
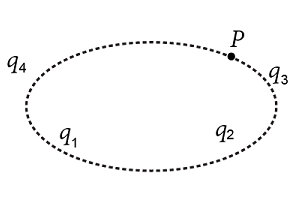
A Gaussian surface encloses two of the four positively charged particles. The particles that contribute to the electric field at the point P on the surface are:
A. ${{q}_{1}}\;and\;{{q}_{2}}$
B. ${{q}_{2}}\;and\;{{q}_{3}}$
C. ${{q}_{1}}\;and\;{{q}_{3}}$
D. ${{q}_{1}}\;,{{q}_{2}},{{q}_{3}}\;and\;{{q}_{4}}$

Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: Use the expression for electric field due to a discrete charge distribution.
Formula used: \[\overrightarrow{E}=\sum\limits_{i=1}^{4}{\dfrac{{{q}_{i}}}{4\pi {{\epsilon }_{0}}r_{i}^{3}}\overrightarrow{{{r}_{i}}}}\]
$\overrightarrow{E}$ is the electric field at the point P due to all the charges
${{q}_{i}}$ are the four charges
$\epsilon_0$ is the permittivity of free space
$\overrightarrow{{{r}_{i}}}$ is the position vector of the point P with respect to the ${{q}_{i}}$ charge
Complete step by step solution:
According to the formula, the electric field at any point is due to the cumulative effect of all the charges present irrespective of the Gaussian surface. Hence, all the four charges ${{q}_{1}},{{q}_{2}},{{q}_{3}}\;and\;{{q}_{4}}$ will contribute to the electric field.
The correct answer is option D.
Additional information:
Coulomb’s law can be derived from Gauss’s law and vice versa. It is one of Maxwell's four equations of electromagnetic interaction. It can be used to find the electric field due to discrete and continuous charge distributions.
Electric field arises due to static charges whereas the magnetic field arises due to dynamic charges. Both are manifestations of the electromagnetic force which is one the fundamental interactions existing in nature. The electromagnetic interaction is mediated by the massless photons. The other fundamental interactions are the gravitational force, the strong nuclear force and the weak nuclear force. The strong interaction is mediated by gluons and the weak interaction is mediated by the W and Z bosons.
Note: The electric flux passing through the point P will be dependent on the Gaussian surface and the charges it encloses, consistent with Gauss’s law. Hence, only the charges q1 and q2 will contribute to the electric flux in this region.
Formula used: \[\overrightarrow{E}=\sum\limits_{i=1}^{4}{\dfrac{{{q}_{i}}}{4\pi {{\epsilon }_{0}}r_{i}^{3}}\overrightarrow{{{r}_{i}}}}\]
$\overrightarrow{E}$ is the electric field at the point P due to all the charges
${{q}_{i}}$ are the four charges
$\epsilon_0$ is the permittivity of free space
$\overrightarrow{{{r}_{i}}}$ is the position vector of the point P with respect to the ${{q}_{i}}$ charge
Complete step by step solution:
According to the formula, the electric field at any point is due to the cumulative effect of all the charges present irrespective of the Gaussian surface. Hence, all the four charges ${{q}_{1}},{{q}_{2}},{{q}_{3}}\;and\;{{q}_{4}}$ will contribute to the electric field.
The correct answer is option D.
Additional information:
Coulomb’s law can be derived from Gauss’s law and vice versa. It is one of Maxwell's four equations of electromagnetic interaction. It can be used to find the electric field due to discrete and continuous charge distributions.
Electric field arises due to static charges whereas the magnetic field arises due to dynamic charges. Both are manifestations of the electromagnetic force which is one the fundamental interactions existing in nature. The electromagnetic interaction is mediated by the massless photons. The other fundamental interactions are the gravitational force, the strong nuclear force and the weak nuclear force. The strong interaction is mediated by gluons and the weak interaction is mediated by the W and Z bosons.
Note: The electric flux passing through the point P will be dependent on the Gaussian surface and the charges it encloses, consistent with Gauss’s law. Hence, only the charges q1 and q2 will contribute to the electric flux in this region.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




