
A big ball of mass M, moving with velocity u strikes a small ball of mass m, which is at rest. Finally small ball attains velocity u and big ball v. What is the value of v:-
(A) $ \left( \dfrac{M-m}{M} \right)u $
(B) $ \left( \dfrac{m}{M+m} \right)u $
(C) $ \dfrac{2m}{M+m} $
(D) $ \left( \dfrac{M}{M+m} \right)v $
Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint: Here, we apply the law of conservation of linear momentum, according to this principle, if two objects collide, then the total momentum before and after will be the same if there is no external force acting on the colliding objects.
i.e., Initial Momentum = Final Momentum
$ {{P}_{i}}={{P}_{f}} $
Use linear momentum formula,
Here, m is the mass of body, v is velocity of body,
Complete step by step solution
We have given,
A big ball having mass = M
Velocity of big ball before collision = u
Mass of small ball = m
Initially small ball is at rest
Hence, velocity of small ball before collision = 0
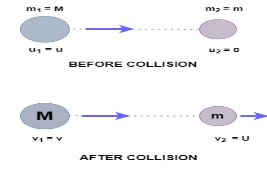
After collision,
Velocity of small ball = u
Velocity of big ball = v
Apply law of conservation of linear momentum
$ {{P}_{i}}={{P}_{f}} $
Here, $ {{P}_{i}} $ is initial linear momentum before collision and $ {{P}_{f}} $ is final linear momentum after collision
$ {{m}_{1}}{{u}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{u}_{2}}={{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}} $ --------(1)
Put, $ {{m}_{1}}=M $ [mass of big ball ]
$ {{m}_{2}}=m $ [mass of small ball]
$ {{u}_{1}}=u $ [velocity of big ball] before collision
$ {{u}_{2}}=0 $ [velocity of small ball] before collision
After collision, $ {{v}_{1}}=v $ [velocity of big ball]
$ {{v}_{2}}=u $ [velocity of small ball]
Put all the values in eq. (1).
Mu $ + $ m(0) = Mv $ + $ mu
Mu = Mv $ + $ mu
Mv = Mu $ - $ mu
$ V=\left( \dfrac{M-m}{M} \right)u $
Hence, option A is correct.
Note
The law of conservation of momentum can be explained from Newton's 2nd law of motion. Newton’s 2nd law of motion says that the rate of change of linear momentum of a body is equal to the net force applied to it, i.e., $ \dfrac{dp}{dt}={{F}_{net}} $ . If net force acting on body is zero, the rate of change of momentum is also zero,
$ \dfrac{dp}{dt}=0 $$ \left[ \because {{F}_{net}}=0 \right] $
P = constant
It means that there is no change in momentum.
i.e., Initial Momentum = Final Momentum
$ {{P}_{i}}={{P}_{f}} $
Use linear momentum formula,
Here, m is the mass of body, v is velocity of body,
Complete step by step solution
We have given,
A big ball having mass = M
Velocity of big ball before collision = u
Mass of small ball = m
Initially small ball is at rest
Hence, velocity of small ball before collision = 0

After collision,
Velocity of small ball = u
Velocity of big ball = v
Apply law of conservation of linear momentum
$ {{P}_{i}}={{P}_{f}} $
Here, $ {{P}_{i}} $ is initial linear momentum before collision and $ {{P}_{f}} $ is final linear momentum after collision
$ {{m}_{1}}{{u}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{u}_{2}}={{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}} $ --------(1)
Put, $ {{m}_{1}}=M $ [mass of big ball ]
$ {{m}_{2}}=m $ [mass of small ball]
$ {{u}_{1}}=u $ [velocity of big ball] before collision
$ {{u}_{2}}=0 $ [velocity of small ball] before collision
After collision, $ {{v}_{1}}=v $ [velocity of big ball]
$ {{v}_{2}}=u $ [velocity of small ball]
Put all the values in eq. (1).
Mu $ + $ m(0) = Mv $ + $ mu
Mu = Mv $ + $ mu
Mv = Mu $ - $ mu
$ V=\left( \dfrac{M-m}{M} \right)u $
Hence, option A is correct.
Note
The law of conservation of momentum can be explained from Newton's 2nd law of motion. Newton’s 2nd law of motion says that the rate of change of linear momentum of a body is equal to the net force applied to it, i.e., $ \dfrac{dp}{dt}={{F}_{net}} $ . If net force acting on body is zero, the rate of change of momentum is also zero,
$ \dfrac{dp}{dt}=0 $$ \left[ \because {{F}_{net}}=0 \right] $
P = constant
It means that there is no change in momentum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




