
A bar magnet is equivalent to:
Answer
524.1k+ views
Hint: A bar magnet is similar to a solenoid because the magnetic field of the bar magnet and a solenoid have the same pattern. When a current-carrying solenoid is hung freely, it stays along the north-south direction, similar to a bar magnet. The bar magnet and a solenoid's magnetic field are uniform and strong. If we were to pass a compass needle in a bar magnet and a solenoid region, we realize that the deflection of the needle is similar in both cases.
Complete answer:
A bar magnet is a quadrilateral or a rectangular piece of an object formed from steel or iron having permanent magnetic characteristics with two poles: south and north. A solenoid is a loop with a length more significant than its diameter and is a sort of electromagnet to create controlled magnetic fields by transferring an electric current through it.
Solenoids and Bar magnets both have attractive and directive characteristics to align themselves with the outer magnetic field.
The magnetic field at the axial location is the equivalent for both. The magnetic moment is identical for both.
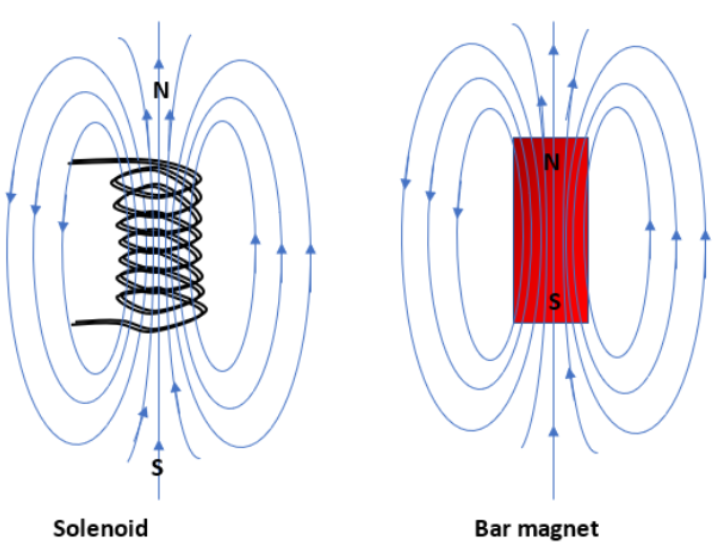
A solenoid is a large coil of round loops of insulated copper wiring. Magnetic field lines are generated around the solenoid when a current is permitted to flow through it. The magnetic field generated by it is comparable to the bar magnet's magnetic field.
When the north pole of the bar magnet is taken near the end joined to the battery's negative terminal, the bar magnet's solenoid repels.
Since the same poles oppose each other, the end connected to the battery's negative terminal acts as the North Pole of solenoid, and the other end acts as the South Pole. Hence, one end of the solenoid acts as the North Pole, and the other end acts as the South Pole.
Note:
The bar magnet is strong, whereas a solenoid is an electromagnet, i.e., it behaves as a magnet only when a current is carried through. When a bar magnet is divided into two halves, both the pieces work as a magnet with the same magnetic characteristics, whereas when a solenoid is split into two halves, it will have more minor fields. The poles of the bar magnet are constant, whereas, for a solenoid, the poles can be changed. The magnetic field's strength of a bar magnet is fixed, i.e., unchanged, whereas the magnetic field's strength of a solenoid depends on the current transfer through it.
Complete answer:
A bar magnet is a quadrilateral or a rectangular piece of an object formed from steel or iron having permanent magnetic characteristics with two poles: south and north. A solenoid is a loop with a length more significant than its diameter and is a sort of electromagnet to create controlled magnetic fields by transferring an electric current through it.
Solenoids and Bar magnets both have attractive and directive characteristics to align themselves with the outer magnetic field.
The magnetic field at the axial location is the equivalent for both. The magnetic moment is identical for both.

A solenoid is a large coil of round loops of insulated copper wiring. Magnetic field lines are generated around the solenoid when a current is permitted to flow through it. The magnetic field generated by it is comparable to the bar magnet's magnetic field.
When the north pole of the bar magnet is taken near the end joined to the battery's negative terminal, the bar magnet's solenoid repels.
Since the same poles oppose each other, the end connected to the battery's negative terminal acts as the North Pole of solenoid, and the other end acts as the South Pole. Hence, one end of the solenoid acts as the North Pole, and the other end acts as the South Pole.
Note:
The bar magnet is strong, whereas a solenoid is an electromagnet, i.e., it behaves as a magnet only when a current is carried through. When a bar magnet is divided into two halves, both the pieces work as a magnet with the same magnetic characteristics, whereas when a solenoid is split into two halves, it will have more minor fields. The poles of the bar magnet are constant, whereas, for a solenoid, the poles can be changed. The magnetic field's strength of a bar magnet is fixed, i.e., unchanged, whereas the magnetic field's strength of a solenoid depends on the current transfer through it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




