
(a) Find out the position of the image of an object situated at A in the plane mirror
(b) Can paheli at B see this image?
(c) Can Boojho at C see this image?
(d) When paheli moves from B to C, where does the image of A move?

Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint:The mirror given is a plane mirror. Recall the way of reflection of the object and its properties. Remember to see the image; the reflected rays of the object, reflected from the mirror must reach the eyes of the person.
Complete answer:
(a) For a plane mirror, the image distance is equal to the object distance and the image is virtual and the same size.The position of the image is exactly behind the mirror in the same vertical line and at the same distance from the mirror. It is shown as
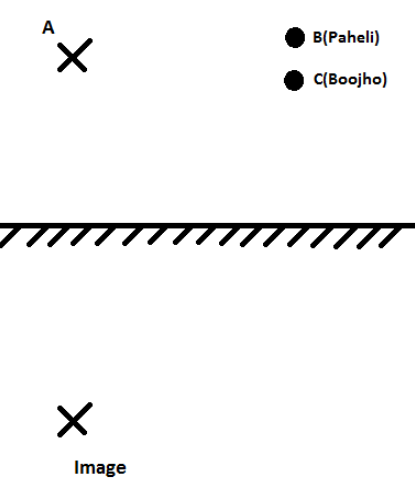
(b) Paheli can see the image since the rays of light can reach the eyes of Paheli.
(c) Boojho can see the image since the rays of light can reach the eyes of Boojho.
(d) When Paheli moves from B to C, the image of the A will remain at the same point. But when she moves from B to C it will look like that image is coming towards her.
Additional information:
When a ray of light falls on a surface, then it can undergo one of the following three phenomena: reflection, refraction, or absorption. When it falls on a normal surface then most of the light gets absorbed. So mirrors are polished surfaces coated with mercury such that they reflect most of the light falling on them. Now based on the type of reflecting surface we can classify mirrors as concave, convex, or plane mirror. Here we will be talking about the plane mirror only. So to form an image we require at least two rays from the object which meet or appear to meet at a point.
Note:Students should know the concepts behind the reflection from mirrors. It is easier to deduce for plane mirrors but tricky for spherical mirrors. For spherical mirrors, mathematical calculations have to be performed using the mirror formula.
Complete answer:
(a) For a plane mirror, the image distance is equal to the object distance and the image is virtual and the same size.The position of the image is exactly behind the mirror in the same vertical line and at the same distance from the mirror. It is shown as

(b) Paheli can see the image since the rays of light can reach the eyes of Paheli.
(c) Boojho can see the image since the rays of light can reach the eyes of Boojho.
(d) When Paheli moves from B to C, the image of the A will remain at the same point. But when she moves from B to C it will look like that image is coming towards her.
Additional information:
When a ray of light falls on a surface, then it can undergo one of the following three phenomena: reflection, refraction, or absorption. When it falls on a normal surface then most of the light gets absorbed. So mirrors are polished surfaces coated with mercury such that they reflect most of the light falling on them. Now based on the type of reflecting surface we can classify mirrors as concave, convex, or plane mirror. Here we will be talking about the plane mirror only. So to form an image we require at least two rays from the object which meet or appear to meet at a point.
Note:Students should know the concepts behind the reflection from mirrors. It is easier to deduce for plane mirrors but tricky for spherical mirrors. For spherical mirrors, mathematical calculations have to be performed using the mirror formula.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




