
A candle of diameter d is floating on a liquid in a cylindrical container of diameter D(D>>d) as shown in figure. It is burning at the rate of 2cm/h. Then, the top of the candle will
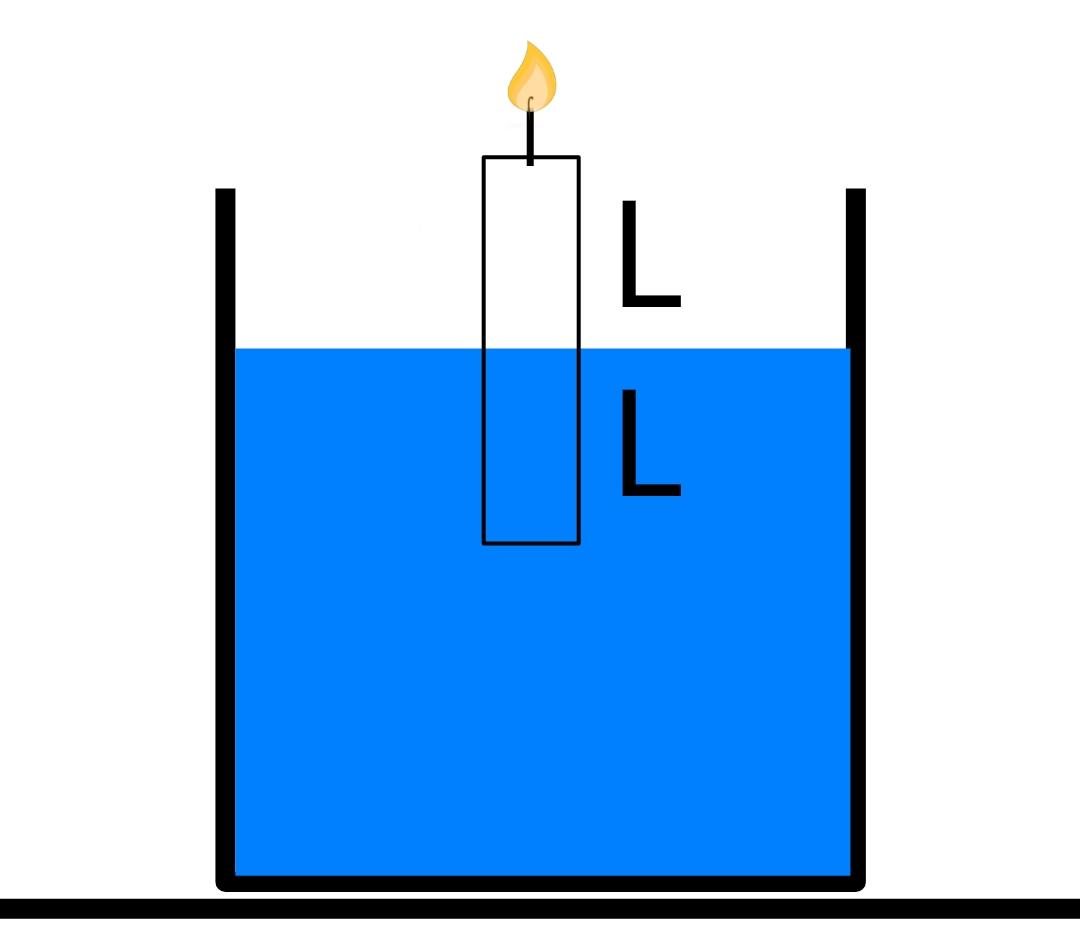
(A) remain at the same height
(B) fall at the rate of 1cm/h
(C) fall at the rate of 2cm/h
(D) go up at the rate of 1cm/h

Answer
460.8k+ views
Hint: From the above condition we can make a perfect (true) assumption that the density of the candle wax is less than the density of the liquid, as it is floating in the liquid. Since the condition (D>>d) is given, we can neglect the fact that the change in the volume of the candle will impact the height of the liquid in the container. Thus, we can assume here that the highest level of the liquid will remain constant.
Complete answer:
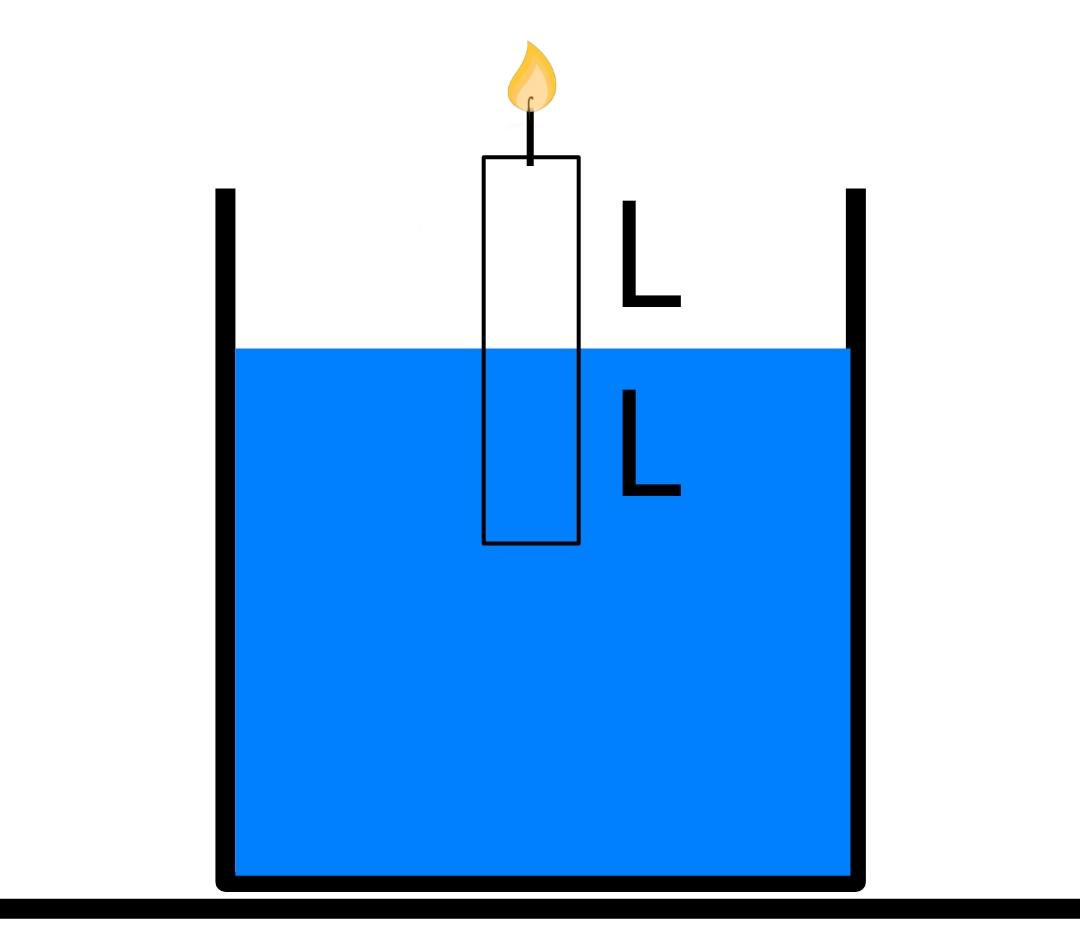
Now we see here that only half of the volume of candle is submerged which means that the weight of half of the volume of the liquid displaced by the candle is equal to the total weight of the candle (by Archimedes principle).
Now,
\[V \times {\rho _{candle}} = \dfrac{V}{2} \times {\rho _{liquid}} \]
\[2{\rho _{candle}} = {\rho _{liquid}} \]
Thus, we are left with the fact that the density of the liquid is twice the density of the candle. Thus, the candle will always remain half inside and half outside of the liquid. So, after an hour, the length of the candle would decrease by 2cm but still half of it would remain in water and half outside. Thus, the fall in the top of the candle would be 1cm. And the candle will rise 1 cm to make itself half submerged in the liquid. Thus, the rate of fall off the top of the candle is 1cm/h.
So, the correct option is (B).
Note:
Now we use the Archimedes Principle that if a body is floating then weight of the liquid displaced by the body is equal to the weight of the body the fact that (D>>d) has given us a lot of advantages on solving the question but if the diameter Of the container D was in significant size compared to that of the diameter of the candle then we would have a different answer as we have to take the level of the liquid in the container in account while solving. But still the candle would have remained half inside the liquid (as it's density is half of the density of the liquid).
Complete answer:

Now we see here that only half of the volume of candle is submerged which means that the weight of half of the volume of the liquid displaced by the candle is equal to the total weight of the candle (by Archimedes principle).
Now,
\[V \times {\rho _{candle}} = \dfrac{V}{2} \times {\rho _{liquid}} \]
\[2{\rho _{candle}} = {\rho _{liquid}} \]
Thus, we are left with the fact that the density of the liquid is twice the density of the candle. Thus, the candle will always remain half inside and half outside of the liquid. So, after an hour, the length of the candle would decrease by 2cm but still half of it would remain in water and half outside. Thus, the fall in the top of the candle would be 1cm. And the candle will rise 1 cm to make itself half submerged in the liquid. Thus, the rate of fall off the top of the candle is 1cm/h.
So, the correct option is (B).
Note:
Now we use the Archimedes Principle that if a body is floating then weight of the liquid displaced by the body is equal to the weight of the body the fact that (D>>d) has given us a lot of advantages on solving the question but if the diameter Of the container D was in significant size compared to that of the diameter of the candle then we would have a different answer as we have to take the level of the liquid in the container in account while solving. But still the candle would have remained half inside the liquid (as it's density is half of the density of the liquid).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




