) The angular momentum of the ball is conserved and the mechanical energy of the ball increases
(C) The angular momentum of the ball is conserved and the mechanical energy of the ball decreases
(D) The mechanical energy the ball is conserved and angular momentum of ball decreases

Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint : The surface is frictionless, thus no energy will be lost. The ball undergoes reverse swing as well. From the definition of the terms angular momentum and the total mechanical energy we will get the correct option.
Formula Used: In the solution we will be using the following formula,
The angular momentum $ L = I \times \omega $ where $ I $ is the moment of inertia and $ \omega $ is the angular velocity.
Complete step by step answer
Mechanical energy is the total amount of kinetic energy and potential energy of an object that is used to do a specific work. Mechanical energy can also be defined as the energy of an element due to its position or motion or both. The potential energy of an object is due to its position and kinetic energy is due to its motion. The potential energy of an object is zero when it is in the movement and kinetic energy is zero when the object is in rest.
Given in the question, when the ball is hit, the string wraps around the pole and the ball spirals inwards sliding on the frictionless surface. Thus mechanical energy is conserved, since there is no friction.
Angular momentum is defined as the property of any rotating object given by moment of inertia times angular velocity.
It is the property of a rotating body given by the product of the moment of inertia and the angular velocity of the rotating object. It is a vector quantity, which implies that here along with magnitude, the direction is also considered.
Thus, angular momentum $ L = I \times \omega $ where $ I $ is the moment of inertia and $ \omega $ is the angular velocity. Angular momentum of the ball decreases due to reverse swing compared to that of initial swing before strike.
The force is conservative. So mechanical energy is conserved (frictionless) and Angular momentum ( $ L = I \times \omega $ ) decreases due to reverse swing compared to that of initial swing before strike.
$ \therefore $ The correct answer is Option D.
Note
Mechanical energy accounts for kinetic and potential energy. Mechanical energy can be found in nature in multiple forms, for instance, one can mention:
Pressurized hot gases or other fluids which have enough potential energy that can be turned into kinetic energy of the flow; Flowing water of the streams and rivers that have enough energy stored in the running water; Wind, or flowing air, which has the same logic as flowing water; Waves, tides, ocean streams, etc.
Formula Used: In the solution we will be using the following formula,
The angular momentum $ L = I \times \omega $ where $ I $ is the moment of inertia and $ \omega $ is the angular velocity.
Complete step by step answer
Mechanical energy is the total amount of kinetic energy and potential energy of an object that is used to do a specific work. Mechanical energy can also be defined as the energy of an element due to its position or motion or both. The potential energy of an object is due to its position and kinetic energy is due to its motion. The potential energy of an object is zero when it is in the movement and kinetic energy is zero when the object is in rest.
Given in the question, when the ball is hit, the string wraps around the pole and the ball spirals inwards sliding on the frictionless surface. Thus mechanical energy is conserved, since there is no friction.
Angular momentum is defined as the property of any rotating object given by moment of inertia times angular velocity.
It is the property of a rotating body given by the product of the moment of inertia and the angular velocity of the rotating object. It is a vector quantity, which implies that here along with magnitude, the direction is also considered.
Thus, angular momentum $ L = I \times \omega $ where $ I $ is the moment of inertia and $ \omega $ is the angular velocity. Angular momentum of the ball decreases due to reverse swing compared to that of initial swing before strike.
The force is conservative. So mechanical energy is conserved (frictionless) and Angular momentum ( $ L = I \times \omega $ ) decreases due to reverse swing compared to that of initial swing before strike.
$ \therefore $ The correct answer is Option D.
Note
Mechanical energy accounts for kinetic and potential energy. Mechanical energy can be found in nature in multiple forms, for instance, one can mention:
Pressurized hot gases or other fluids which have enough potential energy that can be turned into kinetic energy of the flow; Flowing water of the streams and rivers that have enough energy stored in the running water; Wind, or flowing air, which has the same logic as flowing water; Waves, tides, ocean streams, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




