
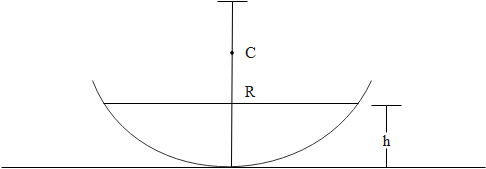
A concave mirror of radius $R$ is kept on a horizontal table. Water (refractive index $=\mu$ ) is poured into it up to a height $h$. Where should an object be placed so that its image is formed on itself?

Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: We know that concave mirrors can produce both real and virtual images; they can be upright (if virtual) or inverted (if real); they can be behind the mirror (if virtual) or in front of the mirror (if real); they can also be enlarged, reduced, or the same size as object. A concave mirror, or converging mirror, has a reflecting surface that is recessed inward (away from the incident light). Concave mirrors reflect light inward to one focal point. They are used to focus light.
Complete step by step answer
The diagram for this question is given as:
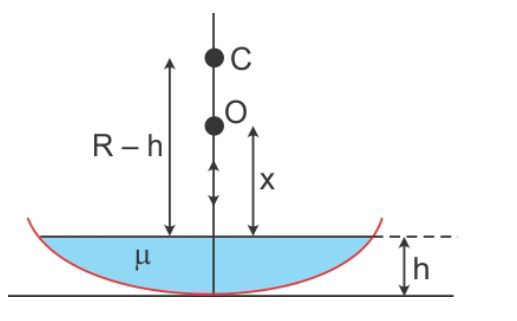
The radius of curvature of the concave mirror is R. Water is poured up to height h.
Now, if the object is placed at the centre of curvature (C) of the mirror, then the image is formed on itself, that is on $\mathrm{C}$.
But, since water of refractive index $\mu$ is poured in it, the object should be placed closer to the surface of water than $\mathrm{C}$.
That is, the object should be placed at O. Let $x$ be the distance from the surface of water.
Now, we have
Refractive index $\mu=\dfrac{\text { Apparent depth }}{\text { Real depth }}$ $\therefore \mu=\dfrac{R-h}{x}$
$\therefore x=\dfrac{R-h}{\mu}$
Note: We know that convex Mirror is a curved mirror where the reflective surface bulges out towards the light source. This bulging out surface reflects light outwards and is not used to focus light. The image looks smaller than the object from the distance but gets larger as the object gets closer to the mirror. The upright images produced by concave mirrors (when the object is in front of F) are magnified images. And the upright images produced by plane mirrors have the same size as the object.
Complete step by step answer
The diagram for this question is given as:

The radius of curvature of the concave mirror is R. Water is poured up to height h.
Now, if the object is placed at the centre of curvature (C) of the mirror, then the image is formed on itself, that is on $\mathrm{C}$.
But, since water of refractive index $\mu$ is poured in it, the object should be placed closer to the surface of water than $\mathrm{C}$.
That is, the object should be placed at O. Let $x$ be the distance from the surface of water.
Now, we have
Refractive index $\mu=\dfrac{\text { Apparent depth }}{\text { Real depth }}$ $\therefore \mu=\dfrac{R-h}{x}$
$\therefore x=\dfrac{R-h}{\mu}$
Note: We know that convex Mirror is a curved mirror where the reflective surface bulges out towards the light source. This bulging out surface reflects light outwards and is not used to focus light. The image looks smaller than the object from the distance but gets larger as the object gets closer to the mirror. The upright images produced by concave mirrors (when the object is in front of F) are magnified images. And the upright images produced by plane mirrors have the same size as the object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




