
A diagram of T.S. of the dicot root is given. Select the option which correctly lab A, B, C, D and E.
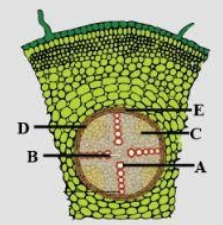
A) A-Protoxylem. B-Metaxylem. C-Phloem. D-Pericycle. E-Endodermis
B) A-Metaxylem. B-Protoxylem-Phloem D-Pericycle. E-Endodermis
C) A-Protoxylem. B-Metaxylem. C-Phloem. D-Endodermis. E-Pericycle
D) A-Metaxylem B-Protoxylem. C-Phloem. D-Endoderm is, E-Pericycle

Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: The internal organization of a dicot root is simple compared to monocot .The distinguished feature of dicot root is that pith is absent in older roots. Typically, it can be divided into three regions. epidermis, cortex and stele.
Complete answer:
Option A: A-Protoxylem. B-Metaxylem. C-Phloem. D-Pericycle. E-Endodermis – Protoxylem is the first-formed xylem that is developed from the procambium. Procambium is a meristematic tissue located next to protoderm. Protoxylem is usually narrow with annular, spiral, or scalariform wall thickenings on the secondary cell wall.
Option B: A-Metaxylem. B-Protoxylem-Phloem D-Pericycle. E-Endodermis. Protoxylem differentiates into metaxylem, which is the later developed element. Protoxylem cells have broader tracheids and vessels with pitted or reticulate walls thickening in the secondary cell walls. Thickenings are formed due to the deposition of lignin.
Option C: A-Protoxylem. B-Metaxylem. C-Phloem. D-Endodermis. E-Pericycle. The endodermis is the central, innermost layer of cortex in dicot roots. Endodermis is characterized by the presence of casparian thickenings. These thickenings are formed by the deposition of suberin and lignin in the secondary walls.
Option D: A-Metaxylem B-Protoxylem. C-Phloem. D-Endoderm is, E-Pericycle. The pericycle is the outermost component of the stele of plants, and it is a cylinder of parenchyma or sclerenchyma cells that lies just inside the endodermis. Pericycle is usually filled with simple parenchyma cells or sometimes sclerenchyma cells.
So the correct answer is Option B.
Note:
In dicot roots, the vascular structures are not numerous and scattered like monocots but they are located in the middle of the root. The xylem is concentrated in the center of the dicot root, with phloem bundles arranged around it and divided by vascular cambium. Vascular cambium is a meristematic tissue which is responsible for the formation of xylem and phloem in plants.
Complete answer:
Option A: A-Protoxylem. B-Metaxylem. C-Phloem. D-Pericycle. E-Endodermis – Protoxylem is the first-formed xylem that is developed from the procambium. Procambium is a meristematic tissue located next to protoderm. Protoxylem is usually narrow with annular, spiral, or scalariform wall thickenings on the secondary cell wall.
Option B: A-Metaxylem. B-Protoxylem-Phloem D-Pericycle. E-Endodermis. Protoxylem differentiates into metaxylem, which is the later developed element. Protoxylem cells have broader tracheids and vessels with pitted or reticulate walls thickening in the secondary cell walls. Thickenings are formed due to the deposition of lignin.
Option C: A-Protoxylem. B-Metaxylem. C-Phloem. D-Endodermis. E-Pericycle. The endodermis is the central, innermost layer of cortex in dicot roots. Endodermis is characterized by the presence of casparian thickenings. These thickenings are formed by the deposition of suberin and lignin in the secondary walls.
Option D: A-Metaxylem B-Protoxylem. C-Phloem. D-Endoderm is, E-Pericycle. The pericycle is the outermost component of the stele of plants, and it is a cylinder of parenchyma or sclerenchyma cells that lies just inside the endodermis. Pericycle is usually filled with simple parenchyma cells or sometimes sclerenchyma cells.
So the correct answer is Option B.
Note:
In dicot roots, the vascular structures are not numerous and scattered like monocots but they are located in the middle of the root. The xylem is concentrated in the center of the dicot root, with phloem bundles arranged around it and divided by vascular cambium. Vascular cambium is a meristematic tissue which is responsible for the formation of xylem and phloem in plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




