
A cilium beats
(a) Asymmetrically by the sweeping action
(b) Symmetrically by the sweeping action
(c) Symmetrically by undulatory action
(d) Asymmetrically by undulatory action
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: They are motile and designed either to move the cell itself or to move the substances over or to round the cell. The first purpose of cilia in mammalian cells is to move the fluid, mucous, or cells over their surface.
Complete step by step answer:
Cilia can be defined as the tiny hair-like projections on the surface of the cell.
These hair-like projections help in sweeping mucus, trapped dust, and other bacterias in the respiratory tracts.
It beats asymmetrically by the sweeping action.
The asymmetrical beating pattern consists of two strokes- effective stroke and recovery stroke.
In an effective stroke, the cilia are straight and generate flow in the same direction as its motion.
Whereas, in recovery stroke, the cilia bend parallel to the surface and creates a relatively weaker backward flow.
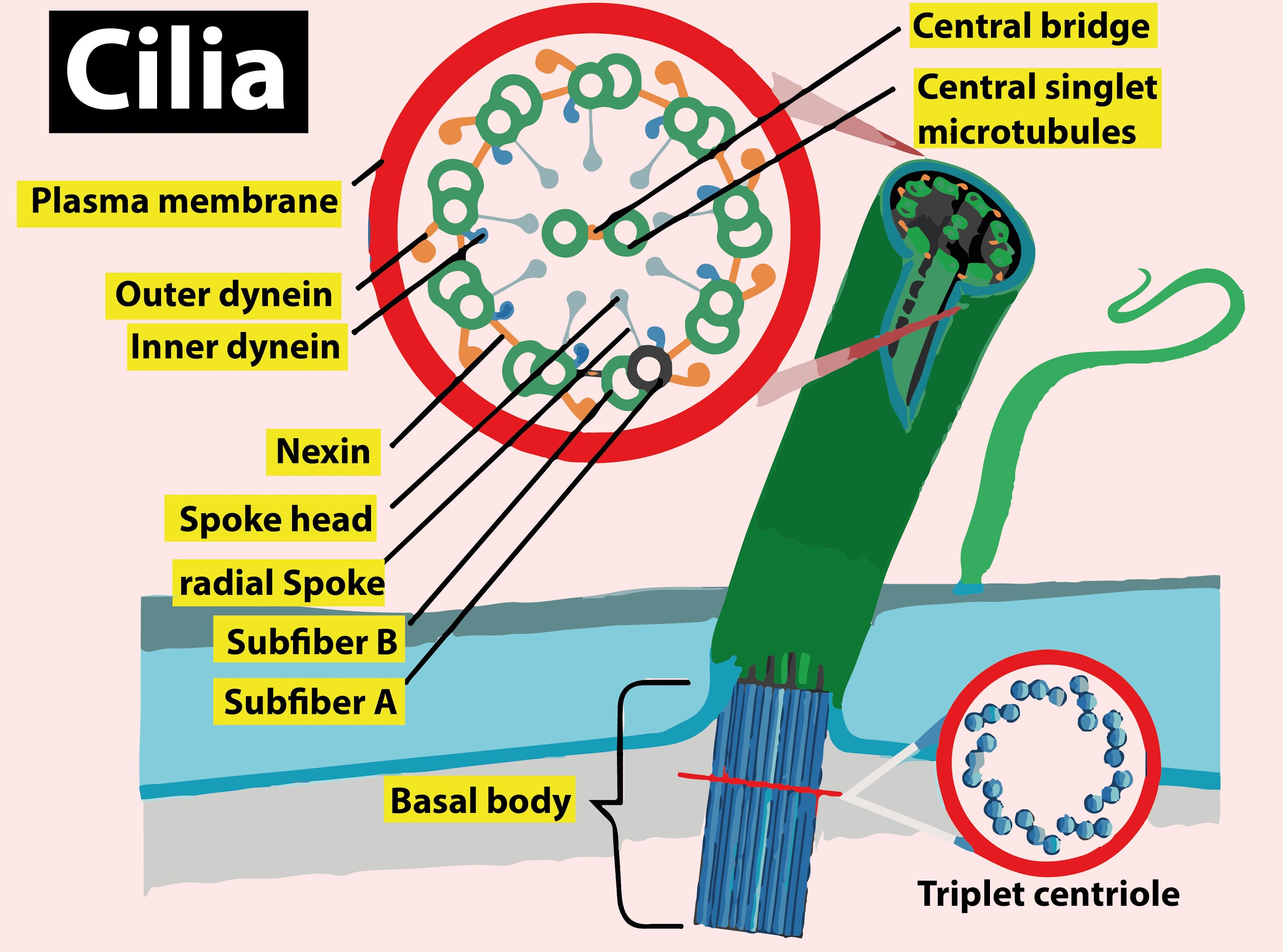
So, the correct answer is, ‘Asymmetrically by the sweeping action.’
Additional Information: Cilium Function: Cilia play an important role in locomotion. This will include the movement of the cell itself, or of other substances and objects past the cell. In some organisms known as ciliates, cilia are responsible for the movement of the organism as a whole. For example, within the unicellular protist Paramecium, cilia cover the surface of the organism and are liable for movement also as feeding. In addition to covering the surface of the organism, cilia also line the oral groove, moving food into the organism’s “mouth”.
Cilia can help to get rid of contaminants from organs or tissue by helping to move fluids over the cell. The lining of the nasopharynx and therefore the trachea are covered in cilia. These ciliated epithelial cells remove the mucus, bacteria, and other debris from the lungs. Another example is that the lining of the fallopian tubes. The cilia here are responsible for helping in fertilization by the movement of the egg towards the uterus. Kinocilia is a specialized type of cilia found on the apical ends of vertebrate hair cells. Along with stereocilia, non-motile collections of actin filaments associated with cilia, they're involved in hearing and balance (mechanoreception).
Note: Beyond the role they play in internal cell movement, microtubules also work together with cilia to form larger structures that work on the outside of the cells. They can combine in very specific arrangements for the formation of cilia and flagella. They flap back and forth for helping the cell in movement.
Complete step by step answer:
Cilia can be defined as the tiny hair-like projections on the surface of the cell.
These hair-like projections help in sweeping mucus, trapped dust, and other bacterias in the respiratory tracts.
It beats asymmetrically by the sweeping action.
The asymmetrical beating pattern consists of two strokes- effective stroke and recovery stroke.
In an effective stroke, the cilia are straight and generate flow in the same direction as its motion.
Whereas, in recovery stroke, the cilia bend parallel to the surface and creates a relatively weaker backward flow.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Asymmetrically by the sweeping action.’
Additional Information: Cilium Function: Cilia play an important role in locomotion. This will include the movement of the cell itself, or of other substances and objects past the cell. In some organisms known as ciliates, cilia are responsible for the movement of the organism as a whole. For example, within the unicellular protist Paramecium, cilia cover the surface of the organism and are liable for movement also as feeding. In addition to covering the surface of the organism, cilia also line the oral groove, moving food into the organism’s “mouth”.
Cilia can help to get rid of contaminants from organs or tissue by helping to move fluids over the cell. The lining of the nasopharynx and therefore the trachea are covered in cilia. These ciliated epithelial cells remove the mucus, bacteria, and other debris from the lungs. Another example is that the lining of the fallopian tubes. The cilia here are responsible for helping in fertilization by the movement of the egg towards the uterus. Kinocilia is a specialized type of cilia found on the apical ends of vertebrate hair cells. Along with stereocilia, non-motile collections of actin filaments associated with cilia, they're involved in hearing and balance (mechanoreception).
Note: Beyond the role they play in internal cell movement, microtubules also work together with cilia to form larger structures that work on the outside of the cells. They can combine in very specific arrangements for the formation of cilia and flagella. They flap back and forth for helping the cell in movement.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




