
A dip needle initially in the magnetic meridian when it shows an angle of dip $\theta $ at a place. The dip circle is rotated through an angle $x$ in the horizontal plane and then it shows an angle of dip $\theta '$. Then, $\dfrac{{\tan \theta }}{{\tan \theta '}}$ will be
A. $\cos x$
B. $\dfrac{1}{{\cos x}}$
C. $\dfrac{1}{{\sin x}}$
D. $\dfrac{1}{{\tan x}}$
Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: The angle of dip or simply dip is an angle made by the total magnetic field of the Earth, with its surface (or horizontal). The dip needle is the device used for measuring dip at a certain place. The change in the dip needle alters the horizontal component, as the dip circle is placed on a horizontal surface.
Formula used:
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{B_V}}}{{{B_H}}}$
Complete answer:
The dip needle or dip circle is a device used to measure the dip angle at a given place. It is perfectly balanced about the horizontal axis. So that the needle is free to swing along the magnetic meridian.
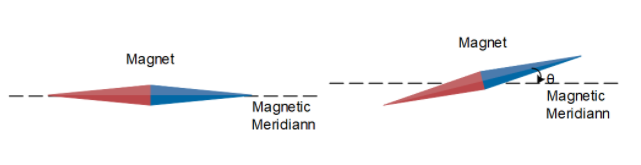
The dip angle is said to be the angle between the earth’s magnetic field and the horizontal. It varies from place to place. Mathematically it is given by,
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{B_V}}}{{{B_H}}}$
Where,
$\theta $ is the dip angle
${B_V}$ it the vertical component of Earth’s magnetic field
${B_H}$ is the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field
According to the condition given in the question, let us say that initially the dip angle is ${\theta _i} = \theta $. Then,
$\eqalign{
& \tan {\theta _i} = \tan \theta = \dfrac{{{B_V}}}{{{B_H}}} \cr
& \cr} $.
Once the dip circle is rotated through an angle $x$ is the vertical component of the earth’s magnetic field remains the same. But, the horizontal component changes to ${B_H}\cos x$. If we assume that the angle now is ${\theta _f} = \theta '$, then
$\eqalign{
& \tan {\theta _f} = \tan \theta ' = \dfrac{{{B_V}}}{{{B_H}\cos x}} \cr
& \cr} $
From the above equations, we can write
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{{\tan {\theta _i}}}{{\tan {\theta _f}}} = \dfrac{{\tan \theta }}{{\tan \theta '}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{B_V}}}{{{B_H}}}}}{{\dfrac{{{B_V}}}{{{B_H}\cos x}}}} = \dfrac{{{B_V}}}{{{B_H}}} \times \dfrac{{{B_H}\cos x}}{{{B_V}}} = \cos x \cr
& \therefore \dfrac{{\tan \theta }}{{\tan \theta '}} = \cos x \cr
& \cr} $
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note:
Don’t be confused - Magnetic dip, dip, and magnetic inclination are interchangeably used for dip angle. Dip angles play a prominent role in the field of aviation. The lines plotted along the places where the dip angle or magnetic dip is the same are known as isoclinic lines. The line drawn joining the points where the dip angle is zero is called the magnetic equator.
Please observe that the magnetic meridian and geographic meridian of earth are completely different. The angle between the magnetic meridian and the geographic median is called the magnetic declination.
Formula used:
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{B_V}}}{{{B_H}}}$
Complete answer:
The dip needle or dip circle is a device used to measure the dip angle at a given place. It is perfectly balanced about the horizontal axis. So that the needle is free to swing along the magnetic meridian.

The dip angle is said to be the angle between the earth’s magnetic field and the horizontal. It varies from place to place. Mathematically it is given by,
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{B_V}}}{{{B_H}}}$
Where,
$\theta $ is the dip angle
${B_V}$ it the vertical component of Earth’s magnetic field
${B_H}$ is the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field
According to the condition given in the question, let us say that initially the dip angle is ${\theta _i} = \theta $. Then,
$\eqalign{
& \tan {\theta _i} = \tan \theta = \dfrac{{{B_V}}}{{{B_H}}} \cr
& \cr} $.
Once the dip circle is rotated through an angle $x$ is the vertical component of the earth’s magnetic field remains the same. But, the horizontal component changes to ${B_H}\cos x$. If we assume that the angle now is ${\theta _f} = \theta '$, then
$\eqalign{
& \tan {\theta _f} = \tan \theta ' = \dfrac{{{B_V}}}{{{B_H}\cos x}} \cr
& \cr} $
From the above equations, we can write
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{{\tan {\theta _i}}}{{\tan {\theta _f}}} = \dfrac{{\tan \theta }}{{\tan \theta '}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{B_V}}}{{{B_H}}}}}{{\dfrac{{{B_V}}}{{{B_H}\cos x}}}} = \dfrac{{{B_V}}}{{{B_H}}} \times \dfrac{{{B_H}\cos x}}{{{B_V}}} = \cos x \cr
& \therefore \dfrac{{\tan \theta }}{{\tan \theta '}} = \cos x \cr
& \cr} $
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note:
Don’t be confused - Magnetic dip, dip, and magnetic inclination are interchangeably used for dip angle. Dip angles play a prominent role in the field of aviation. The lines plotted along the places where the dip angle or magnetic dip is the same are known as isoclinic lines. The line drawn joining the points where the dip angle is zero is called the magnetic equator.
Please observe that the magnetic meridian and geographic meridian of earth are completely different. The angle between the magnetic meridian and the geographic median is called the magnetic declination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




