
A biological catalyst is essentially
(a) An enzyme
(b) A carbohydrate
(c) An amino acid
(d) A nitrogenous base
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: They speed up reactions by bringing reactants together and reducing the activation energy required to start the reaction although they are not changed in the reaction. It is unique in nature and shows a varying degree of specificities, while they are highly specific for a particular substrate.
Complete answer:
- Enzyme Catalysis: These are catalysts in the living system. The rate of any biological event can be altered by substances as enzymes.
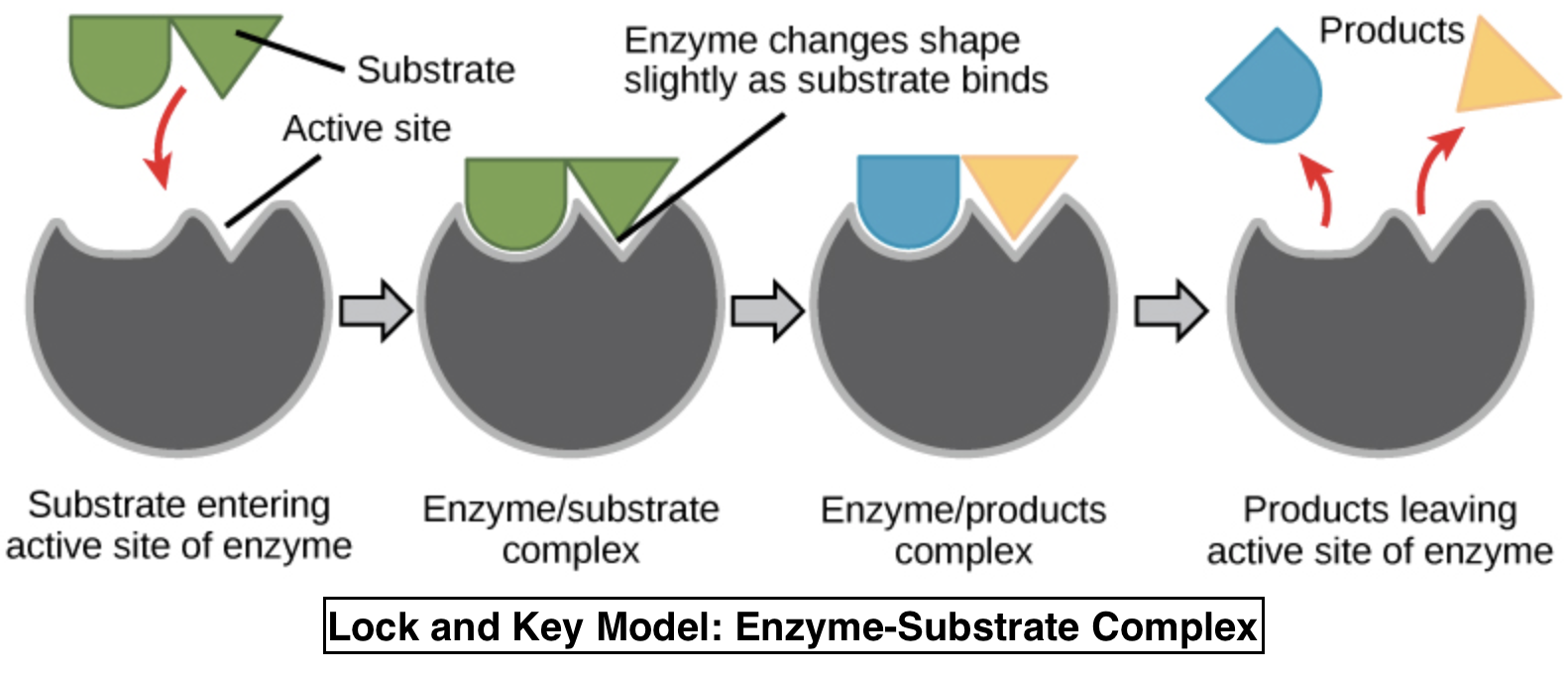
These are basically proteins, and catalyst activity is structure explicit.
- Enzyme catalysis is the expansion in the rate of a chemical response by the active site of a protein.
- Enzymes are the macromolecular natural catalysts. These are profoundly particular catalysts significantly quickening both the rate and explicitness of metabolic reaction. All enzymes are insoluble since they exist in the colloidal state. Urease is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea, which can form ammonia and carbon dioxide.
Additional information: Enzymes are specific in nature and they have a particular shape, consequently, only a specific substrate will fit its active site. There are two theories of enzyme activity: Lock and Key and Induced Fit. The lock and key theory describe that only a specific substrate will fit a specific active site, much the same as a key fit a lock. Induced Fit, in like manner, expresses that enzymes wrap around substrates, attracted to one another by opposite charges, forming an enzyme-substrate complex.
So the correct answer is ‘An enzyme’.
Note: Enzymes are incredibly effective and have extraordinary catalytic power, changing around 100 to 10,000 substrate molecules into product every second and continuing from 103 to 108 to multiple times quicker than the uncatalyzed reaction. Enzymes don’t affect the equilibrium constant notwithstanding the increase in the conversion rate of the substrate into the product.
Complete answer:
- Enzyme Catalysis: These are catalysts in the living system. The rate of any biological event can be altered by substances as enzymes.

These are basically proteins, and catalyst activity is structure explicit.
- Enzyme catalysis is the expansion in the rate of a chemical response by the active site of a protein.
- Enzymes are the macromolecular natural catalysts. These are profoundly particular catalysts significantly quickening both the rate and explicitness of metabolic reaction. All enzymes are insoluble since they exist in the colloidal state. Urease is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea, which can form ammonia and carbon dioxide.
Additional information: Enzymes are specific in nature and they have a particular shape, consequently, only a specific substrate will fit its active site. There are two theories of enzyme activity: Lock and Key and Induced Fit. The lock and key theory describe that only a specific substrate will fit a specific active site, much the same as a key fit a lock. Induced Fit, in like manner, expresses that enzymes wrap around substrates, attracted to one another by opposite charges, forming an enzyme-substrate complex.
So the correct answer is ‘An enzyme’.
Note: Enzymes are incredibly effective and have extraordinary catalytic power, changing around 100 to 10,000 substrate molecules into product every second and continuing from 103 to 108 to multiple times quicker than the uncatalyzed reaction. Enzymes don’t affect the equilibrium constant notwithstanding the increase in the conversion rate of the substrate into the product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




