
A cell that lacks chloroplast does not _______.
Answer
521.1k+ views
Hint: Chloroplasts are the cell organelles in plants that convert light energy into a stable energy using the photosynthetic process. Life sustains on the Earth by this process. The chloroplasts also provide for the synthesis of fatty acids, isoprenoids, membrane lipids, tetrapyrroles, starch, and hormones in plants.
Complete answer:
Chloroplasts play a crucial part within the process of photosynthesis in plants. The chloroplast absorbs the energy in sunlight and uses it to supply food which is made using the process of photosynthesis. Thus, if a cell lacks chloroplast, it cannot synthesise food and hence cannot liberarte oxygen, which is a product of photosynthesis.
Functions of Chloroplasts:
Food producers: A chloroplast may be a green organelle which some eukaryotes, like plants and algae, have in their cells. It's responsible for photosynthesis which is the method which produces the energy which the organism must survive. A chloroplast uses energy from light to form food from $CO_2$ and $H_2$O.
Green appearance: Chloroplasts are made from pigments which absorb sunlight, especially blue and red light and reflect green light. That's why they seem green in colour.
Slow down the atmospheric phenomenon: Human cells haven't any chloroplasts. Despite this, chloroplasts are essential to human life. These organelles in plants and algae lookout of the oxygen production on earth. They also absorb enormous amounts of $CO_2$ during the method of photosynthesis, removing it from the atmosphere and helping to limit the atmospheric phenomenon.
Note:
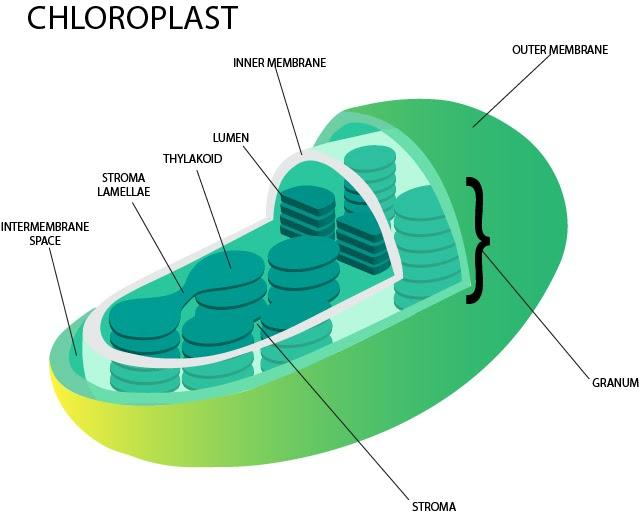
Chloroplasts are enclosed by an envelope of two membranes which encompass a complex membrane system, the thylakoids, including grana and lamellae. Additionally, starch grains, plastoglobules, stromules, eyespots, pyrenoids, etc. also are important structures of chloroplasts. It's widely accepted that chloroplasts evolved from a free-living photosynthetic cyanobacterium, which was engulfed by a eukaryotic cell.
Complete answer:
Chloroplasts play a crucial part within the process of photosynthesis in plants. The chloroplast absorbs the energy in sunlight and uses it to supply food which is made using the process of photosynthesis. Thus, if a cell lacks chloroplast, it cannot synthesise food and hence cannot liberarte oxygen, which is a product of photosynthesis.
Functions of Chloroplasts:
Food producers: A chloroplast may be a green organelle which some eukaryotes, like plants and algae, have in their cells. It's responsible for photosynthesis which is the method which produces the energy which the organism must survive. A chloroplast uses energy from light to form food from $CO_2$ and $H_2$O.
Green appearance: Chloroplasts are made from pigments which absorb sunlight, especially blue and red light and reflect green light. That's why they seem green in colour.
Slow down the atmospheric phenomenon: Human cells haven't any chloroplasts. Despite this, chloroplasts are essential to human life. These organelles in plants and algae lookout of the oxygen production on earth. They also absorb enormous amounts of $CO_2$ during the method of photosynthesis, removing it from the atmosphere and helping to limit the atmospheric phenomenon.

Note:
Chloroplasts are enclosed by an envelope of two membranes which encompass a complex membrane system, the thylakoids, including grana and lamellae. Additionally, starch grains, plastoglobules, stromules, eyespots, pyrenoids, etc. also are important structures of chloroplasts. It's widely accepted that chloroplasts evolved from a free-living photosynthetic cyanobacterium, which was engulfed by a eukaryotic cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




