
A condition where an individual heterozygous for two pairs of linked genes (AaBb) possesses the two dominant genes on one homologous chromosome pair and two recessives on the other, is said to be
A) Cis-arrangement
B) Trans-arrangement
C) Partly cis partly trans
D) More than one option is correct
Answer
513k+ views
Hint: When genes are present close together on the same chromosome, they are known as linked genes. This means that the alleles that are already together on one chromosome will be inherited as a unit more frequently.
Complete answer:
Sometimes, two traits can be seen together and are inherited together. These genes are present in close proximity to each other. This is known as linkage. For example, in the case of corn, the traits for colour and fullness of the kernel are usually carried on one gene, and the recessive alleles for these traits are carried on another gene.
When both the dominant or recessive alleles for two traits are carried on the same chromosome, it is known as cis arrangement as shown in the figure below.
When recessive and dominant alleles for the different traits are carried on the same chromosome, then it is known as trans arrangement as shown in the figure below.
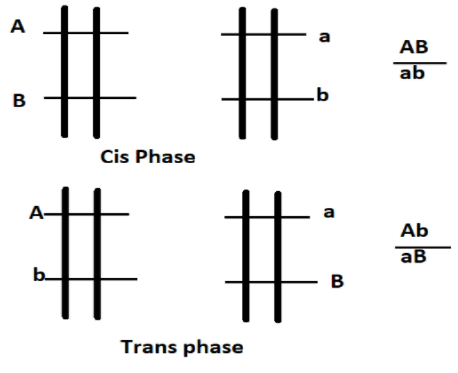
In case the dominant alleles are partially present on the same chromosomes and partially on different chromosomes, then it is known as partly cis partly trans arrangement. According to the question an individual has heterozygous for two pairs of linked genes (AaBb) possesses the two dominant genes on one homologous chromosome pair and two recessive genes on the other.
Additional Information: Genetic linkage is the tendency of DNA sequences that are close to each other on a chromosome to be inherited together during the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction. Two genetic markers which are close to each other are highly unlikely to be separated into different chromatids during the chromosomal crossover.
Thus the correct answer is option ‘C’.
Note: When the genes are on different chromosomes, or far apart on the same chromosomes, they group differently. This means that when the genes go into gametes, the allele received for one gene does not affect the allele received for the other gene. In the case of double heterozygous organisms (AaBb), this causes the formation of all the four possible types of gametes with equal or 25% frequency.
Complete answer:
Sometimes, two traits can be seen together and are inherited together. These genes are present in close proximity to each other. This is known as linkage. For example, in the case of corn, the traits for colour and fullness of the kernel are usually carried on one gene, and the recessive alleles for these traits are carried on another gene.
When both the dominant or recessive alleles for two traits are carried on the same chromosome, it is known as cis arrangement as shown in the figure below.
When recessive and dominant alleles for the different traits are carried on the same chromosome, then it is known as trans arrangement as shown in the figure below.

In case the dominant alleles are partially present on the same chromosomes and partially on different chromosomes, then it is known as partly cis partly trans arrangement. According to the question an individual has heterozygous for two pairs of linked genes (AaBb) possesses the two dominant genes on one homologous chromosome pair and two recessive genes on the other.
Additional Information: Genetic linkage is the tendency of DNA sequences that are close to each other on a chromosome to be inherited together during the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction. Two genetic markers which are close to each other are highly unlikely to be separated into different chromatids during the chromosomal crossover.
Thus the correct answer is option ‘C’.
Note: When the genes are on different chromosomes, or far apart on the same chromosomes, they group differently. This means that when the genes go into gametes, the allele received for one gene does not affect the allele received for the other gene. In the case of double heterozygous organisms (AaBb), this causes the formation of all the four possible types of gametes with equal or 25% frequency.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




