
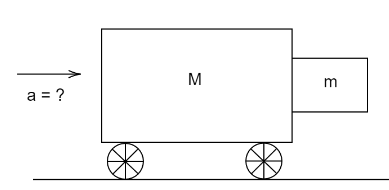
A cart of mass \[M\] has a block of mass \[m\] in contact with it as shown in the figure. The coefficient of friction between the block and the cart is \[\mu \] . What should be the minimum acceleration of the cart so that the block of mass \[m\] does not fall?

Answer
498k+ views
Hint: In this question, let us assume the cart of mass \[M\] moves with an acceleration \[a{\text{ m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\]. Thus, a pseudo force \[ma\] acts on the small block of mass \[m\] and it must be equal to the normal force between the blocks for horizontal equilibrium. The force of friction \[\mu N\] will act in the upward direction and must be equal to \[mg\] so that the block does not fall. From this condition, we can find out the minimum acceleration required.
Formula used:
\[F = ma\]
Where \[F\] is the total force, \[m\] is the mass of the system and \[a\] is the net acceleration of the system.
\[f = \mu N\]
Where, \[f\] is the limiting frictional force, \[\mu \] is the coefficient of friction and \[N\] is the normal force acting.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us assume the cart of mass \[M\] is moving with an acceleration of \[a{\text{ m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\]. It is in contact with a block of mass \[m\] such that the coefficient of friction between the cart and block is \[\mu \]. A normal force \[N\] acts on the block in the horizontal direction.As the cart is accelerating a pseudo force \[F = ma\] acts in the opposite direction of acceleration
For horizontal equilibrium,
\[N = F = ma\]
Frictional force \[f = \mu N\] acts in the upward direction. For block to be in equilibrium frictional force must balance its weight,
\[f \geqslant mg\]
\[ \Rightarrow \mu N \geqslant mg\]
Substituting \[N = F = ma\],
\[ \Rightarrow \mu ma \geqslant mg\]
\[ \therefore a \geqslant \dfrac{g}{\mu }\]
Thus, minimum acceleration so that the block does not fall must be \[\dfrac{g}{\mu }{\text{ m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\].
Note: Pseudo force is an imaginary force like frictional force and comes in effect when the frame of reference has started acceleration compared to a non-accelerating frame. It always acts in the opposite direction of the motion. The work done by a pseudo force is zero as it acts to appear on the body.
Formula used:
\[F = ma\]
Where \[F\] is the total force, \[m\] is the mass of the system and \[a\] is the net acceleration of the system.
\[f = \mu N\]
Where, \[f\] is the limiting frictional force, \[\mu \] is the coefficient of friction and \[N\] is the normal force acting.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us assume the cart of mass \[M\] is moving with an acceleration of \[a{\text{ m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\]. It is in contact with a block of mass \[m\] such that the coefficient of friction between the cart and block is \[\mu \]. A normal force \[N\] acts on the block in the horizontal direction.As the cart is accelerating a pseudo force \[F = ma\] acts in the opposite direction of acceleration
For horizontal equilibrium,
\[N = F = ma\]
Frictional force \[f = \mu N\] acts in the upward direction. For block to be in equilibrium frictional force must balance its weight,
\[f \geqslant mg\]
\[ \Rightarrow \mu N \geqslant mg\]
Substituting \[N = F = ma\],
\[ \Rightarrow \mu ma \geqslant mg\]
\[ \therefore a \geqslant \dfrac{g}{\mu }\]
Thus, minimum acceleration so that the block does not fall must be \[\dfrac{g}{\mu }{\text{ m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\].
Note: Pseudo force is an imaginary force like frictional force and comes in effect when the frame of reference has started acceleration compared to a non-accelerating frame. It always acts in the opposite direction of the motion. The work done by a pseudo force is zero as it acts to appear on the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




