
A cubical block of side 7cm is surmounted by hemisphere. What is the greatest diameter the hemisphere can have? Find the total surface area (TSA) of the solid.
Answer
614.7k+ views
- Hint: to solve this question we will use some formulae which are given as, the formula for TSA of a cube of side a is given by \[6{{a}^{2}}\], the formula for the base of the hemisphere is given by the area of circle of radius r, which is \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\], and the formula for CSA of hemisphere is given by \[2\pi {{r}^{2}}\], where r is the radius of the hemisphere.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given that the cubical block of side 7cm is surmounted by hemisphere.
We have to find the greatest diameter the hemisphere can have. And the total surface area of the solid.
The figure which illustrates the given situation of the question is given as below.
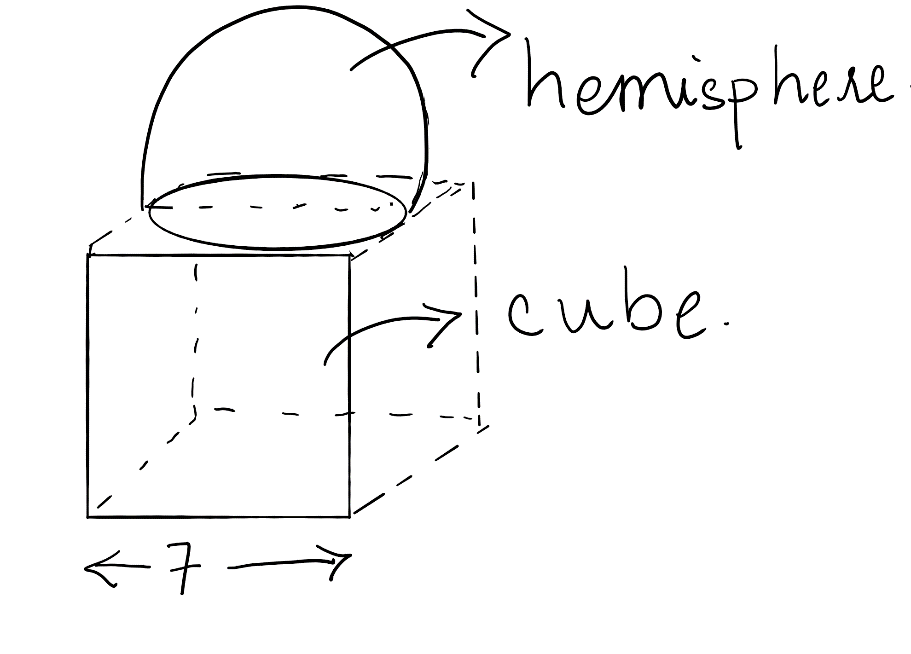
Therefore, we see as the hemisphere is mounted on the cubical block. So, observing the figure we get that the diameter of the hemisphere is equal to the side of the cube, which is 7cm.
So, we get that the diameter of the hemisphere is 7cm.
Then the radius r would be \[\dfrac{7}{2}=3.5cm\].
Now we have to determine the total surface area of the generated solid.
Observing the figure, we see that the base of the hemisphere is covered inside one side of the cube. Therefore, we need to subtract the area of base of the hemisphere.
So, the TSA of the solid = TSA of cube - Area of base of hemisphere + CSA of hemisphere……(i)
The formula for TSA of a cube of side a is given by \[6{{a}^{2}}\].
The formula for the base of the hemisphere is given by the area of the circle of radius r, which is \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\].
Again, the formula for CSA of the hemisphere is given by \[2\pi {{r}^{2}}\], where r is the radius of the hemisphere.
Substituting the above stated formulae in equation (i) and substituting the value of side of the cube as a = 7cm and the radius of the hemisphere as r = 3.5cm, we get the TSA of generated solid as,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow TSA=6\times 7{}^\text{2}-~\pi \times \left( 3.5 \right){}^\text{2}+\text{ }2\times \pi \times \left( 3.5 \right){}^\text{2} \\
& \Rightarrow TSA=6\times 7{}^\text{2}+\pi \times \left( 3.5 \right){}^\text{2} \\
& \Rightarrow TSA\text{ }=\text{ }332.\text{ }465\text{ }cm{}^\text{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, we got the Total surface area (TSA) of the generated solid is \[332.\text{ }465\text{ }cm{}^\text{2}\].
Note: The possibility of error in these types of questions can be at the point where you have to calculate the TSA of the generated solid. Always keep in mind that because the base of the hemisphere is covered inside one side of the cube, therefore we need to subtract the area of the base of the hemisphere to obtain the result.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given that the cubical block of side 7cm is surmounted by hemisphere.
We have to find the greatest diameter the hemisphere can have. And the total surface area of the solid.
The figure which illustrates the given situation of the question is given as below.

Therefore, we see as the hemisphere is mounted on the cubical block. So, observing the figure we get that the diameter of the hemisphere is equal to the side of the cube, which is 7cm.
So, we get that the diameter of the hemisphere is 7cm.
Then the radius r would be \[\dfrac{7}{2}=3.5cm\].
Now we have to determine the total surface area of the generated solid.
Observing the figure, we see that the base of the hemisphere is covered inside one side of the cube. Therefore, we need to subtract the area of base of the hemisphere.
So, the TSA of the solid = TSA of cube - Area of base of hemisphere + CSA of hemisphere……(i)
The formula for TSA of a cube of side a is given by \[6{{a}^{2}}\].
The formula for the base of the hemisphere is given by the area of the circle of radius r, which is \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\].
Again, the formula for CSA of the hemisphere is given by \[2\pi {{r}^{2}}\], where r is the radius of the hemisphere.
Substituting the above stated formulae in equation (i) and substituting the value of side of the cube as a = 7cm and the radius of the hemisphere as r = 3.5cm, we get the TSA of generated solid as,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow TSA=6\times 7{}^\text{2}-~\pi \times \left( 3.5 \right){}^\text{2}+\text{ }2\times \pi \times \left( 3.5 \right){}^\text{2} \\
& \Rightarrow TSA=6\times 7{}^\text{2}+\pi \times \left( 3.5 \right){}^\text{2} \\
& \Rightarrow TSA\text{ }=\text{ }332.\text{ }465\text{ }cm{}^\text{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, we got the Total surface area (TSA) of the generated solid is \[332.\text{ }465\text{ }cm{}^\text{2}\].
Note: The possibility of error in these types of questions can be at the point where you have to calculate the TSA of the generated solid. Always keep in mind that because the base of the hemisphere is covered inside one side of the cube, therefore we need to subtract the area of the base of the hemisphere to obtain the result.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




