
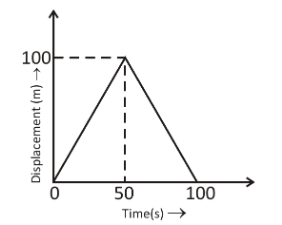
A girl walks along a straight path to drop a letter in the letterbox and comes back to her initial position. Her displacement-time graph is shown in figure. Plot a velocity-time graph for the same.

Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint:We will use the formula which gives velocity i.e. velocity is defined as displacement per unit time. As the displacement increases, the velocity is positive. Velocity is taken to be negative as the displacement decreases. Positive velocity will be plotted above the horizontal axis. Negative velocity is plotted below the horizontal axis.
Formula used:
Using velocity formula,
\[v = \dfrac{{\Delta d}}{{\Delta t}}\] …… (1)
Where,
\[v\] is velocity
\[\Delta d\] is displacement
\[\Delta t\] is changing in time.
Complete step by step answer:
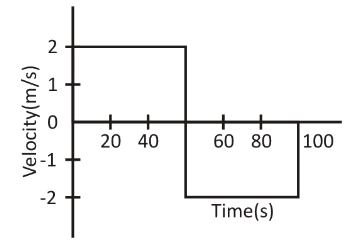
From the graph we know that, velocity time graph is a straight line and the velocity of the girl is constant.Here, displacement is \[\Delta d = 100\], and \[\Delta t = 50\].So,For the initial \[50\,{\text{s}}\] , the velocity will be,
$v = \dfrac{{\Delta d}}{{\Delta t}} \\
\Rightarrow v = \dfrac{{100}}{{50}} \\
\Rightarrow v = 2\,{\text{m}}/{\text{s}} \\$
And the next \[50\,{\text{s}}\] the velocity is taken in negative because displacement is becoming zero,
$v = \dfrac{{\Delta d}}{{\Delta t}} \\
\Rightarrow v = \dfrac{{0 - 100}}{{50}} \\
\therefore v = - 2\,{\text{m}}/{\text{s}}$
Therefore, the velocity-time graph is as shown in the figure below.
Additional information:
Velocity: The velocity of an object, with respect to a frame of reference, is the rate of change of its position and is a function of time. Velocity is equal to the speed and direction of motion of an object specification. In kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that explains the motion of bodies, velocity is a basic concept.
Note:Remember that a negative acceleration implies that in the negative direction, the change in the velocity points. The velocity may be in the positive direction, for example, and the object will slow down or the velocity could be in the negative direction and the object will speed up. Velocity tracks motion beginning in one position and continuing to another. There are countless functional velocity uses, but one of the most common reasons for calculating velocity is to determine how quickly you (or something in motion) will arrive from a given position at a destination. The factors influencing an object's terminal velocity include its mass. Gravity-due acceleration, \[g\] .
Formula used:
Using velocity formula,
\[v = \dfrac{{\Delta d}}{{\Delta t}}\] …… (1)
Where,
\[v\] is velocity
\[\Delta d\] is displacement
\[\Delta t\] is changing in time.
Complete step by step answer:
From the graph we know that, velocity time graph is a straight line and the velocity of the girl is constant.Here, displacement is \[\Delta d = 100\], and \[\Delta t = 50\].So,For the initial \[50\,{\text{s}}\] , the velocity will be,
$v = \dfrac{{\Delta d}}{{\Delta t}} \\
\Rightarrow v = \dfrac{{100}}{{50}} \\
\Rightarrow v = 2\,{\text{m}}/{\text{s}} \\$
And the next \[50\,{\text{s}}\] the velocity is taken in negative because displacement is becoming zero,
$v = \dfrac{{\Delta d}}{{\Delta t}} \\
\Rightarrow v = \dfrac{{0 - 100}}{{50}} \\
\therefore v = - 2\,{\text{m}}/{\text{s}}$
Therefore, the velocity-time graph is as shown in the figure below.

Additional information:
Velocity: The velocity of an object, with respect to a frame of reference, is the rate of change of its position and is a function of time. Velocity is equal to the speed and direction of motion of an object specification. In kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that explains the motion of bodies, velocity is a basic concept.
Note:Remember that a negative acceleration implies that in the negative direction, the change in the velocity points. The velocity may be in the positive direction, for example, and the object will slow down or the velocity could be in the negative direction and the object will speed up. Velocity tracks motion beginning in one position and continuing to another. There are countless functional velocity uses, but one of the most common reasons for calculating velocity is to determine how quickly you (or something in motion) will arrive from a given position at a destination. The factors influencing an object's terminal velocity include its mass. Gravity-due acceleration, \[g\] .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




