
(a) Give a schematic outline of photorespiration.
(b) Differentiate between photophosphorylation and photorespiration
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: Photorespiration is a process which involves loss of fixed carbon as CO2, in plants in the presence of light it is initiated in chloroplasts. This process does not produce ATP or NADPH and is a wasteful process.
Complete answer:
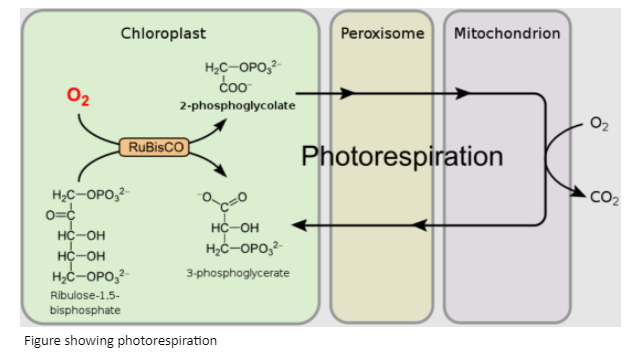
a) Photorespiration.
Photorespiration is usually a wasteful process and is not performed in the $C_4$ plants that are plants that possess kranz anatomy. In this the mesophyll cells are found around the bundle-sheath cells forming a ring. The number of chloroplasts is more in bundle sheath cells as compared to mesophyll cells.
Mechanism of photorespiration:
- Photorespiration occurs usually when there is high concentration of oxygen.
- Under such circumstances, RuBisCO, the enzyme that catalyses the carboxylation of RuBP during the first step of the Calvin cycle, functions as an oxygenase.
- Some $O_2$, does bind to RuBisCO and hence $CO_2$, fixation is decreased.
- The RuBP binds with $O_2$, to form one molecule of PGA (3C compound) and phosphoglycolate (2C compound) in the pathway of photorespiration.
- There is neither the synthesis of sugar, nor of ATP. Rather, it results in the release of $CO_2$, with the utilisation of ATP. It leads to a 25 percent loss of the fixed $CO_2$. $O_2$, is first utilized in chloroplast and then in peroxisomes.
- This process is also called the $C_2$ cycle. This requires organelles such as chloroplast peroxisome and mitochondria.
b) Differentiate between photophosphorylation and photorespiration
Note: The structural adaptation of $C_4$ plants help in photorespiration. The PEP carboxylase is present in the chloroplast of mesophyll cells. It helps in fixing carbon dioxide even at low concentrations. So, light reaction and evolution of oxygen takes place in mesophyll cells.
Complete answer:
a) Photorespiration.
Photorespiration is usually a wasteful process and is not performed in the $C_4$ plants that are plants that possess kranz anatomy. In this the mesophyll cells are found around the bundle-sheath cells forming a ring. The number of chloroplasts is more in bundle sheath cells as compared to mesophyll cells.
Mechanism of photorespiration:
- Photorespiration occurs usually when there is high concentration of oxygen.
- Under such circumstances, RuBisCO, the enzyme that catalyses the carboxylation of RuBP during the first step of the Calvin cycle, functions as an oxygenase.
- Some $O_2$, does bind to RuBisCO and hence $CO_2$, fixation is decreased.
- The RuBP binds with $O_2$, to form one molecule of PGA (3C compound) and phosphoglycolate (2C compound) in the pathway of photorespiration.
- There is neither the synthesis of sugar, nor of ATP. Rather, it results in the release of $CO_2$, with the utilisation of ATP. It leads to a 25 percent loss of the fixed $CO_2$. $O_2$, is first utilized in chloroplast and then in peroxisomes.
- This process is also called the $C_2$ cycle. This requires organelles such as chloroplast peroxisome and mitochondria.

b) Differentiate between photophosphorylation and photorespiration
| Photophosphorylation | Photorespiration |
| Photophosphorylation is referred to as the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate in the presence of light. | On the other hand, photorespiration is a manner which includes loss of fixed carbon as $CO_2$ in plants in the presence of light. |
| Photophosphorylation happens and occurs in chloroplasts. | Photorespiration is initiated in chloroplasts, but it additionally involves peroxisomes and mitochondria. |
| Photophosphorylation is a beneficial procedure as it entails the formation of ATP. | Photorespiration is a wasteful manner as it does not produce ATP. Photorespiration consumes energy. |
| Photophosphorylation is of two types- cyclic and non-cyclic. | Photorespiration is solely cyclic. |
| Photophosphorylation occurs in bacteria nicely as in plants. Cyclic photophosphorylation takes place in bacteria and non-cyclic photophosphorylation happens in inexperienced plants. | Photorespiration occurs only in $C_3$ plants. |
| Photophosphorylation is a vital technique for photosynthesis | Photorespiration is no longer essential. |
Note: The structural adaptation of $C_4$ plants help in photorespiration. The PEP carboxylase is present in the chloroplast of mesophyll cells. It helps in fixing carbon dioxide even at low concentrations. So, light reaction and evolution of oxygen takes place in mesophyll cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




