
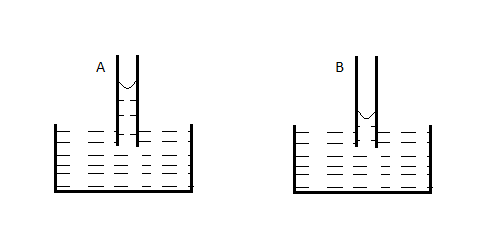
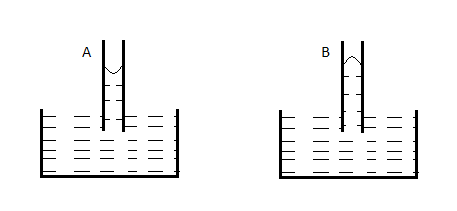
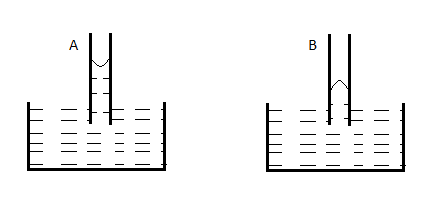
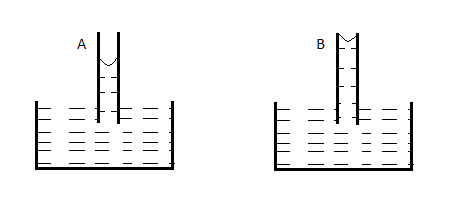
A capillary tube (A) is dipped in water. Another identical tube (B) is dipped in a soap-water solution. Which of the following shows the relative nature of the liquid columns in the two tubes?
A.
B.
C.
D.




Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: This question can be solved by using the formula for the capillary rise in a tube dipped in a liquid. When soap is added to water, the surface tension decreases. The nature of the surface of the liquid (concave or convex) depends whether the liquid is more adhesive or cohesive in nature. Water and soap solutions are very adhesive in nature.
Formula used:
The capillary rise height $h$ of a liquid of density $\rho $ and surface tension $T$ in a cylindrical tube of radius $r$ which s dipped in the liquid is given by
$h=\dfrac{2T\cos \theta }{r\rho g}$
where $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and $\theta $ is the angle of contact of the liquid with the surface of the capillary tube.
Complete step by step answer:
As explained in the hint, we can solve this problem by using the formula for the capillary rise height of a liquid in a capillary tube dipped in the liquid.
The capillary rise height $h$ of a liquid of density $\rho $ and surface tension $T$ in a cylindrical tube of radius $r$ which s dipped in the liquid is given by
$h=\dfrac{2T\cos \theta }{r\rho g}$ --(1)
where $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and $\theta $ is the angle of contact of the liquid with the surface of the capillary tube.
Now, soap solution has a much lower surface tension than water and approximately the same density. Hence from equation (1), we can see that the soap solution will rise to a lower height in the capillary tube than pure water will.
---(2)
Also, both soap solution and water are very adhesive in nature. What this means is that they have more affinity for molecules of a different surface rather than towards their own molecules. Hence, the surface of the liquid tries to curve upwards as it gets attracted by the surface of the capillary tube.
Hence, it forms a concave surface.
Therefore, both soap solution and pure water will form a concave surface inside the capillary tube. --(3)
The only figure that satisfies both conditions (2) and (3) is A).
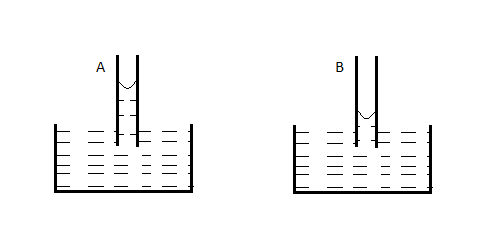
Hence, the correct option is A)
Note: Students often get confused and do not understand the effect that soap has on the surface tension of water. An easy way to remember that soap decreases the surface tension of water is to keep in mind that we add soap while cleaning clothes. This decreases the surface tension of the water and allows the dirt mixed with the soap to separate out easily from the clothes, since the surface tension of the water does not let the dirt escape from the clothes by breaking its surface.
Formula used:
The capillary rise height $h$ of a liquid of density $\rho $ and surface tension $T$ in a cylindrical tube of radius $r$ which s dipped in the liquid is given by
$h=\dfrac{2T\cos \theta }{r\rho g}$
where $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and $\theta $ is the angle of contact of the liquid with the surface of the capillary tube.
Complete step by step answer:
As explained in the hint, we can solve this problem by using the formula for the capillary rise height of a liquid in a capillary tube dipped in the liquid.
The capillary rise height $h$ of a liquid of density $\rho $ and surface tension $T$ in a cylindrical tube of radius $r$ which s dipped in the liquid is given by
$h=\dfrac{2T\cos \theta }{r\rho g}$ --(1)
where $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and $\theta $ is the angle of contact of the liquid with the surface of the capillary tube.
Now, soap solution has a much lower surface tension than water and approximately the same density. Hence from equation (1), we can see that the soap solution will rise to a lower height in the capillary tube than pure water will.
---(2)
Also, both soap solution and water are very adhesive in nature. What this means is that they have more affinity for molecules of a different surface rather than towards their own molecules. Hence, the surface of the liquid tries to curve upwards as it gets attracted by the surface of the capillary tube.
Hence, it forms a concave surface.
Therefore, both soap solution and pure water will form a concave surface inside the capillary tube. --(3)
The only figure that satisfies both conditions (2) and (3) is A).

Hence, the correct option is A)
Note: Students often get confused and do not understand the effect that soap has on the surface tension of water. An easy way to remember that soap decreases the surface tension of water is to keep in mind that we add soap while cleaning clothes. This decreases the surface tension of the water and allows the dirt mixed with the soap to separate out easily from the clothes, since the surface tension of the water does not let the dirt escape from the clothes by breaking its surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




