
A boat which has a speed of 5 km/hr in still water crosses a river of width 1km along the shortest path in 15 minutes. The velocity of the river water in km/hr is
A. 1
B. 3
C. 4
D. 41
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: To find the solution of the given question, we will find the distance covered by the boat in 15 mins, then apply the formula of Pythagoras theorem to find the distance covered by the river in 15 mins. Then find the velocity of the river water. Velocity of an object is defined as the rate of change of its position with respect to a frame of reference.
Formula used:
Pythagoras theorem, ${\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AC} \right)^2}$
Complete answer:
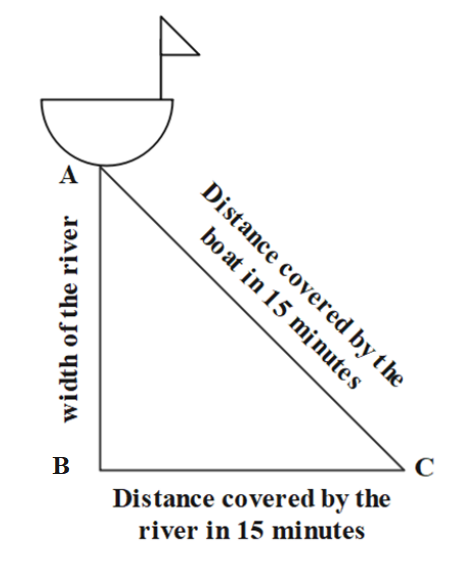
We will draw a diagram for the given situation, for a better understanding of the question
Speed of the boat in still water $ = 5km/hr$
Width of the river $ = 1km$
Time taken by the boat to cross the river $ = 15\min s = \dfrac{{15}}{{60}}hr = \dfrac{1}{4}hr$ ; 1hr = 60mins
Let us assume the velocity of the river be x km/hr
Now, distance covered by the boat in $\dfrac{1}{4}hr$ $ = \left( {5 \times \dfrac{1}{4}} \right)km$ $ = 1.25km$
Due to the flow of the river the boat will move in the direction AC, which is the shortest possible path for the boat.
So, AC = 1.25km
Width of the river, AB = 1km
Here, BC is the other bank of the river so the width AB of the river will be perpendicular to BC.
i.e. $\angle B = {90^ \circ }$
Applying Pythagoras theorem in $\Delta ABC$
$\eqalign{
& {\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AC} \right)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( 1 \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2} = {\left( {1.25} \right)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( {BC} \right)^2} = {\left( {1.25} \right)^2} - {\left( 1 \right)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( {BC} \right)^2} = 1.5625 - 1 \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( {BC} \right)^2} = 0.5625 \cr
& \Rightarrow BC = 0.75km \cr} $
This means that the distance covered by the river water in 15 mins is 0.25km.
Thus, velocity of the river $ = \dfrac{{0.75km}}{{15km}} = \dfrac{{0.75km}}{{1/4hr}} = \left( {0.75 \times 4} \right)km/hr = 3km/hr$
So, the correct answer is “Option b”.
Note:
Relative velocity is defined as the vector difference between the velocities of the two bodies with respect to each other. All the motions are relative to some frame of reference. For example, if a body is at rest it means that it is not in motion. This means that it is being described with respect to a frame of reference which is moving together with the body.
Formula used:
Pythagoras theorem, ${\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AC} \right)^2}$
Complete answer:
We will draw a diagram for the given situation, for a better understanding of the question

Speed of the boat in still water $ = 5km/hr$
Width of the river $ = 1km$
Time taken by the boat to cross the river $ = 15\min s = \dfrac{{15}}{{60}}hr = \dfrac{1}{4}hr$ ; 1hr = 60mins
Let us assume the velocity of the river be x km/hr
Now, distance covered by the boat in $\dfrac{1}{4}hr$ $ = \left( {5 \times \dfrac{1}{4}} \right)km$ $ = 1.25km$
Due to the flow of the river the boat will move in the direction AC, which is the shortest possible path for the boat.
So, AC = 1.25km
Width of the river, AB = 1km
Here, BC is the other bank of the river so the width AB of the river will be perpendicular to BC.
i.e. $\angle B = {90^ \circ }$
Applying Pythagoras theorem in $\Delta ABC$
$\eqalign{
& {\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AC} \right)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( 1 \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2} = {\left( {1.25} \right)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( {BC} \right)^2} = {\left( {1.25} \right)^2} - {\left( 1 \right)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( {BC} \right)^2} = 1.5625 - 1 \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( {BC} \right)^2} = 0.5625 \cr
& \Rightarrow BC = 0.75km \cr} $
This means that the distance covered by the river water in 15 mins is 0.25km.
Thus, velocity of the river $ = \dfrac{{0.75km}}{{15km}} = \dfrac{{0.75km}}{{1/4hr}} = \left( {0.75 \times 4} \right)km/hr = 3km/hr$
So, the correct answer is “Option b”.
Note:
Relative velocity is defined as the vector difference between the velocities of the two bodies with respect to each other. All the motions are relative to some frame of reference. For example, if a body is at rest it means that it is not in motion. This means that it is being described with respect to a frame of reference which is moving together with the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




