
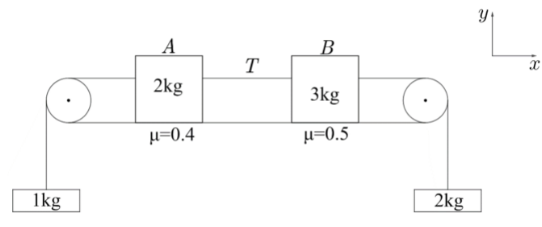
A block system is shown in figure. Frictional force on $2kg$ is ${{f}_{1}}$ and on $3kg$ is ${{f}_{2}}$ and $T$ is tension in the string connecting block A and B. Which of the following is correct?
A. ${{f}_{1}}=8\hat{i},{{f}_{2}}=-15\hat{i},T=2N$
B. ${{f}_{1}}=5\hat{i},{{f}_{2}}=-15\hat{i},T=5N$
C. ${{f}_{1}}=-8\hat{i},{{f}_{2}}=-15\hat{i},T=2N$
D. ${{f}_{1}}=-5\hat{i},{{f}_{2}}=-15\hat{i},T=5N$

Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint:Draw the free body diagram of all the blocks and balance the forces. A free body diagram is a sketch of an object of interest with the entire surrounding object stripped away and all the forces acting on the body are shown, it helps to visualize all the forces acting on a single object.
Complete step by step answer:
The blocks of $1kg$ and $2kg$ will experience gravitational force in downward direction due to their weight. Gravitation force on $2kg$ block $W=mg$, take g=$10$ $m{{s}^{-2}}$
$W=2\times 10 \\
\Rightarrow W=20N \\ $
Gravitation force on $1kg$ block $W=mg$, take g=$10$ $m{{s}^{-2}}$
$W=1\times 10 \\
\Rightarrow W=10N \\ $
Free body diagram of Block B
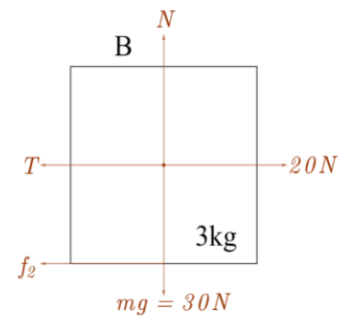
Normal force (N) is a contact force that is felt when a surface pushes against an object that is placed on that surface and is perpendicular to the surface that an object contacts.
Since the body is not going anywhere in a vertical direction, upward and downward force will be equal in magnitude.
$N=mg$, here mass of the block is $3kg$.
$N=3\times 10=30N$
Normal force on block B is $30N$. Frictional force is the resistance force against motion of one object moving relative to another. It is in the opposite direction to motion of the object.
${{f}_{2\max }}=\mu N =0.5\times 30=15N \\ $ ($\mu =0.5$ for block B and N represents normal reaction)
Let the block B start moving in x direction with acceleration a.
$ma=20-T-{{f}_{2}}$
$3a=20-T-{{f}_{2}}.........\left( 1 \right)$
Since the block is at rest a=$0$, the equation will become;
$20=T+{{f}_{2}}............\left( 2 \right)$
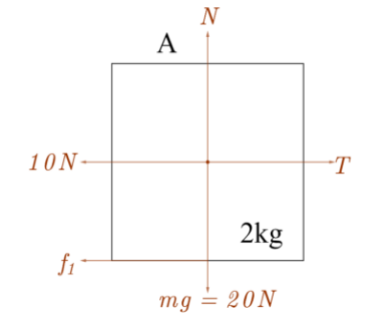
Since the body is not going anywhere in a vertical direction, upward and downward force will be equal in magnitude.
$N=mg$, here mass of the block is $2kg$
$N=2\times 10=20N$
${{f}_{1\max }}=\mu N =0.4\times 20=8N \\ $ ($\mu =0.4$ for block A and N represents normal reaction)
Let the block B start moving in x direction with acceleration a.
$2a=T-10-{{f}_{1}}........\left( 3 \right)$
Since the block is at rest a=$0$, the equation will become;
$T-{{f}_{1}}=10$ .............$\left( 4 \right)$
Add $\left( 2 \right)and\left( 4 \right)$
${{f}_{1}}+{{f}_{2}}=10.......\left( 5 \right)$
Using $\left( 2 \right),\left( 4 \right)and\left( 5 \right)$
We will get ${{f}_{1}}=-5\hat{i},{{f}_{2}}=-15\hat{i},T=5N$
Therefore option D is the correct answer.
Note: Friction always slows a motion and amount of friction depends on the material from which those two surfaces are made. To stop the motion block A will provide $5N$ friction and block B will give $15N$ friction.
Complete step by step answer:
The blocks of $1kg$ and $2kg$ will experience gravitational force in downward direction due to their weight. Gravitation force on $2kg$ block $W=mg$, take g=$10$ $m{{s}^{-2}}$
$W=2\times 10 \\
\Rightarrow W=20N \\ $
Gravitation force on $1kg$ block $W=mg$, take g=$10$ $m{{s}^{-2}}$
$W=1\times 10 \\
\Rightarrow W=10N \\ $
Free body diagram of Block B

Normal force (N) is a contact force that is felt when a surface pushes against an object that is placed on that surface and is perpendicular to the surface that an object contacts.
Since the body is not going anywhere in a vertical direction, upward and downward force will be equal in magnitude.
$N=mg$, here mass of the block is $3kg$.
$N=3\times 10=30N$
Normal force on block B is $30N$. Frictional force is the resistance force against motion of one object moving relative to another. It is in the opposite direction to motion of the object.
${{f}_{2\max }}=\mu N =0.5\times 30=15N \\ $ ($\mu =0.5$ for block B and N represents normal reaction)
Let the block B start moving in x direction with acceleration a.
$ma=20-T-{{f}_{2}}$
$3a=20-T-{{f}_{2}}.........\left( 1 \right)$
Since the block is at rest a=$0$, the equation will become;
$20=T+{{f}_{2}}............\left( 2 \right)$

Since the body is not going anywhere in a vertical direction, upward and downward force will be equal in magnitude.
$N=mg$, here mass of the block is $2kg$
$N=2\times 10=20N$
${{f}_{1\max }}=\mu N =0.4\times 20=8N \\ $ ($\mu =0.4$ for block A and N represents normal reaction)
Let the block B start moving in x direction with acceleration a.
$2a=T-10-{{f}_{1}}........\left( 3 \right)$
Since the block is at rest a=$0$, the equation will become;
$T-{{f}_{1}}=10$ .............$\left( 4 \right)$
Add $\left( 2 \right)and\left( 4 \right)$
${{f}_{1}}+{{f}_{2}}=10.......\left( 5 \right)$
Using $\left( 2 \right),\left( 4 \right)and\left( 5 \right)$
We will get ${{f}_{1}}=-5\hat{i},{{f}_{2}}=-15\hat{i},T=5N$
Therefore option D is the correct answer.
Note: Friction always slows a motion and amount of friction depends on the material from which those two surfaces are made. To stop the motion block A will provide $5N$ friction and block B will give $15N$ friction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




