
A bomb is dropped from an aeroplane when it is directly above a target at a height of 1000 m. The aeroplane is moving horizontally with a speed of 500km/h. By how much distance will the bomb miss the target?
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: A bomb is dropped from a moving aeroplane. We know that the bomb will have a velocity in the direction of motion of the aeroplane. And its velocity along the y direction will be zero. By using the equations of motion we can solve for time of flight. Thus we have time and speed is already given, using this we can solve for distance.
Formula used:
Third kinematic equation,
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
$\text{distance=speed }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ time}$
Complete answer:
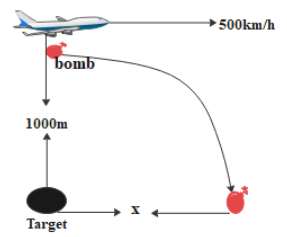
We have an aeroplane moving horizontally in the x direction with a velocity 500km/h.
A bomb is dropped from the plane when it is right above its target.
The height from the target to the plane is given as 1000m.
We know that when the bomb is dropped from a moving plane, the bomb will have a velocity in the horizontal direction. Hence the bomb will not hit the target; it will fall at a distance ‘x’ from the target.
We can say that the initial velocity of the bomb in the vertical direction will be zero.
${{v}_{y(initial)}}={{u}_{y}}=0$
By the third kinematic equation, we have
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Here displacement, ‘s’ in y direction is 1000m, initial velocity is zero and acceleration ‘a’ is the acceleration due to gravity $g=10m/{{s}^{2}}$.
Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& {{s}_{y}}={{u}_{y}}t+\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}} \\
& 1000=0+\dfrac{1}{2}\times 10\times {{t}^{2}} \\
& t=10\sqrt{2}\sec \\
\end{align}$
Now we have time of flight $t=10\sqrt{2}\sec $
We have the horizontal velocity,
$\begin{align}
& v=500km/h \\
& v=500\times \dfrac{5}{18} \\
& v=138.889m/s \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the distance from the target to the bomb ‘x’ will be
$\begin{align}
& x=v\times t \\
& x=138.889\times 10\sqrt{2} \\
& x=1964m \\
& x=1.964km \\
\end{align}$
Hence the bomb missed the target by 1.96km.
Note:
Here the motion of the bomb is projectile motion and the bomb is a projectile.
A projectile motion is the motion of a body only under the influence of gravity. The body in projectile motion is a projectile.
Here the initial velocity of the bomb is zero because we are not giving any kind of external velocity to the bomb. The bomb is just dropped and it continues to fall only with the influence of gravity.
Formula used:
Third kinematic equation,
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
$\text{distance=speed }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ time}$
Complete answer:

We have an aeroplane moving horizontally in the x direction with a velocity 500km/h.
A bomb is dropped from the plane when it is right above its target.
The height from the target to the plane is given as 1000m.
We know that when the bomb is dropped from a moving plane, the bomb will have a velocity in the horizontal direction. Hence the bomb will not hit the target; it will fall at a distance ‘x’ from the target.
We can say that the initial velocity of the bomb in the vertical direction will be zero.
${{v}_{y(initial)}}={{u}_{y}}=0$
By the third kinematic equation, we have
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Here displacement, ‘s’ in y direction is 1000m, initial velocity is zero and acceleration ‘a’ is the acceleration due to gravity $g=10m/{{s}^{2}}$.
Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& {{s}_{y}}={{u}_{y}}t+\dfrac{1}{2}g{{t}^{2}} \\
& 1000=0+\dfrac{1}{2}\times 10\times {{t}^{2}} \\
& t=10\sqrt{2}\sec \\
\end{align}$
Now we have time of flight $t=10\sqrt{2}\sec $
We have the horizontal velocity,
$\begin{align}
& v=500km/h \\
& v=500\times \dfrac{5}{18} \\
& v=138.889m/s \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the distance from the target to the bomb ‘x’ will be
$\begin{align}
& x=v\times t \\
& x=138.889\times 10\sqrt{2} \\
& x=1964m \\
& x=1.964km \\
\end{align}$
Hence the bomb missed the target by 1.96km.
Note:
Here the motion of the bomb is projectile motion and the bomb is a projectile.
A projectile motion is the motion of a body only under the influence of gravity. The body in projectile motion is a projectile.
Here the initial velocity of the bomb is zero because we are not giving any kind of external velocity to the bomb. The bomb is just dropped and it continues to fall only with the influence of gravity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




