
A copper wire, 3mm in diameter, is wound about a cylinder whose length is 12cm and diameter 10cm, so as to cover the curved surface of the cylinder. Find the length and mass of the wire, assuming the density of copper to be \[8.88g/c{m^3}\]. ( Use \[\pi = 3.14\]).
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint :- Here first of all we had to change all the values in similar units. And after that we have to find the number of rounds to cover the full length of the cylinder. The formulas of curved surface area of cylinder = \[2\pi r\] and Density = \[\dfrac{{{\text{mass}}}}{{{\text{volume}}}}\] can also be used in this question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us show you the diagram which helps us to understand the question much more.
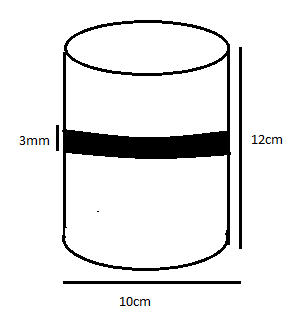
As we know that diameter of wire = 3mm 0r 0.3 cm
Therefore one round of wire will cover 0.3cm height of cylinder and total height of cylinder is 12cm.
So, total number of rounds in which wire will cover the total height is equal to
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\dfrac{{{\text{height of cylinder}}}}{{{\text{diameter of wire}}}} = \dfrac{{12}}{{0.3}} = 40\]rounds
Now as we know that length of wire to complete one round must be equal to the circumference or curved surface area of cylinder which is equal to
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[2\pi r = 10\pi \] ( radius =\[\dfrac{{{\text{diameter}}}}{2} = 5\])
Now the total length of wire that is required to cover the whole cylinder must be equal to the product of total number of rounds and length of wire to complete one round.
So, length of wire = \[40 \times 10\pi = 400\pi \]
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[1256\]cm ( putting \[\pi = 3.14\])
As we know that the density of copper is \[8.88g/c{m^3}\].
And Density = \[\dfrac{{{\text{mass}}}}{{{\text{volume}}}}\] , we had to find the mass here and for that we must know the volume of copper wire.
As we know that here volume of wire is equal to product of total area of wire and the length of wire required to cover the whole cylinder.
So, volume = \[\pi {r^2} \times length\] ( \[r = \dfrac{d}{2} = \dfrac{{0.3}}{2}\]cm )
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[\pi \times {\left( {\dfrac{{0.3}}{2}} \right)^2} \times 1256\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[3.14 \times \dfrac{{0.09}}{4} \times 1256 = 88.73c{m^3}\]
Now from the density formula we come to know that density * volume = mass
So, putting the values of density and volume will give us the mass.
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[{\text{8}}{{.88 \times 88}}{\text{.73 = 787}}{\text{.83gm}}\]
So, the length of wire = 1256cm
And mass of wire = \[{\text{787}}{\text{.83gm}}\]( approx. )
Note :- Whenever we come up with this type of problem we should always find the length of wire for one round and then we will produce it with the total number of rounds so this will make the question a bit easy. And we should also know that the area of wire must be \[\pi {r^2}\]because the wire is so thin to find its area so we had to assume the area of wire with the formula of area of circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us show you the diagram which helps us to understand the question much more.

As we know that diameter of wire = 3mm 0r 0.3 cm
Therefore one round of wire will cover 0.3cm height of cylinder and total height of cylinder is 12cm.
So, total number of rounds in which wire will cover the total height is equal to
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[\dfrac{{{\text{height of cylinder}}}}{{{\text{diameter of wire}}}} = \dfrac{{12}}{{0.3}} = 40\]rounds
Now as we know that length of wire to complete one round must be equal to the circumference or curved surface area of cylinder which is equal to
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[2\pi r = 10\pi \] ( radius =\[\dfrac{{{\text{diameter}}}}{2} = 5\])
Now the total length of wire that is required to cover the whole cylinder must be equal to the product of total number of rounds and length of wire to complete one round.
So, length of wire = \[40 \times 10\pi = 400\pi \]
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[1256\]cm ( putting \[\pi = 3.14\])
As we know that the density of copper is \[8.88g/c{m^3}\].
And Density = \[\dfrac{{{\text{mass}}}}{{{\text{volume}}}}\] , we had to find the mass here and for that we must know the volume of copper wire.
As we know that here volume of wire is equal to product of total area of wire and the length of wire required to cover the whole cylinder.
So, volume = \[\pi {r^2} \times length\] ( \[r = \dfrac{d}{2} = \dfrac{{0.3}}{2}\]cm )
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[\pi \times {\left( {\dfrac{{0.3}}{2}} \right)^2} \times 1256\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[3.14 \times \dfrac{{0.09}}{4} \times 1256 = 88.73c{m^3}\]
Now from the density formula we come to know that density * volume = mass
So, putting the values of density and volume will give us the mass.
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[{\text{8}}{{.88 \times 88}}{\text{.73 = 787}}{\text{.83gm}}\]
So, the length of wire = 1256cm
And mass of wire = \[{\text{787}}{\text{.83gm}}\]( approx. )
Note :- Whenever we come up with this type of problem we should always find the length of wire for one round and then we will produce it with the total number of rounds so this will make the question a bit easy. And we should also know that the area of wire must be \[\pi {r^2}\]because the wire is so thin to find its area so we had to assume the area of wire with the formula of area of circle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





