
a. Explain the process of DNA Replication with the help of a schematic diagram.
b. In which phase of the cell cycle does replication occur in eukaryotes? What would happen if the cell division is not followed after DNA Replication.
Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint: DNA or the Deoxyribonucleic Acid is the genetic material of eukaryotic organisms. This double helically oriented molecule contains information, which regulates all the vital functions of the body such as growth, development, reproduction as well as overall functioning.
Complete Answer:
(a). The biological process which consists of the formation of two identical daughter DNAs from one parent DNA molecule is known as DNA replication. The process of replication is a complex process, which includes several steps, and is to happen with great precision, and fault in the process of replication can cause many adverse events in the body of the organism.
- The initial step occurring in the process of DNA is the unwinding of the double helix structure of the molecule at specific sites known as the Ori or the Origin of Replication. An enzyme known as ‘Helicase’ catalyzes the process, by breaking the hydrogen bonds, present in between the bases, which holds together the strands. The various bases are Adenine(A), Thymine(T), Guanine(G), and Cytosine(C) where A binds with T utilizing two hydrogen bonds, while C binds with G utilizing three hydrogen bonds.
- The site which is exposed while the strands are separated is known as the Replication fork and is a Y- shaped structure. The separated strands, thus function as the template for the production of two DNA molecules.
- The two strands are complementary to each other since one strand has an orientation of 3’-5’, known as the leading strand moving towards the direction of the replication fork, while the other strand has an orientation of 5’-3’, known as the lagging strand and directed away from the replication fork. These two strands are involved in the process of replication, by different steps, due to the difference in the orientation.
- A primer molecule, which is a short RNA fragment, gets bound to the leading strand. This fragment is synthesized with the help of an enzyme known as Primase. The primer molecule is the initiator molecule for the whole replication process. The whole process is catalyzed by an enzyme known as the DNA Polymerase. The enzyme acts on the leading strand, and moves along the length of it, and adds the corresponding complementary nucleotides along the length. This process is continuous.
- The Primase enzu=ymes produces several primers along the direction of the lagging strand. These fragments are known as the Okazaki Fragments and are joined at a later stage by the enzyme DNA Ligase. Once ligation is done, the primers are then removed from the strands, by the Exonuclease enzyme.
- After the process, there is a proofreading mechanism involved, so that no mistakes happen during the whole process. DNA ligase eventually seals up the separated strands to form the final double-stranded DNA molecule. The process is known as semi-conservative and semi-discontinuous, semi-conservative since out of the two daughter DNA molecules present, each has one new strand and one old strand from the parent molecule. And semi-discontinuous since, only the synthesis along the leading strand occurs continuously, while in the lagging strand, several smaller strands are synthesized initially and later joined together. Once this replication process is completed, the DNA chain formed gets oriented into its specific Double-helix structure.
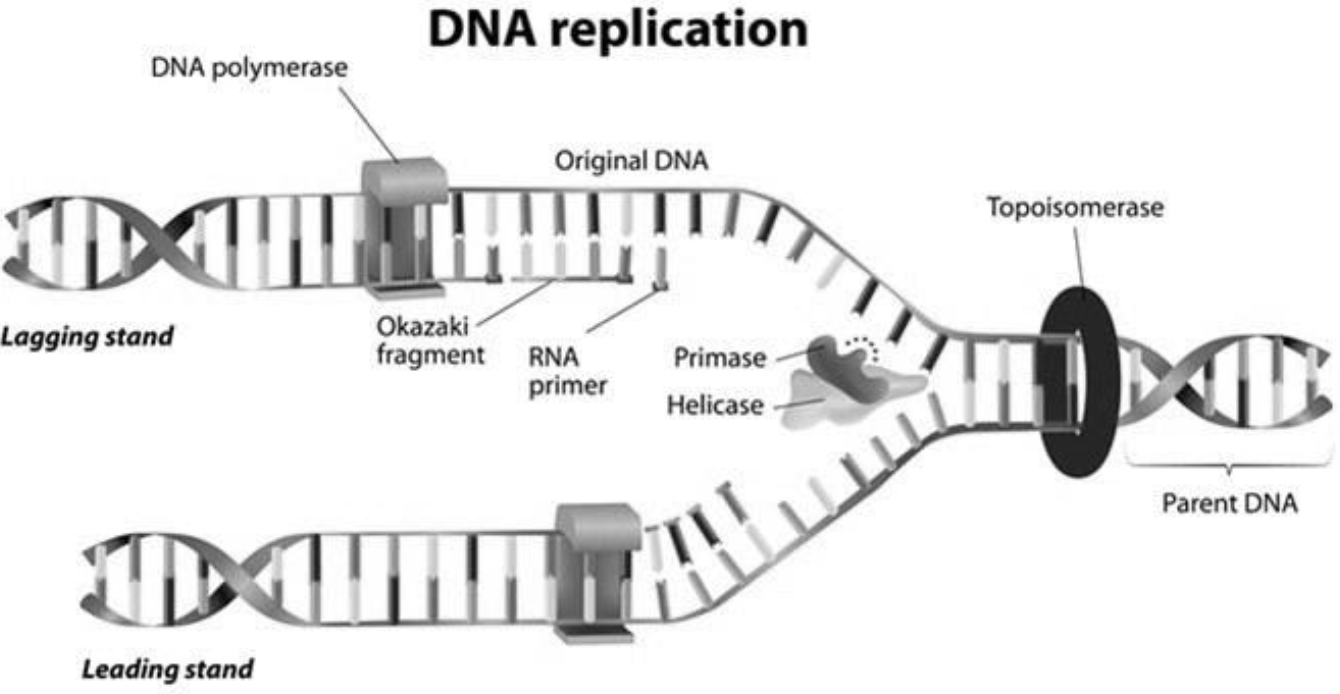
Figure: DNA Replication
(b). In eukaryotic cells, the S-Phase of the Synthetic Phase of the cell cycle is the phase where DNA replication occurs. If cell division is absent, after DNA replication, the replicated DNA molecules won't be distributed equally among the daughter nuclei. The DNA hence accumulates inside the cell and results in abnormal cell expansion due to an increased cell volume.
Note: DNA replication is usually a well-regulated process. But errors can happen. A wide range of chronic disorders can occur due to the abnormalities occurring. The most common mistake is due to the insertion of an abnormal or faulty base pair. The most common disease due to these is cancers.
Complete Answer:
(a). The biological process which consists of the formation of two identical daughter DNAs from one parent DNA molecule is known as DNA replication. The process of replication is a complex process, which includes several steps, and is to happen with great precision, and fault in the process of replication can cause many adverse events in the body of the organism.
- The initial step occurring in the process of DNA is the unwinding of the double helix structure of the molecule at specific sites known as the Ori or the Origin of Replication. An enzyme known as ‘Helicase’ catalyzes the process, by breaking the hydrogen bonds, present in between the bases, which holds together the strands. The various bases are Adenine(A), Thymine(T), Guanine(G), and Cytosine(C) where A binds with T utilizing two hydrogen bonds, while C binds with G utilizing three hydrogen bonds.
- The site which is exposed while the strands are separated is known as the Replication fork and is a Y- shaped structure. The separated strands, thus function as the template for the production of two DNA molecules.
- The two strands are complementary to each other since one strand has an orientation of 3’-5’, known as the leading strand moving towards the direction of the replication fork, while the other strand has an orientation of 5’-3’, known as the lagging strand and directed away from the replication fork. These two strands are involved in the process of replication, by different steps, due to the difference in the orientation.
- A primer molecule, which is a short RNA fragment, gets bound to the leading strand. This fragment is synthesized with the help of an enzyme known as Primase. The primer molecule is the initiator molecule for the whole replication process. The whole process is catalyzed by an enzyme known as the DNA Polymerase. The enzyme acts on the leading strand, and moves along the length of it, and adds the corresponding complementary nucleotides along the length. This process is continuous.
- The Primase enzu=ymes produces several primers along the direction of the lagging strand. These fragments are known as the Okazaki Fragments and are joined at a later stage by the enzyme DNA Ligase. Once ligation is done, the primers are then removed from the strands, by the Exonuclease enzyme.
- After the process, there is a proofreading mechanism involved, so that no mistakes happen during the whole process. DNA ligase eventually seals up the separated strands to form the final double-stranded DNA molecule. The process is known as semi-conservative and semi-discontinuous, semi-conservative since out of the two daughter DNA molecules present, each has one new strand and one old strand from the parent molecule. And semi-discontinuous since, only the synthesis along the leading strand occurs continuously, while in the lagging strand, several smaller strands are synthesized initially and later joined together. Once this replication process is completed, the DNA chain formed gets oriented into its specific Double-helix structure.

Figure: DNA Replication
(b). In eukaryotic cells, the S-Phase of the Synthetic Phase of the cell cycle is the phase where DNA replication occurs. If cell division is absent, after DNA replication, the replicated DNA molecules won't be distributed equally among the daughter nuclei. The DNA hence accumulates inside the cell and results in abnormal cell expansion due to an increased cell volume.
Note: DNA replication is usually a well-regulated process. But errors can happen. A wide range of chronic disorders can occur due to the abnormalities occurring. The most common mistake is due to the insertion of an abnormal or faulty base pair. The most common disease due to these is cancers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




