
A copper rod of mass \[m\] slides under gravity on two smooth parallel rails, with separation \[l\] and set at an angle of \[\theta \] with the horizontal. At the bottom, rails are joined by a resistance \[R\]. There is a uniform magnetic field \[B\] normal to the plane of the rails, as shown in the figure. The terminal speed of the copper rod is :
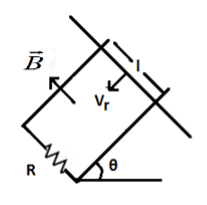
\[\begin{align}
& A)\dfrac{mgR\cos \theta }{{{B}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}} \\
& B)\dfrac{mgR\sin \theta }{{{B}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}} \\
& C)\dfrac{mgR\tan \theta }{{{B}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}} \\
& D)\dfrac{mgR\cot \theta }{{{B}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: Here, the copper rod is sliding under gravity. Due to the applied magnetic field, a force will be acting on the rod, and this force is proportional to the current in through the rod, its length, the applied magnetic field and the angle between magnetic field and copper rod. And a motional emf is also induced in the rod, which is proportional to the velocity of the conductor.
Formula used:
\[{{F}_{B}}=ilB\sin \theta \]
\[I=\dfrac{V}{R}\]
\[e=Bl{{v}_{T}}\]
Complete answer:
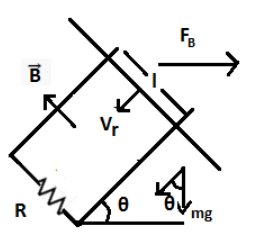
We have,
\[{{F}_{B}}=ilB\sin \theta \]
Where,
\[i\] is the current
\[l\] is the length of the conductor
\[B\] is the magnetic field
\[\theta \] is the angle between the rod and the magnetic field.
Here, magnetic field is acting perpendicular on the rod, \[\theta =90\]
Then,
Force,\[{{F}_{B}}=ilB\]
The force due to gravity is also acting downwards. Then, equating the horizontal component of forces at equilibrium,
\[mg\sin \theta -ilB=0\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta =ilB\] ---------- 1
We know that,
\[I=\dfrac{V}{R}\] -------------- 2
Where,
\[V\] is potential
\[R\] is resistance
Here, due the magnetic field, an emf is induced in the rod, then, potential will be equal to the induced emf.
\[V=e\]
Then, equation 2 becomes,
\[I=\dfrac{e}{R}\]
Substitute the above equation, in 1, we get,
\[mg\sin \theta =\dfrac{e}{R}lB\] ----------- 3
Since, the rod reached its terminal velocity, motional emf will be,
\[e=Bl{{v}_{T}}\]
Where,
\[{{v}_{T}}\]is the terminal velocity
Then,
Equation 3 becomes,
\[mg\sin \theta =\dfrac{Bl{{v}_{T}}}{R}\left( Bl \right)\Rightarrow {{v}_{T}}=\dfrac{\left( mg\sin \theta \right)R}{{{B}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}}\]
Therefore, the answer is option B.
Note:
Terminal velocity is a steady speed achieved by an object freely falling through a liquid or gas. An object released from rest will increase its speed until it attains the terminal velocity. When an object is forced to move faster than its terminal velocity, it will slow down to this constant velocity upon releasing.
Formula used:
\[{{F}_{B}}=ilB\sin \theta \]
\[I=\dfrac{V}{R}\]
\[e=Bl{{v}_{T}}\]
Complete answer:

We have,
\[{{F}_{B}}=ilB\sin \theta \]
Where,
\[i\] is the current
\[l\] is the length of the conductor
\[B\] is the magnetic field
\[\theta \] is the angle between the rod and the magnetic field.
Here, magnetic field is acting perpendicular on the rod, \[\theta =90\]
Then,
Force,\[{{F}_{B}}=ilB\]
The force due to gravity is also acting downwards. Then, equating the horizontal component of forces at equilibrium,
\[mg\sin \theta -ilB=0\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta =ilB\] ---------- 1
We know that,
\[I=\dfrac{V}{R}\] -------------- 2
Where,
\[V\] is potential
\[R\] is resistance
Here, due the magnetic field, an emf is induced in the rod, then, potential will be equal to the induced emf.
\[V=e\]
Then, equation 2 becomes,
\[I=\dfrac{e}{R}\]
Substitute the above equation, in 1, we get,
\[mg\sin \theta =\dfrac{e}{R}lB\] ----------- 3
Since, the rod reached its terminal velocity, motional emf will be,
\[e=Bl{{v}_{T}}\]
Where,
\[{{v}_{T}}\]is the terminal velocity
Then,
Equation 3 becomes,
\[mg\sin \theta =\dfrac{Bl{{v}_{T}}}{R}\left( Bl \right)\Rightarrow {{v}_{T}}=\dfrac{\left( mg\sin \theta \right)R}{{{B}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}}\]
Therefore, the answer is option B.
Note:
Terminal velocity is a steady speed achieved by an object freely falling through a liquid or gas. An object released from rest will increase its speed until it attains the terminal velocity. When an object is forced to move faster than its terminal velocity, it will slow down to this constant velocity upon releasing.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




