
What is a cell junction? Describe different types of cell junctions.
Answer
479.1k+ views
Hint: Cell junctions are the structures that are found in the plasma membrane of different cells. These are present in animal cells and help in linking and communication between adjacent cells. Some junctions also allow the transfer of small molecules across them.
Complete answer:
• Cell junctions are the connections formed between the plasma membranes of adjacent cells in animal tissues. They provide contact or adhesion between neighboring cells.
• Multiprotein complexes provide contact between adjacent cells or between cell and extracellular matrix make-up cell junctions.
• There are three major types of cell junctions as follows:
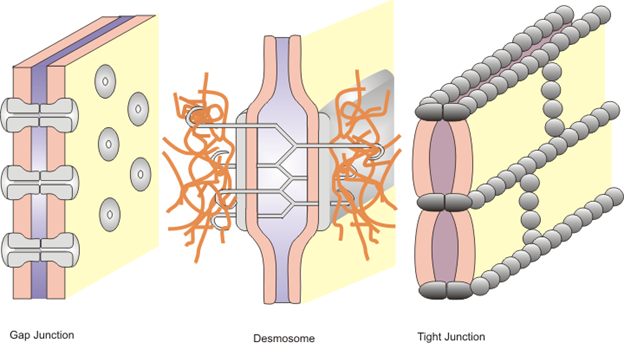
Tight Junctions: The outer layer of adjacent cells fuse and do not allow the materials to pass through. They act as a barrier. These are formed between epithelial cells.
Gap Junctions: These are intercellular channels formed between adjacent cells. They allow direct communication among cells. Small molecules, ions and electrical impulses move between cells through gap junctions. These can be found in nerve cells, hepatocytes etc.
Anchoring Junctions: These cell junctions are anchored to one another and attach to components of the extracellular matrix. They keep the cells together and provide structural cohesion to the tissues. Examples of adherens junctions are- desmosomes and hemidesmosomes.
• Types of cell junctions can be seen in the below image:
Note:
Following are the functions of cell junctions:
1. Tight junction seals together the epithelium.
2. Tight junctions act as a barrier to prevent leakage of substances.
3. Gap junctions help in moving small molecules across the cells and allow communication between cells.
4. Gap junctions allow transfer of electrical impulse in nerve cells.
5. Adherens junctions provide attachment of cell to cell or cell to extracellular matrix.
Complete answer:
• Cell junctions are the connections formed between the plasma membranes of adjacent cells in animal tissues. They provide contact or adhesion between neighboring cells.
• Multiprotein complexes provide contact between adjacent cells or between cell and extracellular matrix make-up cell junctions.
• There are three major types of cell junctions as follows:
Tight Junctions: The outer layer of adjacent cells fuse and do not allow the materials to pass through. They act as a barrier. These are formed between epithelial cells.
Gap Junctions: These are intercellular channels formed between adjacent cells. They allow direct communication among cells. Small molecules, ions and electrical impulses move between cells through gap junctions. These can be found in nerve cells, hepatocytes etc.
Anchoring Junctions: These cell junctions are anchored to one another and attach to components of the extracellular matrix. They keep the cells together and provide structural cohesion to the tissues. Examples of adherens junctions are- desmosomes and hemidesmosomes.
• Types of cell junctions can be seen in the below image:

Note:
Following are the functions of cell junctions:
1. Tight junction seals together the epithelium.
2. Tight junctions act as a barrier to prevent leakage of substances.
3. Gap junctions help in moving small molecules across the cells and allow communication between cells.
4. Gap junctions allow transfer of electrical impulse in nerve cells.
5. Adherens junctions provide attachment of cell to cell or cell to extracellular matrix.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




