
A compound can be divided into two equal halves and contains even $n$ asymmetric carbon atoms .The number of stereoisomers is:
A. ${2^n}$
B. $2(n + 1)$
C. ${2^{(\dfrac{n}{2} - 1)}}$
D. ${2^{n - 1}} + {2^{(\dfrac{n}{2} - 1)}}$
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: A chiral carbon shows optical isomerism by changing the spatial arrangements of the functional groups which are attached to the central carbon atom.
meso isomer is a non-optically active member of a set of stereoisomers, at least two of which are optically active.
The stereoisomers include meso isomers as well as optical isomers, so in order to calculate the number of stereoisomers, the addition of both isomers is required.
Complete step by step answer:
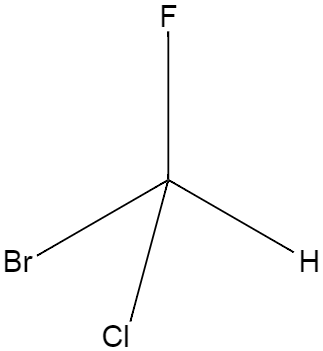
A chiral carbon is a type of carbon which has four different functional groups attached to it, for instance a carbon with which a hydrogen along with three different halogens are attached. A diagram is shown below.
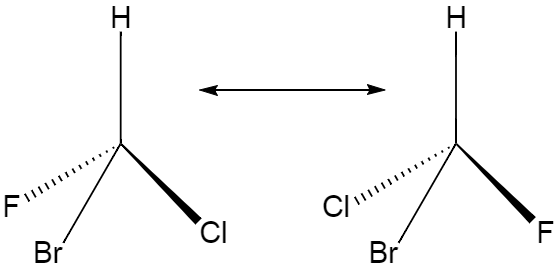
Optical isomerism is a type of isomerism where both the isomeric structures have same molecules and connectivity between atoms but different spatial arrangements. Given below is an example of optical isomerism.
For a chiral carbon atom optical isomerism is determined by a compound division suppose if a compound is not divided then optical isomerism shows ${{2}^{n}}$ and meso isomers are zero
Now I am explaining what are known as meso isomers.
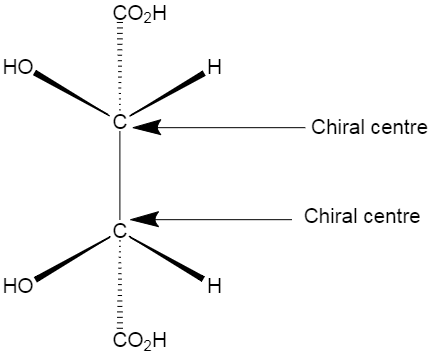
meso isomer is a non-optically active member of a set of stereoisomers, at least two of which are optically active. Example of a meso isomer is shown below.
Optical isomers are $2$ compounds which contain the same number and kinds of atoms, bonds are different spatial arrangements of the atoms, but which have non-superimposable mirror images.
Now if a compound is divided then we should check whether they are even or odd.
If they are even then the optical isomer are ${{2}^{n-1}}$ and meso isomers are ${{2}^{(\dfrac{n}{2}-1)}}$.
If they are odd then optical isomers are ${{2}^{n-1}}$ and meso isomers are ${{2}^{(\dfrac{n-1}{2})}}$.
So according to question the compound can be divided into two equal halves so $n$is even according to even it has both optical isomer ${{2}^{n-1}}$ and meso isomers are ${{2}^{(\dfrac{n}{2}-1)}}$
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Additional information:
One stereoisomer, called the cis stereoisomer, has both of the double-bond hydrogens on the identical side of the covalent bond, while the other stereoisomer, called the trans stereoisomer, has the $2$ hydrogens on opposite sides of the covalent bond
Note: The chirality of an organic molecule is responsible for the optical isomerism experienced by them, in other words, with each change in spatial arrangement of the molecule, a new isomer is established. The total number of stereoisomers of a compound is the sum of optical isomers and the meso isomers created by the compound.
meso isomer is a non-optically active member of a set of stereoisomers, at least two of which are optically active.
The stereoisomers include meso isomers as well as optical isomers, so in order to calculate the number of stereoisomers, the addition of both isomers is required.
Complete step by step answer:
A chiral carbon is a type of carbon which has four different functional groups attached to it, for instance a carbon with which a hydrogen along with three different halogens are attached. A diagram is shown below.

Optical isomerism is a type of isomerism where both the isomeric structures have same molecules and connectivity between atoms but different spatial arrangements. Given below is an example of optical isomerism.

For a chiral carbon atom optical isomerism is determined by a compound division suppose if a compound is not divided then optical isomerism shows ${{2}^{n}}$ and meso isomers are zero
Now I am explaining what are known as meso isomers.
meso isomer is a non-optically active member of a set of stereoisomers, at least two of which are optically active. Example of a meso isomer is shown below.

Optical isomers are $2$ compounds which contain the same number and kinds of atoms, bonds are different spatial arrangements of the atoms, but which have non-superimposable mirror images.
Now if a compound is divided then we should check whether they are even or odd.
If they are even then the optical isomer are ${{2}^{n-1}}$ and meso isomers are ${{2}^{(\dfrac{n}{2}-1)}}$.
If they are odd then optical isomers are ${{2}^{n-1}}$ and meso isomers are ${{2}^{(\dfrac{n-1}{2})}}$.
So according to question the compound can be divided into two equal halves so $n$is even according to even it has both optical isomer ${{2}^{n-1}}$ and meso isomers are ${{2}^{(\dfrac{n}{2}-1)}}$
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Additional information:
One stereoisomer, called the cis stereoisomer, has both of the double-bond hydrogens on the identical side of the covalent bond, while the other stereoisomer, called the trans stereoisomer, has the $2$ hydrogens on opposite sides of the covalent bond
Note: The chirality of an organic molecule is responsible for the optical isomerism experienced by them, in other words, with each change in spatial arrangement of the molecule, a new isomer is established. The total number of stereoisomers of a compound is the sum of optical isomers and the meso isomers created by the compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




