
a) Draw a schematic diagram of a box type solar cooker. Name two components of a solar cooker which are responsible to increase the temperature inside the solar cooker and explain their function. State three advantages and three limitations of solar cookers.
b) Write difference between electromagnet and permanent magnet.
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: Box Type Solar Cooker: It comprises a rectangular box which is made up of wood or plastic and is painted dull black. The inner walls of the box are painted black to increase heat absorption and are covered with glass plates. It also has a mirror to focus the rays of the sun so that higher temperature can be achieved.
Complete step by step solution:
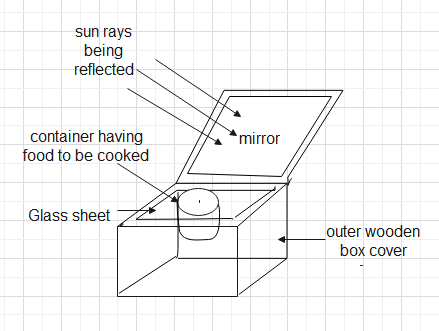
Fig. Schematic diagram of box type solar cooker
Components of solar cooker which are responsible to increase the temperature inside the solar are plane mirror, glass sheet, black paint inside the cooker
Functions of these components are:
i. Plane mirror has a special feature to maximise the amount of light entering the solar cooker.
ii. Glass sheet-traps infra-red radiations which produces green-house effect.
iii. Black paint absorbs radiation
Advantages of solar cooker are:
i. Saves conventional fuels like coal, LPG, kerosene
ii. It does not produce any type of smoke and thus it is environment friendly.
iii. Nutrients of food remain as they are and do not get destroyed while cooking.
iv. Maximum of four food items can be cooked simultaneously at the same time.
Disadvantages of solar cooker are:
i. Solar cookers cannot be used at night or at times when sunlight is not available.
ii. If the day is cloudy then solar light is not sufficient to cook the food inside the solar cooker.
iii. Direction of reflection of the solar cooker needs to change from time to time so that solar light falls perpendicular and maximum light is absorbed.
iv. Solar cooker cannot be used for frying or baking purposes.
b) Difference between electromagnet and permanent magnet.
Note: Exact solar cooker is a bit more complex than that shown in the diagram. The diagram shown is sufficient at primary level.
Permanent magnets can be made of different materials like ceramic, alnico, samarium-cobalt, and neodymium. These magnets have larger holding strength in comparison to the size of material. An electromagnet operates based electricity. Magnetic force is generated when the electricity is on and magnetic field becomes zero when the electric current is disconnected. A simple electromagnet can be created by wrapping conductive wire in tight coils around a ferrous core. When electricity is supplied to the wire, a magnetic field is created and it becomes zero when the electrical current is made zero or when the switch is turned off.
Complete step by step solution:

Fig. Schematic diagram of box type solar cooker
Components of solar cooker which are responsible to increase the temperature inside the solar are plane mirror, glass sheet, black paint inside the cooker
Functions of these components are:
i. Plane mirror has a special feature to maximise the amount of light entering the solar cooker.
ii. Glass sheet-traps infra-red radiations which produces green-house effect.
iii. Black paint absorbs radiation
Advantages of solar cooker are:
i. Saves conventional fuels like coal, LPG, kerosene
ii. It does not produce any type of smoke and thus it is environment friendly.
iii. Nutrients of food remain as they are and do not get destroyed while cooking.
iv. Maximum of four food items can be cooked simultaneously at the same time.
Disadvantages of solar cooker are:
i. Solar cookers cannot be used at night or at times when sunlight is not available.
ii. If the day is cloudy then solar light is not sufficient to cook the food inside the solar cooker.
iii. Direction of reflection of the solar cooker needs to change from time to time so that solar light falls perpendicular and maximum light is absorbed.
iv. Solar cooker cannot be used for frying or baking purposes.
b) Difference between electromagnet and permanent magnet.
| S. No. | Electromagnet | Permanent magnet |
| 1. | It is made from a coil of wire which acts as a magnet when an electric current passes through it. | It is an object made from a material that is magnetized and then it creates its own persistent magnetic field. |
| 2. | An electromagnetic magnet displays magnetic properties only when an electric current is passed through it. | A permanent magnet shows magnetic behaviour only when it is magnetized. It acts as a magnetic field even if the external magnetic field is removed. |
| 3. | The strength of an electromagnet can be adjusted by the amount of electric current allowed to flow into it. | It’s strength depends upon the material used making the permanent magnet. Strength of the magnetic field cannot be varied once fixed. |
| 4. | The direction of the magnetic field can be changed in electromagnets. | The direction of the magnetic field created by the permanent magnet cannot be changed. |
| 5. | The electromagnets are generally made of soft iron. | The permanent magnet is usually made of hard iron. |
Note: Exact solar cooker is a bit more complex than that shown in the diagram. The diagram shown is sufficient at primary level.
Permanent magnets can be made of different materials like ceramic, alnico, samarium-cobalt, and neodymium. These magnets have larger holding strength in comparison to the size of material. An electromagnet operates based electricity. Magnetic force is generated when the electricity is on and magnetic field becomes zero when the electric current is disconnected. A simple electromagnet can be created by wrapping conductive wire in tight coils around a ferrous core. When electricity is supplied to the wire, a magnetic field is created and it becomes zero when the electrical current is made zero or when the switch is turned off.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




