
A cart of mass $m$ is placed on a smooth horizontal surface. A pendulum of mass $m$ is released from rest as shown in the figure. Then we can say that,
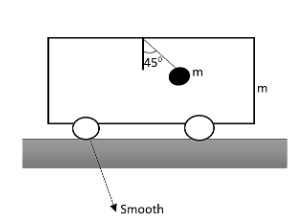
A. The velocity of cart just after release will be V to 0
B. The acceleration of the cart just after release will be $\dfrac{g}{3}$.
C. The velocity of the pendulum relative to the cart just after the release will be Vrel to 0
D. acceleration of the pendulum relative to the cart just after release will be $\dfrac{g}{3}$.

Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: First of all find the velocity of the body at the time of release. Then calculate the accelerations of the pendulum in two cases. And then compare them with the options given. These all may help us to solve this question.
Complete answer:
The whole system is released from rest, the velocity of the cart and pendulum will be zero just after the release from rest. Hence the options A and C tend to be correct. Let us draw the free body diagram of the pendulum.
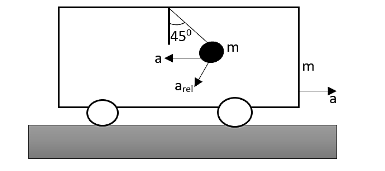
Let us assume that the acceleration of the cart is $a$ and \[{{a}_{rel}}\] be the relative acceleration of the pendulum. Therefore we can write that,
$mg\sin 45{}^\circ +ma\cos 45{}^\circ =m{{a}_{rel}}$……… (1)
Where $m$ be the mass of the pendulum as well as the cart, $g$ be the acceleration due to gravity, $45{}^\circ $ be the angle between the pendulum and the normal.
The tension on the string of the pendulum will be,
$T\cos 45{}^\circ =ma$…………. (2)
And also we can write that,
\[mg\cos 45{}^\circ =T+ma\sin 45{}^\circ \]
The value of mass multiplied with the acceleration will be given as,
\[ma=m\left( {{a}_{rel}}\cos 45{}^\circ +a \right)\]…….. (3)
Where \[{{a}_{rel}}\] be the relative acceleration.
From the above equations (1), (2) and (3), we can write that the acceleration will be,
$a=\dfrac{g}{3}$
And the relative acceleration will be,
${{a}_{rel}}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}g}{3}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A,B and C”.
Note:
Acceleration is defined as the rate of variation of the velocity. The relative acceleration refers to the acceleration felt by an observer in a frame of another object in another frame. It is the comparison of the accelerations of two bodies.
Complete answer:
The whole system is released from rest, the velocity of the cart and pendulum will be zero just after the release from rest. Hence the options A and C tend to be correct. Let us draw the free body diagram of the pendulum.

Let us assume that the acceleration of the cart is $a$ and \[{{a}_{rel}}\] be the relative acceleration of the pendulum. Therefore we can write that,
$mg\sin 45{}^\circ +ma\cos 45{}^\circ =m{{a}_{rel}}$……… (1)
Where $m$ be the mass of the pendulum as well as the cart, $g$ be the acceleration due to gravity, $45{}^\circ $ be the angle between the pendulum and the normal.
The tension on the string of the pendulum will be,
$T\cos 45{}^\circ =ma$…………. (2)
And also we can write that,
\[mg\cos 45{}^\circ =T+ma\sin 45{}^\circ \]
The value of mass multiplied with the acceleration will be given as,
\[ma=m\left( {{a}_{rel}}\cos 45{}^\circ +a \right)\]…….. (3)
Where \[{{a}_{rel}}\] be the relative acceleration.
From the above equations (1), (2) and (3), we can write that the acceleration will be,
$a=\dfrac{g}{3}$
And the relative acceleration will be,
${{a}_{rel}}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}g}{3}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A,B and C”.
Note:
Acceleration is defined as the rate of variation of the velocity. The relative acceleration refers to the acceleration felt by an observer in a frame of another object in another frame. It is the comparison of the accelerations of two bodies.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




