
A functional isomer of 1-butyne is:
A. 2 -butyne
B. 1-butene
C. 2-butene
D. 1,3-butadiene
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Functional isomerism is the type of isomerism in which molecules have the same chemical formula but different functional groups attached.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of 1-butyne is –
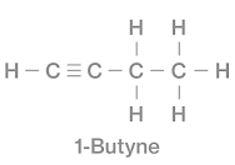
That of 1,3-butadiene is –
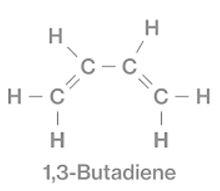
1 butene has the structure –
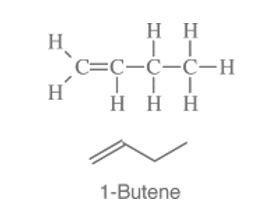
2 butene has the structure –
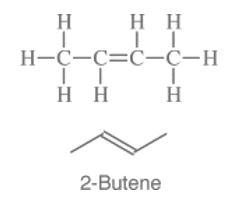
2 butyne-
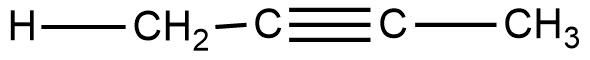
From these figures we can see that, molecular formula of both 1-butyne and 1,3-butadiene is \[{{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_6}\]. But their functional group is different. 1-butyne has \[( - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{C}} - )\]triple bond whereas 1,3-butadiene has double bond \[( - {\text{C = C}} - )\]d. Hence, 1,3-butadiene is the functional isomer of 1-butyne.
So, option D is correct.
Additional information:
In an organic molecule, different atoms are linked to each other with different types of bonds and hence isomerism arises. Functional isomerism is a type of structural isomerism. Apart from functional isomerism, there are five more types of structural isomerism found. These are as follows -
Chain isomerism –
Two compounds having the same molecular formula but show different branched structures show chain isomerism.
Position isomerism –
Two compounds which have the same molecular formula but the position of double/triple bond varies in the chain show position isomerism.
In the above example, 1-butene and 2-butene are examples of position isomerism.
Metamerism –
This type of isomerism arises due to the presence of different alkyl chains on each side of the functional group.
Tautomerism –
When a compound shows two or more interconvertible structures which differ only in terms of relative position of atomic nucleus are called tautomers of each other and the phenomenon is called tautomerism.
Ring chain isomerism-
In ring chain type of isomerism, one structure has a long chain while the other has a ring but the molecular formulas for both are the same.
Note: Remember, when given compounds have the same molecular formula but different functional groups, they are functional isomers of each other. On the other hand, if the position of double/triple bond is different but the molecular formula is same, they show position isomerism.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of 1-butyne is –

That of 1,3-butadiene is –

1 butene has the structure –

2 butene has the structure –

2 butyne-
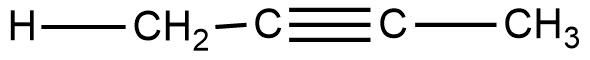
From these figures we can see that, molecular formula of both 1-butyne and 1,3-butadiene is \[{{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_6}\]. But their functional group is different. 1-butyne has \[( - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{C}} - )\]triple bond whereas 1,3-butadiene has double bond \[( - {\text{C = C}} - )\]d. Hence, 1,3-butadiene is the functional isomer of 1-butyne.
So, option D is correct.
Additional information:
In an organic molecule, different atoms are linked to each other with different types of bonds and hence isomerism arises. Functional isomerism is a type of structural isomerism. Apart from functional isomerism, there are five more types of structural isomerism found. These are as follows -
Chain isomerism –
Two compounds having the same molecular formula but show different branched structures show chain isomerism.
Position isomerism –
Two compounds which have the same molecular formula but the position of double/triple bond varies in the chain show position isomerism.
In the above example, 1-butene and 2-butene are examples of position isomerism.
Metamerism –
This type of isomerism arises due to the presence of different alkyl chains on each side of the functional group.
Tautomerism –
When a compound shows two or more interconvertible structures which differ only in terms of relative position of atomic nucleus are called tautomers of each other and the phenomenon is called tautomerism.
Ring chain isomerism-
In ring chain type of isomerism, one structure has a long chain while the other has a ring but the molecular formulas for both are the same.
Note: Remember, when given compounds have the same molecular formula but different functional groups, they are functional isomers of each other. On the other hand, if the position of double/triple bond is different but the molecular formula is same, they show position isomerism.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




