
A cartoon of an antibody is given, select the option with correct labelling which is indicating antigen-binding sites.
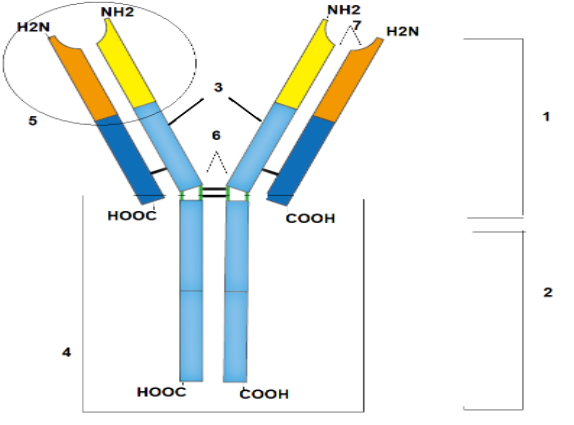
A) 5
B) 3
C) 6
D) 7

Answer
504.6k+ views
Hint: Antibodies are the biomolecules that are synthesised by the immune cells in response to antigens. Antigens are toxins that are produced by foreign particles or microorganisms. The antibodies are specific for antigen.
Complete answer:
Antibodies or immunoglobulins are the proteins that are produced by the immune system. They identify foreign pathogens like bacteria and viruses and neutralises them.
Structure of Antibody-
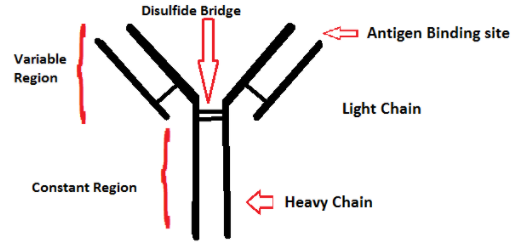
They are Y-shaped proteins that consist of 4 polypeptide chains that is two heavy chains and two light chains that are identical. The two chains heavy and light are held together by the disulphide bond so as to form a flexible Y shape. The chain is made up of variable and constant regions. These variable and constant domains are present within the light and heavy chain. The shape is maintained by the disulphide bond.
Let us discuss the structure in detail according to the figure given:
i) Light chain- It is the small polypeptide unit on the antibody.
ii) Heavy chain- It determines the class of antibody.
iii) Variable region of the light chain- It is composed of 110-130 amino acids and it gives specificity to the antigen-binding region.
iv) Constant region on a heavy chain- It decides the mechanism on how to destroy the antigen.
v) Antigen binding site- It is a small region that contains 15-20 amino acids and contains part of both heavy and light chain
vi) Disulphide bond- It is present between two chains.
vii) Variable region in the heavy chain.
Therefore the correct answer is option ‘A’.
Note: The major five classes of antibodies are IgM, IgA, IgE, IgG, IgD. This is classified in accordance to the constant region and the function. The main function of antibodies is to neutralise antigen and bring about immune response.
Complete answer:
Antibodies or immunoglobulins are the proteins that are produced by the immune system. They identify foreign pathogens like bacteria and viruses and neutralises them.
Structure of Antibody-
They are Y-shaped proteins that consist of 4 polypeptide chains that is two heavy chains and two light chains that are identical. The two chains heavy and light are held together by the disulphide bond so as to form a flexible Y shape. The chain is made up of variable and constant regions. These variable and constant domains are present within the light and heavy chain. The shape is maintained by the disulphide bond.
Let us discuss the structure in detail according to the figure given:
i) Light chain- It is the small polypeptide unit on the antibody.
ii) Heavy chain- It determines the class of antibody.
iii) Variable region of the light chain- It is composed of 110-130 amino acids and it gives specificity to the antigen-binding region.
iv) Constant region on a heavy chain- It decides the mechanism on how to destroy the antigen.
v) Antigen binding site- It is a small region that contains 15-20 amino acids and contains part of both heavy and light chain
vi) Disulphide bond- It is present between two chains.
vii) Variable region in the heavy chain.

Therefore the correct answer is option ‘A’.
Note: The major five classes of antibodies are IgM, IgA, IgE, IgG, IgD. This is classified in accordance to the constant region and the function. The main function of antibodies is to neutralise antigen and bring about immune response.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




